Method and system for determining roadway support area and support mode
A technology for roadway support and area, which is applied in earthwork drilling, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of not distinguishing between temporary support and permanent support, high roadway support and maintenance costs, and failure to consider support. The problem of project timeliness and other issues has achieved the effect of reducing support costs and maintenance costs, improving construction progress and construction quality, and reducing the difficulty of decision-making.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
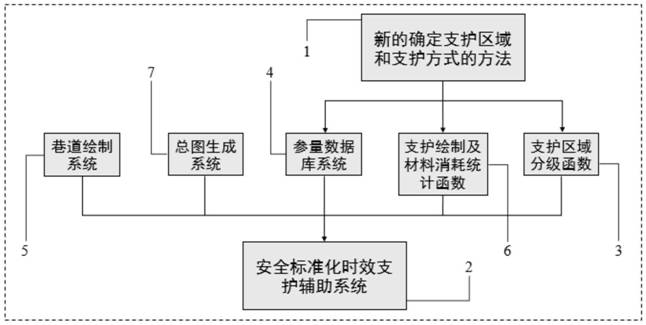
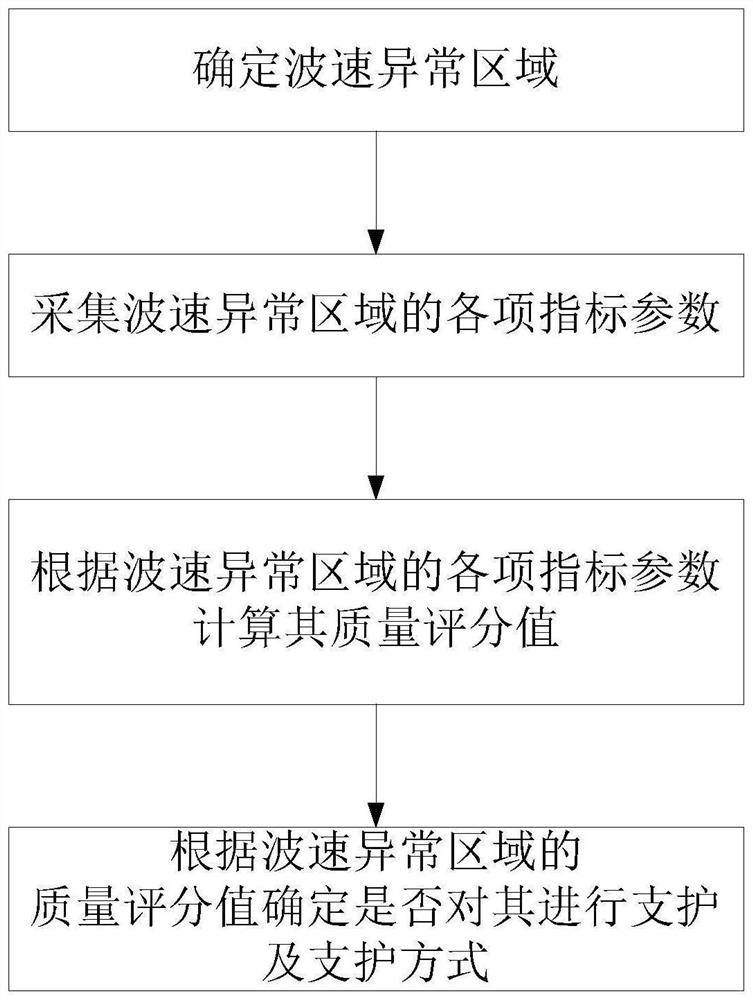
[0049] This embodiment provides a method for determining the roadway support area and support mode, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0050] Step 1. Use the microseismic monitoring system installed underground to determine the abnormal wave velocity areas in the roadway excavation face, such as low-velocity areas and high-speed areas;
[0051] Step 2, carry out exploration, geophysical prospecting and test collection of various index parameters for each wave velocity anomaly area;
[0052] Step 3, according to the index parameters collected in step 2, calculate the quality score value G of each wave velocity abnormal region;
[0053] Step 4. Determine the support area and support method according to the quality score value G, that is, determine which areas with abnormal wave velocity need to be supported and determine the corresponding support method.
Embodiment 2
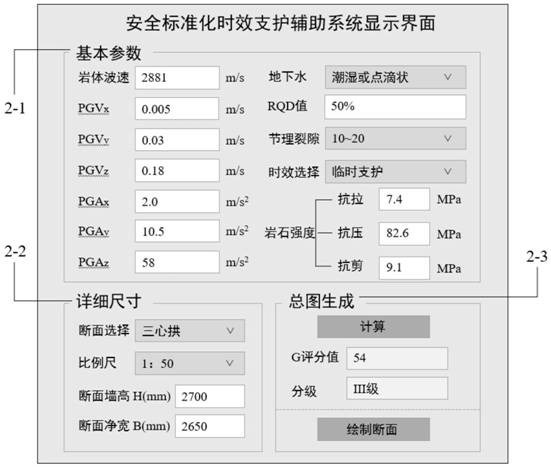
[0055] This embodiment is based on embodiment 1, and in said step 2, index parameters include RQD, rock mass wave velocity V 波 , peak seismic velocity PGV, peak seismic acceleration PGA, groundwater condition W (determined in combination with basic quality index BQ of rock mass), joint frequency J w and rock strength Q; where the seismic peak velocity PGV includes the seismic peak velocity PGV in the three directions of x, y, and z x 、PGV y and PGV z ;Earthquake peak acceleration PGA includes earthquake peak acceleration PGA in three directions of x, y, and z x 、PGA y and PGA z ;Therefore, a total of 11 indicator parameters are included.
[0056] The joint frequency J w Refers to the number of joints per meter distance (articles / m); the RQD, rock mass wave velocity V 波 , joint frequency J w and the value of rock strength Q can be determined based on existing technologies.
Embodiment 3
[0058] In this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 2, the peak seismic velocity PGV and peak seismic acceleration PGA are parameters related to the source mechanism (source type, vibration direction), which can invert the source type.
[0059] Its solution process is as follows:
[0060] First, the full waveform inversion method is used to invert the seismic moment tensor M(M xx ,M yy ,M zz ,M xy ,M xz ,M yz ), different source types (four sources of pure compression failure, pure shear failure, pure explosion failure, and pure tension failure) can be described by the combination of seismic moment tensors;
[0061] The displacement response is then calculated using Green's functions (GFs) to model the propagation of seismic waves between the source and sensor locations:
[0062] u n (s,t)=M pq *G np,q (s,t;ε,t 0 )n,p,q=x,y,z
[0063] u n (s, t) represents the displacement in the n direction at time t at the field point s recorded by the sensor, M pq Indicates t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com