Memory controller and memory control system
A technology of memory controller and memory, which is applied in the direction of instruments, various digital computer combinations, electrical digital data processing, etc., and can solve the problems of increasing system overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
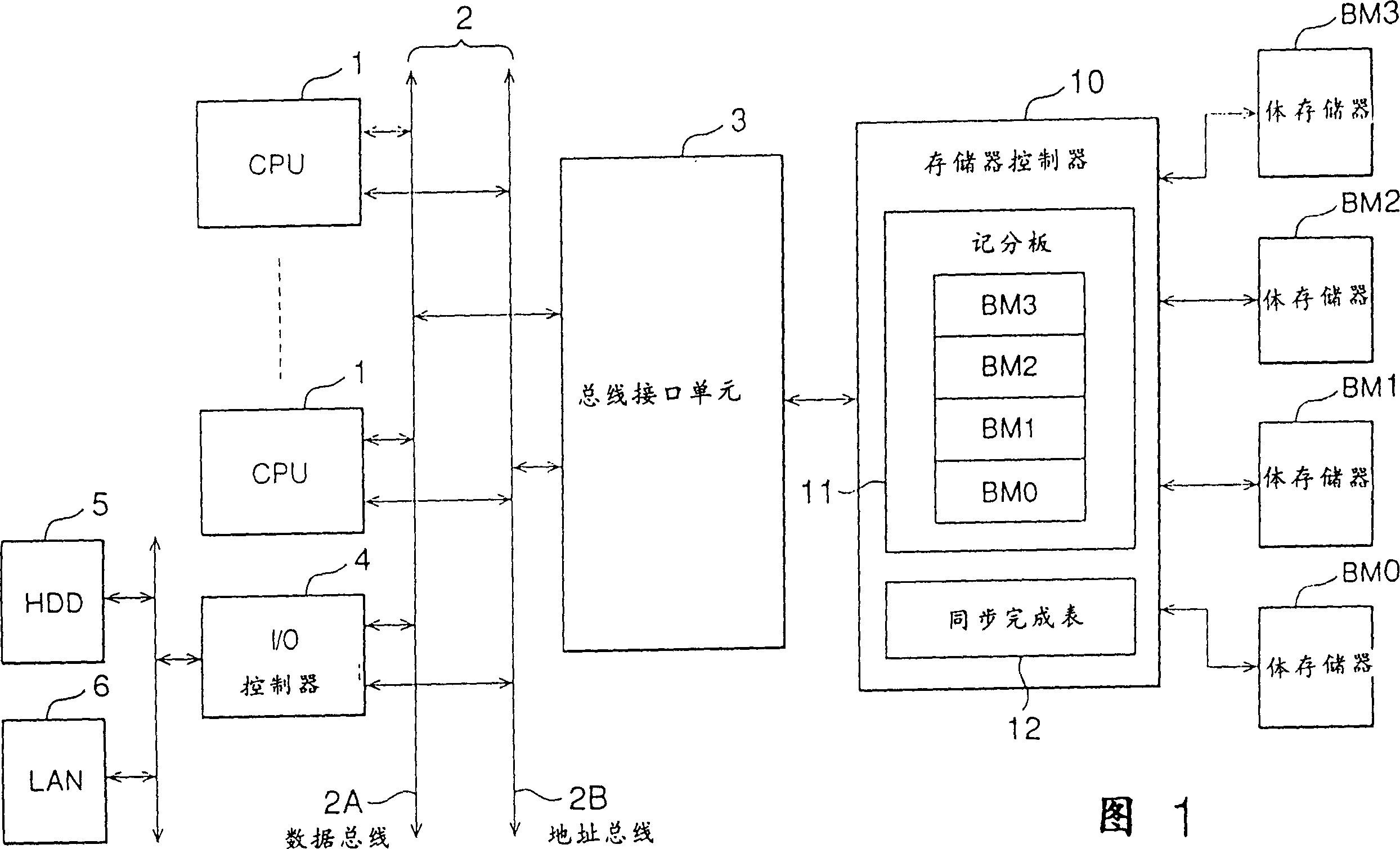
[0088] In the following, reference will be made to Figure 3 to Figure 4 The operation of the first embodiment is briefly described.
[0089]As described above, the memory controller 10 of this embodiment controls the bank memories BM0 to BM3 corresponding to the four memory areas 0 to 3 by the 4-way interleave function. The memory controller 10 shown in FIG. 3 includes execution units 108 , 118 , 128 , 138 and scoreboards 100 , 110 , 120 , 130 , which are separately provided for the four memory banks BM0 to BM3 . In the scoreboards 100, 110, 120, 130, the valid flag is represented by "Val", the issue enable flag is represented by "Fn", and the synchronization flag is represented by "SYNC".
[0090] like Figure 4 As shown, after receiving a memory access instruction from the processor bus 2, the bus interface unit 3 transmits the instruction to the memory controller 10 (step S1). When receiving a memory access command to one of the memory areas 0 to 3, the memory controller ...
no. 2 example
[0134] As shown in FIG. 17 , the second embodiment of the present invention is to add an entry 160 for synchronization conditions in the synchronization completion table 12 . The entry 160 is an item for indicating a synchronization condition related to a request from the same requester (processor) or a synchronization condition related to the same address (here, it is assumed that the condition is applied to the same address). The rest of the system structure and constitution of the memory controller 10 are the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0135] The above structure realizes the function of executing continuous instructions (continuous operation) that do not satisfy the synchronization condition and will not be affected by the synchronization operation. Among the operations satisfying the synchronization condition, operations performed after the synchronization operation are prohibited from being performed earlier than operations performed before the synchronizati...
no. 3 example
[0168] The third embodiment of the present invention is such a system, it can simultaneously realize the processing function of a plurality of synchronous instructions and comprises a memory controller 10, this memory controller 10 has a plurality of synchronization flags (SYNC flags) provided with multilevel The scoreboard and a synchronization completion table are provided with multi-level synchronization completion markers (SYNC completion). Subsequent synchronization operations are not retried until all synchronization levels have been used.
[0169] In the third embodiment, synchronization processing is performed in the order in which synchronization operations are performed. In particular, where synchronous operations A, B, and C are received, they are executed in the following order; operations received before synchronous operation A, operations received between synchronous operations A and B, operations received between synchronous operations B and Operations received...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com