Preparation method of composite material, composite material and application thereof
A technology of composite materials and polymers, which is applied in the field of preparation of organic porous polymer composite materials, can solve the problems of reducing the resistance of precursor solution, the difficulty of combining MOFs and loading materials, and uneven spreading, so as to improve the mass transfer rate and The effect of adsorption efficiency, fast adsorption rate and easy molding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
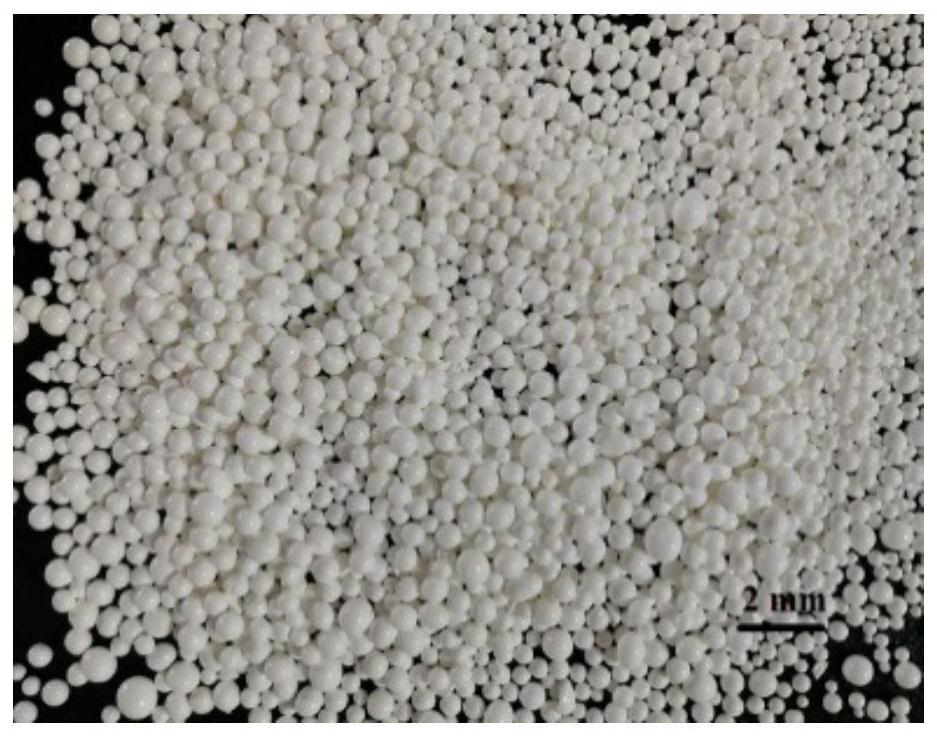
[0032] Accurately weigh 1.6 g of acrylamide, 0.4 g of N,N-methylenebisacrylamide, 0.1 g of Poloxamer F127, and 0.03 g of ammonium persulfate, dissolved in 5 ml of deionized water, and ultrasonicated for 5 min to obtain the aqueous phase; 11ml of toluene and 5ml of cyclohexane were mixed uniformly to obtain the oil phase; the water phase was uniformly stirred at a rotational speed of 3000r / min, the oil phase was added to the water phase, and the stirring was continued for 5 minutes to finally form a uniform and stable emulsion. Measure 15ml of toluene, 15ml of carbon tetrachloride, and 60ml of cyclohexane, add 0.15g of ethyl cellulose and mix them uniformly as the third phase, pour the emulsion into the third phase under nitrogen protection, and rotate at 350r / min. Then, 14 drops of reducing agent N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine were added, and cross-linking polymerization was carried out at 65°C for 30min. After solidification, the balls were taken out and washed with eth...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The preparation process of polyacrylamide particles is the same as that of Example 1. Accurately weigh 2.1 g of metal salt zirconium chloride, measure 7.5 ml of acetic acid, dissolve it in 15 ml of N,N-dimethylformamide by ultrasonic to obtain solution A, then weigh 1.1 g of fumaric acid, and measure 1.0 ml of trisulfuric acid. Ethylamine was ultrasonically dissolved in 15ml of N,N-dimethylformamide to obtain B solution, and then A solution and B solution were ultrasonically mixed to obtain a precursor solution, which was poured into 0.3 g of dried polypropylene In the flask of amide particles, the flask was reacted in an oil bath at 85 °C for 24 h, and MOFs particles were grown on the macropore surface of the porous polymer. After washing and drying at 150 °C for 24 h, the MOFs / polyacrylamide composite material was obtained.
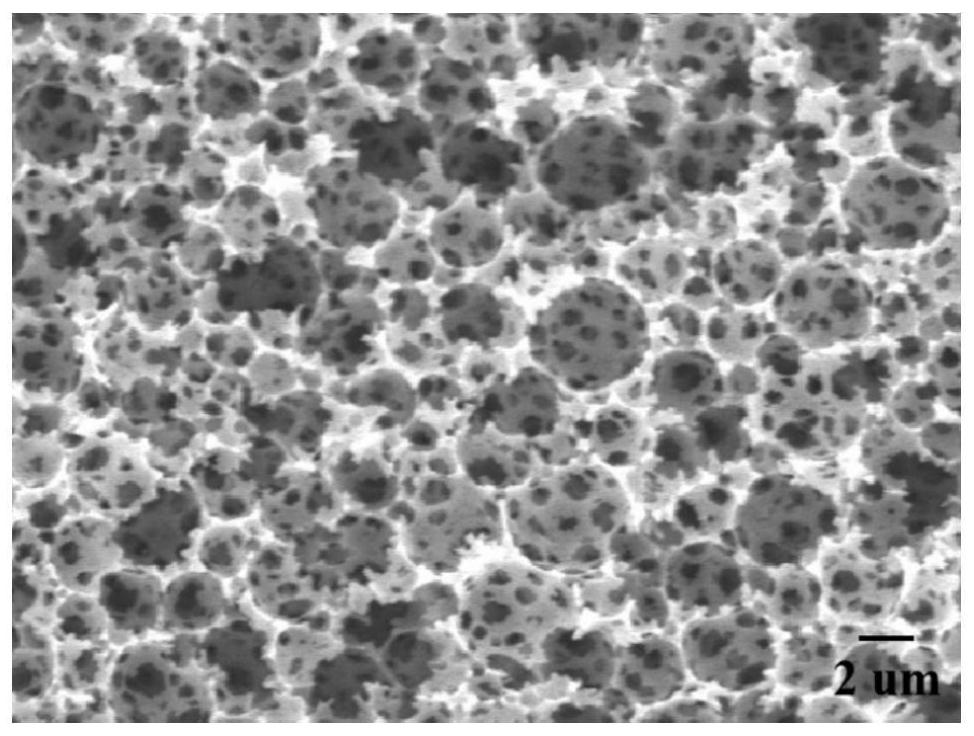
[0037] The scanning electron microscope image of the internal pore structure of the MOFs / polyacrylamide composite prepared in this example is sh...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The preparation process of polyacrylamide particles is the same as that of Example 1. Accurately weigh 2.1g of metal salt zirconium chloride, measure 15ml of acetic acid, dissolve it in 15ml of N,N-dimethylformamide by ultrasonic to obtain solution A, then weigh 1.1g of fumaric acid and measure 2.0ml of trimethylamine Ultrasonic dissolving in 15ml N,N-dimethylformamide to obtain B solution, then ultrasonically mixing A solution and B solution to obtain a precursor solution, which was poured into 0.3g dried polyacrylamide particles The flask was reacted in an oil bath at 100 °C for 24 h, and MOFs particles were grown on the macroporous surface of the porous polymer. After washing, the solvent was removed in a vacuum drying oven for 24 h for activation to obtain MOFs / polyacrylamide composite material. .
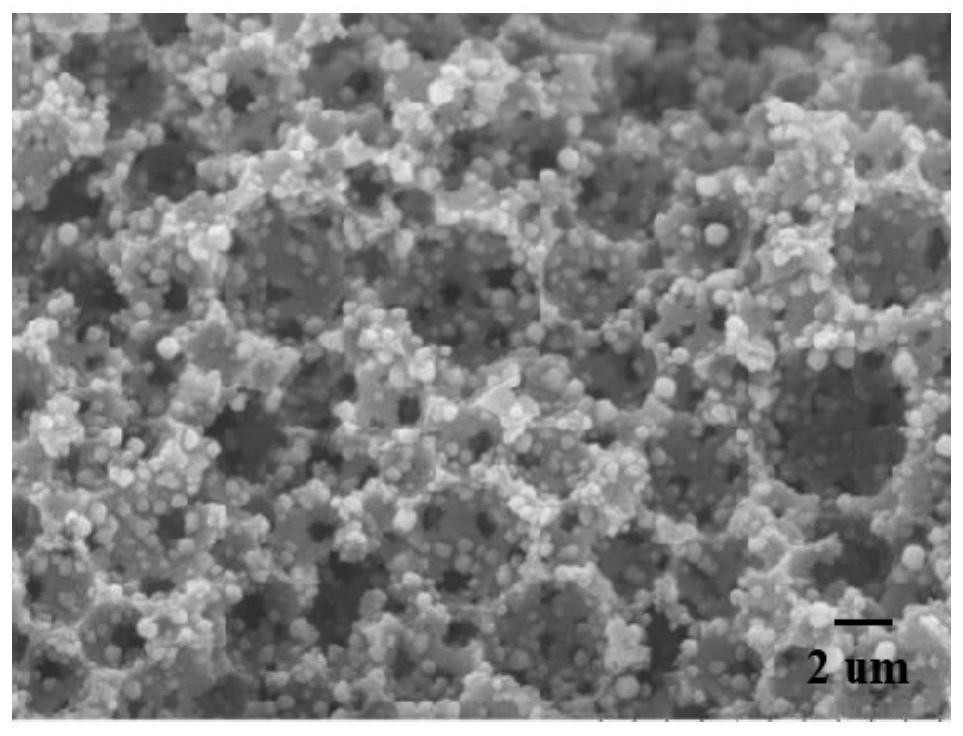
[0040] The scanning electron microscope image of the internal pore structure of the MOFs / polyacrylamide composite prepared in this example is shown in Figure 5 , it c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com