Mobile cast-in-situ bored pile construction platform and method
A technology for drilling cast-in-place piles and construction platforms, which is applied to sheet pile walls, infrastructure engineering, bridge applications, etc., can solve the problems of large coverage, large investment, and many input materials of drilling platforms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A mobile bored pile construction method is applied to any one of claims 1-4, comprising the following steps:
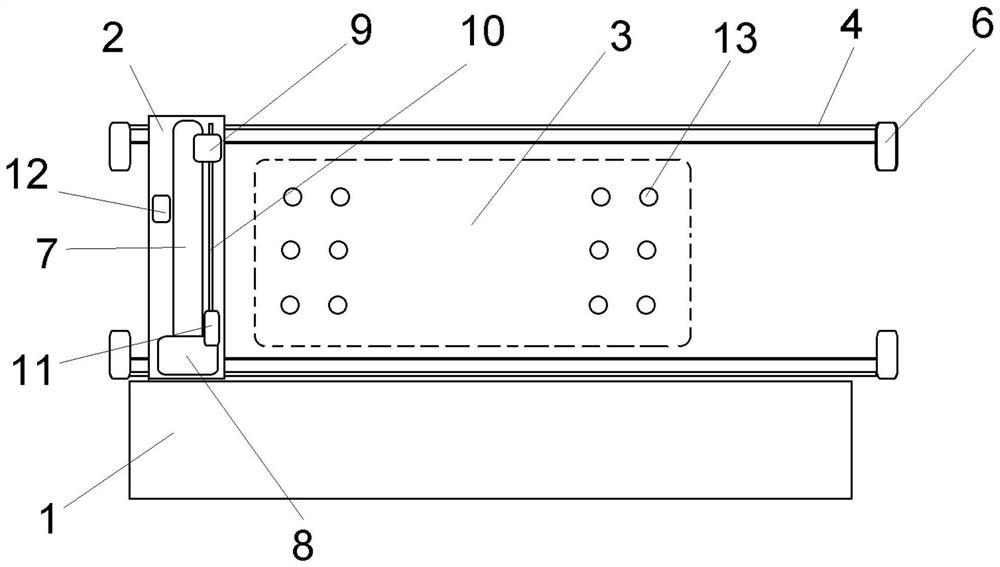
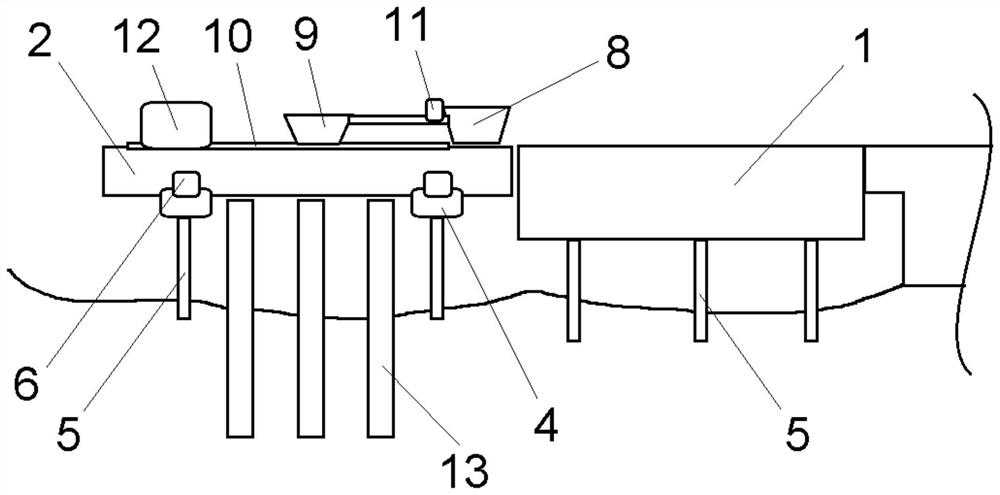
[0036] S1, preparing concrete and constructing the conduit 13;
[0037] S2. Make the support trestle 2 and the orifice hopper 9 in place through the driving device, and calibrate the detection rope;
[0038] S3, the orifice hopper 9 adopts double hopper form perfusion, the orifice hopper 9 is 3-4 cubic meters, and the auxiliary hopper 8 is 6-8 cubic meters;
[0039] S4. Concrete pouring exceeds the design pile top elevation until the hole overflows with concrete;
[0040] S5, vibrate the concrete within 3m of the pile top to ensure that the pile top concrete is dense;
[0041] S6. After the filling is completed, clean the conduit 13 and the auxiliary hopper 8 and orifice hopper 9;
[0042] S7. After the construction of the pile foundation is completed, the acoustic measurement tube is used for detection; the four acoustic measurement tubes are evenly arrange...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A mobile bored pile construction method is applied to any one of claims 1-4, comprising the following steps:
[0061] S1. Preparing concrete, pre-splicing the conduit 13, and testing the waterproofing of the seat;
[0062] S2. Make the support trestle 2 and the orifice hopper 9 in place through the driving device, and calibrate the detection rope;
[0063] S3. Fill the auxiliary hopper 8 with concrete, open the ball valve of the orifice hopper 9, and at the same time, two concrete trucks inject concrete into the orifice hopper 9 at the maximum flow rate and start pouring the back-sealing concrete until the back-sealing is completed;
[0064] S4. Detect the pouring height of the concrete by the measuring rope, and calculate the embedding depth of the conduit 13;
[0065] S5. When the embedment depth of the conduit 13 reaches 6m, pull out a section of 3m conduit 13, pull out 12 conduits 13 in total during the concrete pouring process, and pull out the remaining conduits ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] For the treatment method of the conduit 13 before perfusion:
[0071] First of all, the main reasons for the water ingress in the conduit 13 are:
[0072] ① The concrete reserves of the bottom cover are insufficient, or although the concrete reserves are sufficient, the distance between the bottom opening of the conduit 13 and the bottom of the hole is too large, and the bottom opening of the conduit 13 cannot be buried after the concrete falls, so that muddy water enters from the bottom opening;
[0073] ② The joint of the conduit 13 is not tight, the rubber pad between the joints is squeezed away by the high-pressure air bag of the conduit 13, or the weld seam is broken, and water flows in from the joint or weld seam;
[0074] ③The conduit 13 is lifted too fast, or the detection is wrong, the bottom opening of the conduit 13 exceeds the original concrete surface, and muddy water pours into the bottom opening.
[0075] The processing methods are:
[0076] ①If it is c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com