Named entity recognition and extraction using genetic programming
A genetic operation and program technology, applied in the field of named entity recognition and extraction using genetic programming, can solve problems such as low efficiency and slow speed, and achieve the effects of reducing manual input and errors, saving computing resources, and reducing the amount of iterative genetic operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
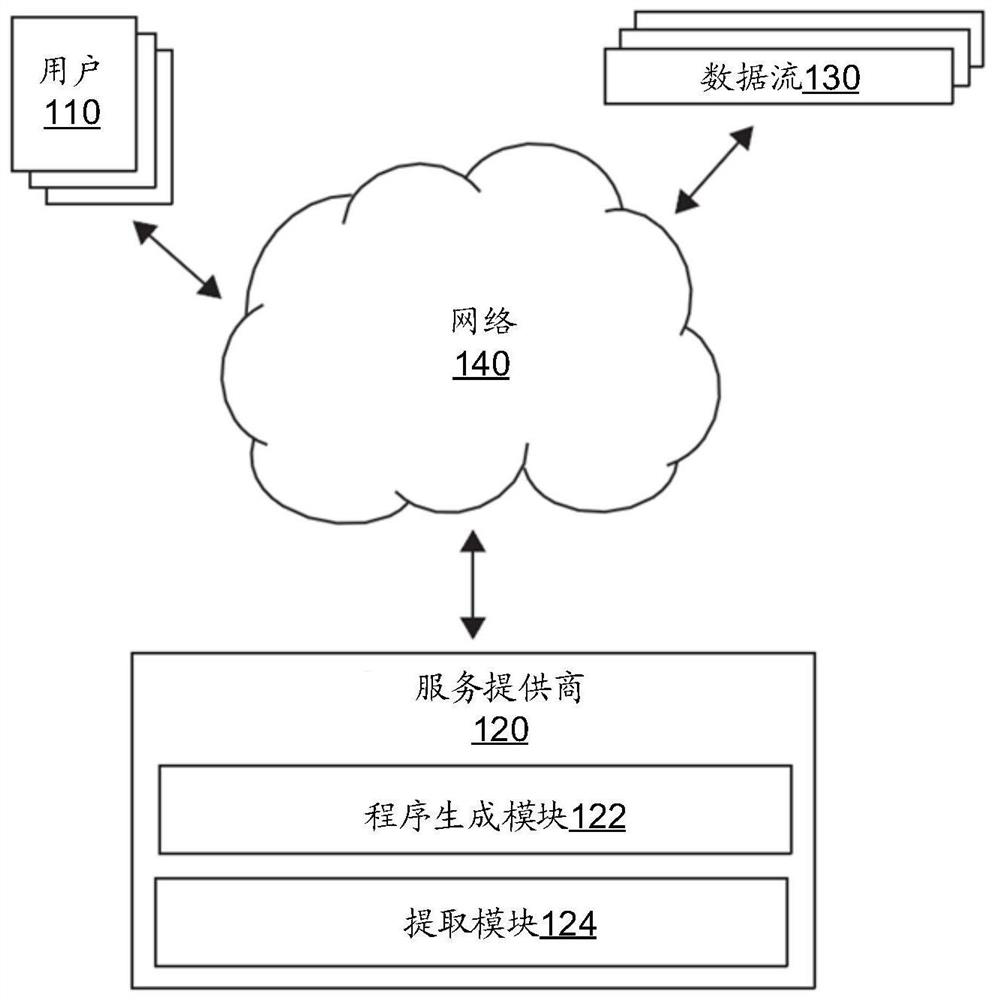
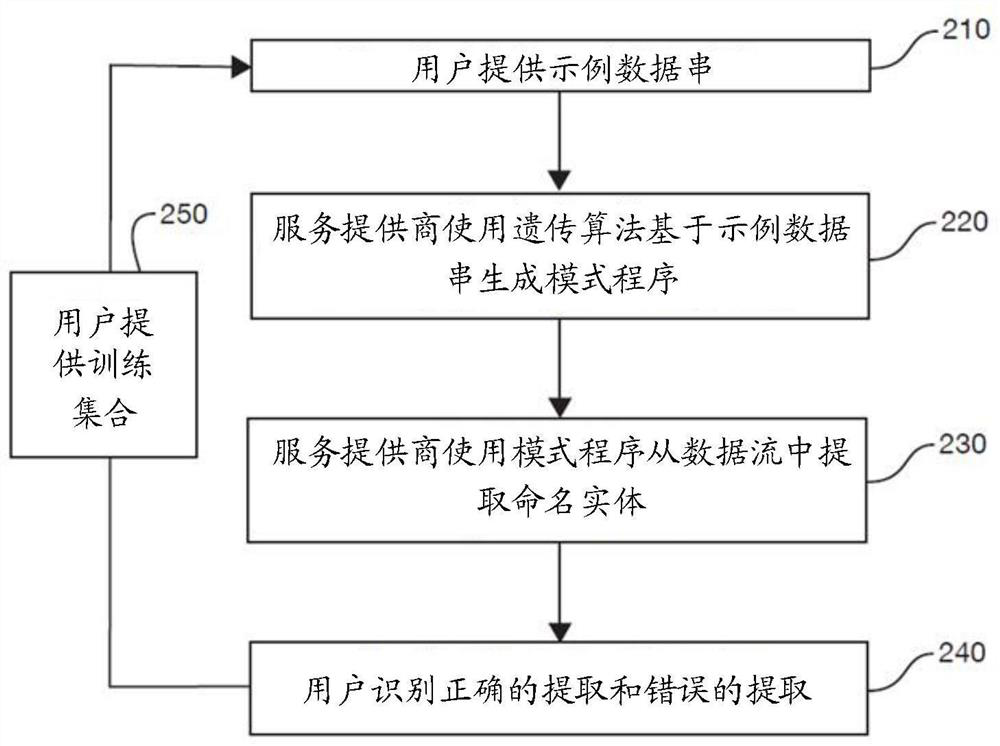
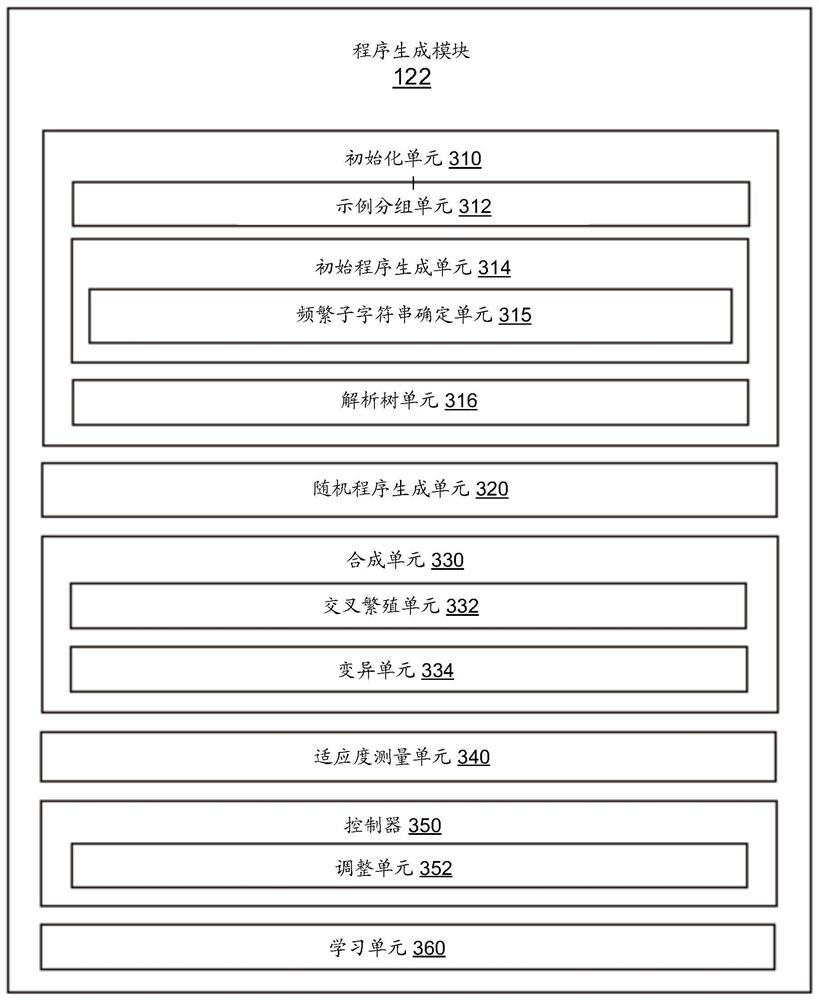
[0021] This paper describes techniques for generating pattern programs using genetic algorithms. Genetic algorithms operate on sample data strings representing categories of data to be identified or extracted by named entity recognition. Such an example data string is called a "positive example" data string. Genetic algorithms can also operate on negative example data strings, which represent data strings that are not positive example data strings, eg, not the target of a named entity recognition task. In an initialization phase, an initial schema program is generated based on sample data strings representing categories of data to be identified or extracted by named entity recognition. In some embodiments, the byte pair encoding technique is used to extract frequent substrings from the sample data string, and each extracted frequent substring is regarded as a single expression unit when generating the initial pattern program. Starting from the initial pattern program, geneti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com