Light splitting system by utilizing electro-optic drive and electro-optic crystal
An electro-optic crystal and spectroscopic system technology, applied in the field of spectroscopic systems, can solve the problems of limiting processing efficiency and weakening of laser single pulse energy dispersion, and achieve the effect of keeping energy constant and meeting the requirements of multi-channel laser processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
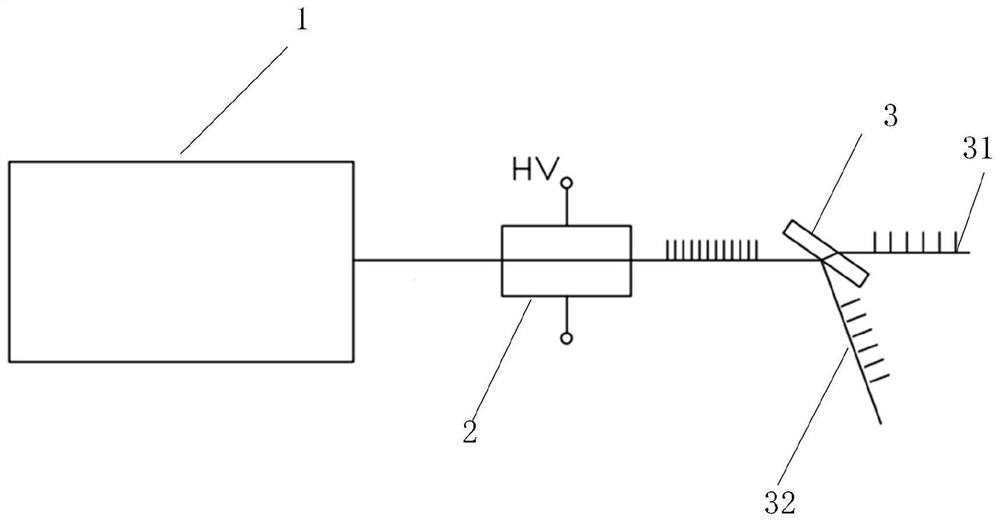
[0026] An embodiment of the present invention provides a spectroscopic system using electro-optic drive and electro-optic crystals, such as figure 1 As shown, the system includes: a laser 1, a first electro-optic crystal 2 and a first polarizer 3;
[0027] Wherein, the laser 1 emits a linearly polarized beam through the first electro-optic crystal 2 and the first polarizer 3 in sequence; a fixed voltage is applied to the first electro-optic crystal 2; the first polarizer 3 divides the linearly polarized beam into a first beam 31 and a second beam 31. Beam 32.
[0028] Through the above system, the electro-optic crystal, high-voltage driving source and polarizer are used to realize the multi-channel and multi-frequency output of the laser, keep the energy unchanged, meet the requirements of multi-channel laser processing, and solve the problem of splitting the laser beam at the same time in the prior art. The dispersion of single pulse energy is weakened, and for laser process...
Embodiment 2
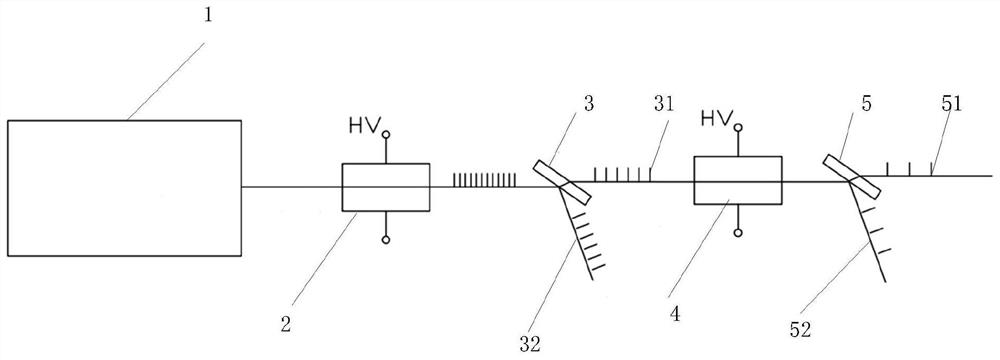
[0035] A spectroscopic system using electro-optic drives and electro-optic crystals, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes: a laser 1, a first electro-optic crystal 2, a first polarizer 3, a second electro-optic crystal 4, and a second polarizer 5;
[0036] Wherein, the laser 1 emits a linearly polarized beam through the first electro-optic crystal 2 and the first polarizer 3 in sequence; a fixed voltage is applied to the first electro-optic crystal 2; the first polarizer 3 divides the linearly polarized beam into a first beam 31 and a second beam 31. Beam 32.
[0037] The first light beam 31 passes through the second electro-optic crystal 4 and the second polarizer 5 in sequence and is divided into a third light beam 51 and a fourth light beam 52 .
[0038] In an embodiment of the present invention, the first light beam 31 is a p-polarized transmitted light beam.
[0039] In an embodiment of the present invention, the second light beam 32 is an S-polarized reflected light...
Embodiment 3
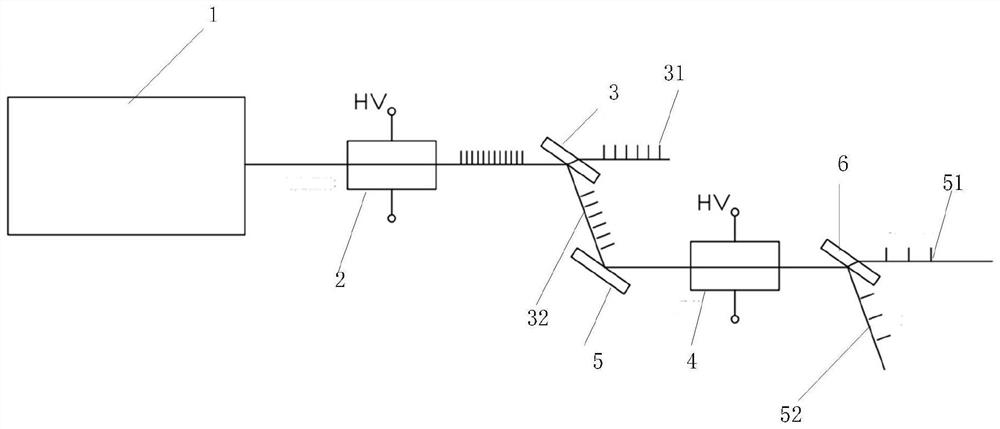
[0045] A spectroscopic system using electro-optic drives and electro-optic crystals, such as image 3 As shown, it includes: a laser 1, a first electro-optic crystal 2, a first polarizer 3, a second electro-optic crystal 4, a second polarizer 5 and a third polarizer 6;
[0046] Wherein, the laser 1 emits a linearly polarized beam through the first electro-optic crystal 2 and the first polarizer 3 in sequence; a fixed voltage is applied to the first electro-optic crystal 2; the first polarizer 3 divides the linearly polarized beam into a first beam 31 and a second beam 31. The light beam 32 ; the second light beam 32 sequentially passes through the second polarizer 5 , the second electro-optic crystal 4 , and the third polarizer 6 to be divided into a third light beam 51 and a fourth light beam 52 .
[0047] In an embodiment of the present invention, the first light beam 31 is a p-polarized transmitted light beam.
[0048] In an embodiment of the present invention, the second ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com