Wireless communication performance test channel simulation system for maglev traffic across steel sleepers
A wireless communication and test channel technology, which is applied in wireless communication, vehicle wireless communication services, large-scale transport vehicles, etc., can solve problems that cannot be simulated and cannot be fully applied to medium and low-speed maglev communication systems, and achieve accurate testing and The effect of the assessment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
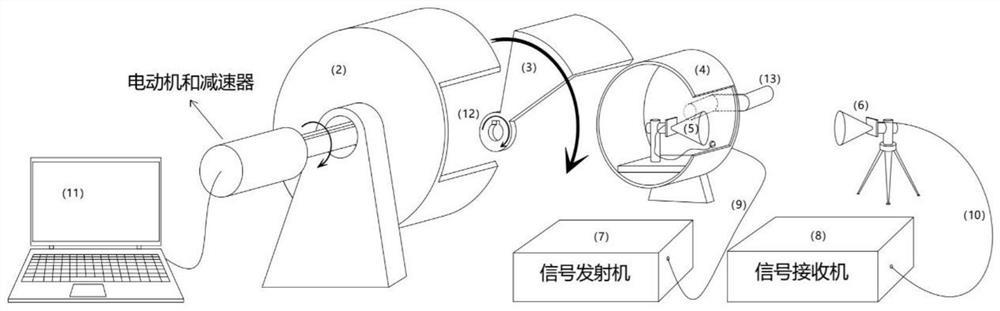
[0037] In this example, see figure 1 and figure 2 , a wireless communication performance test channel simulation system for maglev traffic crossing steel sleepers, comprising two cylindrical shells 2, 4 with slots, and a fan-shaped rotatable metal baffle is placed between the two shells 2, 4 3. The metal baffle 3 is externally connected to the motor and the reducer 1. The motor and the reducer 1 communicate through the serial port of the control computer 11, and send instructions to rotate at a constant speed, rotate at a variable speed and stop rotating. During the rotation, the baffle 3 will block the two-layer shell The slits of 2 and 4 form a wireless communication channel that can be changed inside and outside the cylinder; the transmitting antenna 5 is placed inside the instrument cylinder, and the radiation direction is aligned with the slit outward, and the radio frequency line 9 is used to communicate with the external signal The transmitter 7 is connected to form a...
Embodiment 2
[0039] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0040] In this embodiment, the control computer 11 controls the motor and the reducer 1 to drive the baffle 3 to rotate at a constant speed, rotate at a variable speed, and stop rotating, and periodically block the signal to form a wireless communication that can change between the inside of the cylinder and the outside of the cylinder. channel.
[0041] When the metal baffle 3 rotates, the space between the transmitting antenna 5 and the receiving antenna 6 will be blocked by the baffle 3, and the signal will be blocked to varying degrees as the metal baffle 3 rotates. This scene simulates a vehicle antenna The process of crossing the steel sleeper; when the metal baffle 3 is in other positions due to the rotation away from the gap 12, there is no shelter between the transmitting and receiving antennas. This scene simulates the scene when the vehicle-mounted antenna is located between two stee...
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment is basically the same as the previous embodiment, and the special features are:
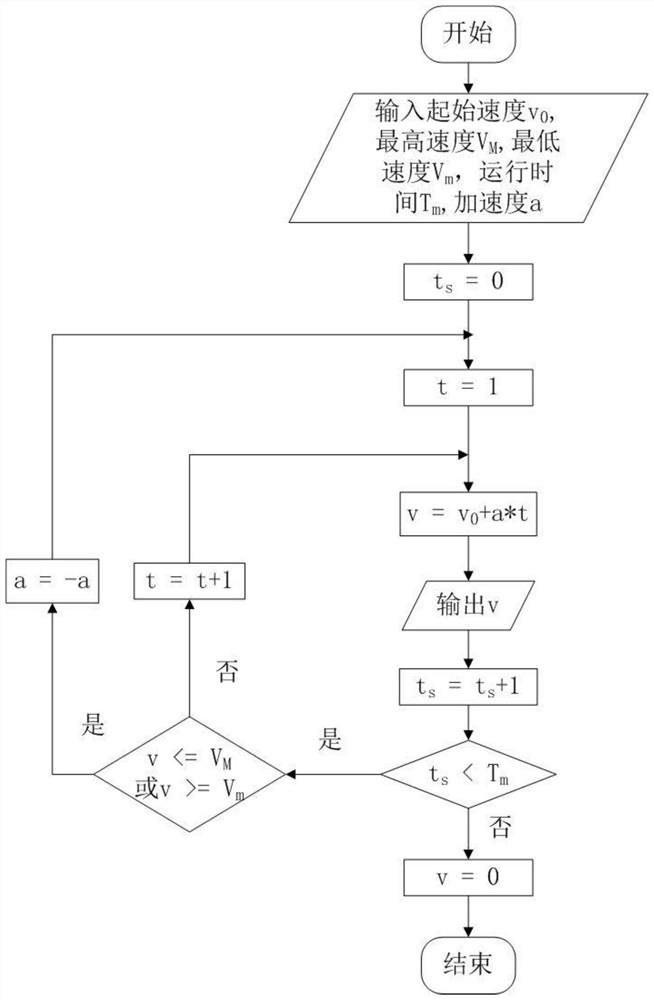
[0045] In this embodiment, the test is simulated when the distance between steel sleepers is fixed or the train runs at a constant speed. Such as figure 1 As shown in the figure, place the transmitting antenna in the instrument, connect the signal transmitter with a radio frequency line, transmit a fixed bandwidth signal, receive it by the receiving antenna placed outside the instrument, and connect it to the spectrum analyzer with a radio frequency line. The control computer runs as figure 2 In the program shown, input the initial speed (such as 5 revolutions / s), input the acceleration 0, and the program running time is 100 seconds. After the calculation of this program, the control motor will drive the baffle to rotate at a constant speed for 100 seconds at a speed of 5 revolutions per second. During the running time, the baffle rotates at a constant speed, and the baf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com