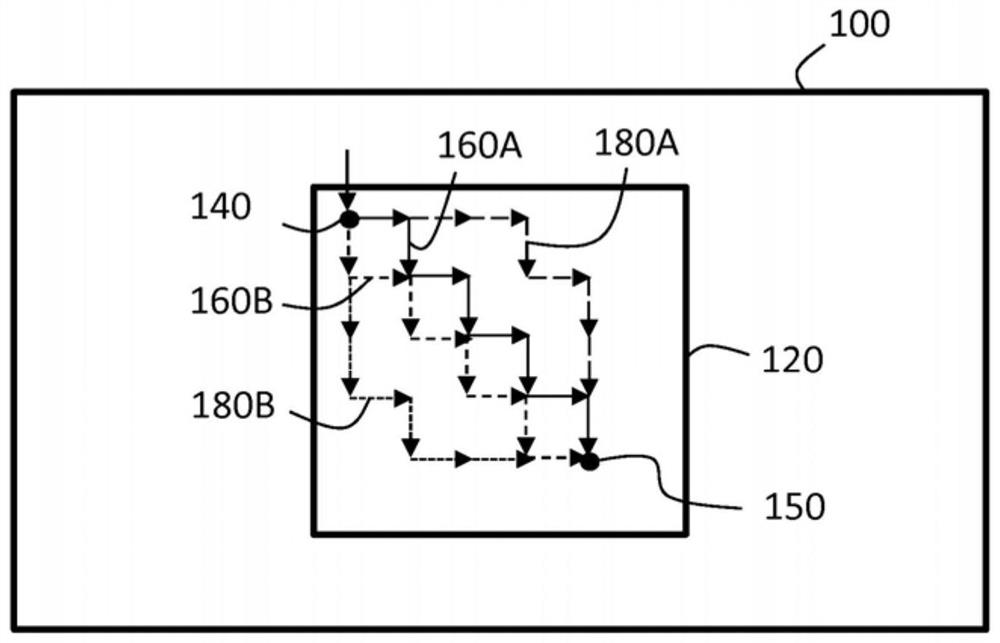
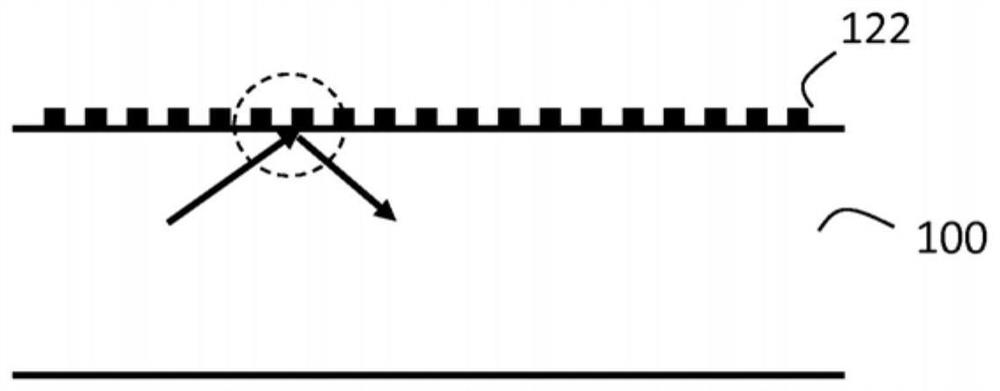
Waveguide element
A technology of waveguide components and waveguides, which is applied in the direction of optical components, light guides, planar/plate light guides, etc., can solve problems such as low-quality waveguide components and waveguide display devices, and problems caused by addition, so as to alleviate calculation problems and practical optics The effect of quality problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] definition
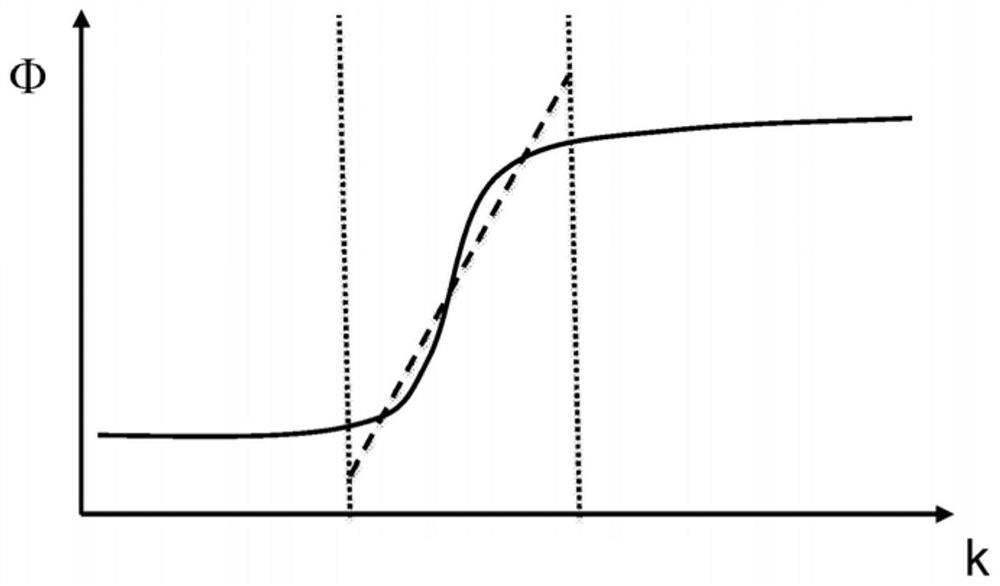
[0014] "Phase function" means as a function of the wave number in the wavelength (wave number) range of interest The phase distribution of the number.
[0015] "Geometrical optical path length" is defined herein as the distance traveled in the waveguide multiplied by the real part of the refractive index of the waveguide material at the wavelength of interest.
[0016] "Physical optical path length" is defined as the slope that linearly approximates the phase function at the wavelength of interest. That is, as the ratio between the phase change and the wave number difference. We note that this approximation is only used to simplify the discussion and does not mean that the phase function is or should be linear or approximately linear.
[0017] The terms "incoherent" and "fully incoherent" describe two light rays whose path length difference exceeds the coherent length in the relevant waveguide material. Specifically, if the slope of the linear approximation to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com