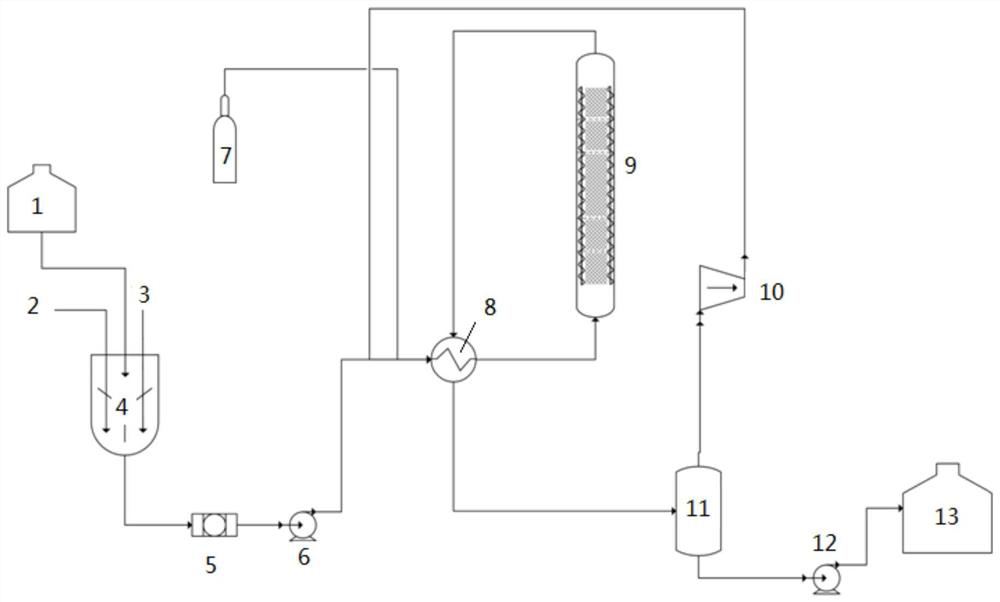
Continuous hydrogenation production device and production method for carbon-carbon double bonds in unsaturated polymer
A carbon double bond, feeding device technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of large operating capital, high warehouse costs, buildings and operation and management costs, so as to reduce auxiliary costs and improve process. Safety, mild reaction conditions and effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0127] Connect the experimental device according to the present invention, add latex raw materials with 5% solid content, colloidal particle size less than 20nm, and 10 phr potassium oleate additive based on raw rubber quality into the raw material pretreatment tank and mix them, then use a metering pump Put the latex into the feeding tube at a flow rate of 10mL / min, mix it with hydrogen at a flow rate of 5000mL / min in the feeding tube, preheat it to 115°C, and enter the hydrogenation reaction with a supported catalyst with an active component loading of 0.1%. After hydrogenation, the latex flows out of the reactor and enters the condensing system, where samples are taken for infrared testing to measure the degree of hydrogenation. When the reaction is over, the H is emptied 2 pressure and drain the latex from the container. Rinse the reaction equipment with clean water.
Embodiment 2
[0129] Connect the experimental device according to the present invention, add latex raw materials with 5% solid content, colloidal particle size less than 20nm, and 10 phr potassium oleate additive based on raw rubber quality into the raw material pretreatment tank and mix them, then use a metering pump Put the latex into the feeding tube at a flow rate of 10mL / min, mix it with hydrogen at a flow rate of 5000mL / min in the feeding tube and preheat it to 115°C, and enter the hydrogenation reaction with a supported catalyst with an active component loading of 0.05%. After hydrogenation, the latex flows out of the reactor and enters the condensing system, where samples are taken for infrared testing to measure the degree of hydrogenation. When the reaction is over, the H is emptied 2 pressure and drain the latex from the container. Rinse the reaction equipment with clean water.
Embodiment 3
[0131] Connect the experimental device according to the present invention, add latex raw materials with 5% solid content, colloidal particle size less than 20nm, and 10 phr potassium oleate additive based on raw rubber quality into the raw material pretreatment tank and mix them, then use a metering pump Put the latex into the feeding tube at a flow rate of 10mL / min, mix it with hydrogen at a flow rate of 5000mL / min in the feeding tube, preheat it to 115°C, and enter the hydrogenation reaction with a supported catalyst with an active component loading of 0.02%. After hydrogenation, the latex flows out of the reactor and enters the condensing system, where samples are taken for infrared testing to measure the degree of hydrogenation. When the reaction is over, the H is emptied 2 pressure and drain the latex from the container. Rinse the reaction equipment with clean water.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com