Preparation method of antagonist functionalized poly-L-lactic acid porous microspheres
A technology of poly-L-lactic acid and porous microspheres, which is applied in the direction of anti-inflammatory agents, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of poor hydrophilicity, increase the load capacity, and improve Effects of drug concentration, inhibition of cellular inflammatory gene expression and factor secretion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The preparation of the BSA nanoparticle of embodiment 1 load antagonist
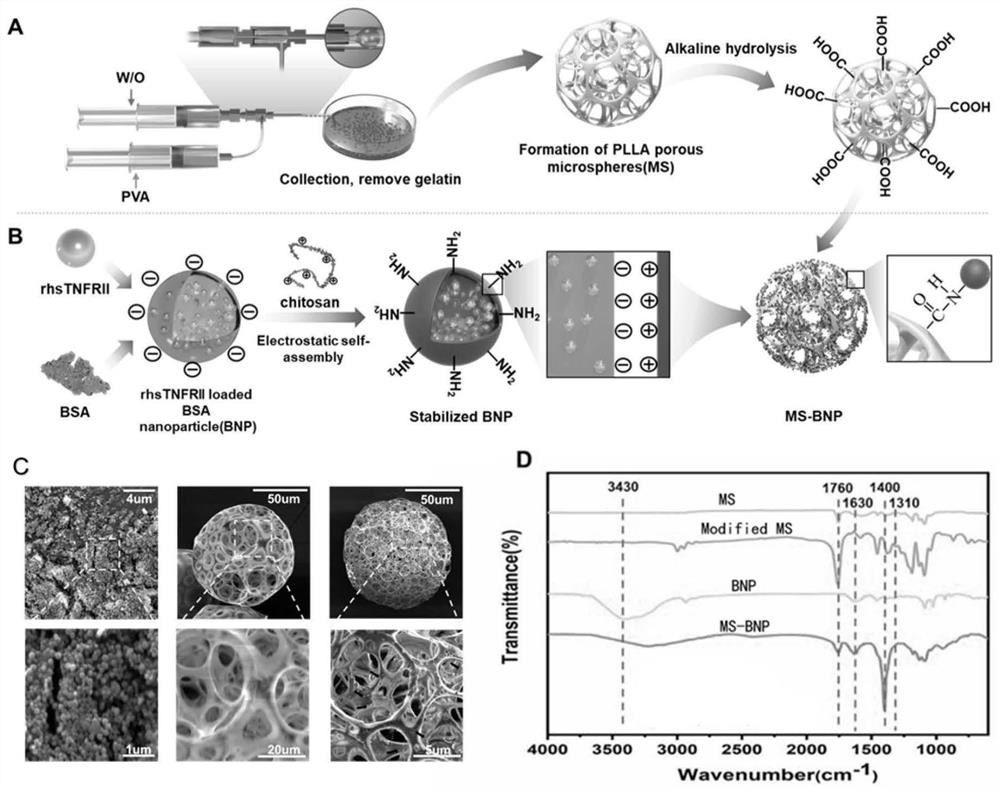
[0027]Add 100 mg of BSA to 10 mL of deionized water and stir evenly, then add 10 μg of antagonist dissolved in phosphate buffer; pump 40 mL of ethanol into the BSA solution containing antagonist at a flow rate of 2 mL / min, and stir overnight at room temperature; Add 40mL of chitosan solution dissolved in 1% acetic acid solution with a concentration of 1mg / mL to the above mixture; then pump in ethanol at a flow rate of 0.5mL / min, stir at room temperature for 8h; centrifuge the obtained nanoparticles at 12000rpm for 20min , washed three times with 50% ethanol solution to prepare antagonist-loaded BSA nanoparticles.
Embodiment 2
[0028] The preparation of embodiment 2 L-polylactic acid porous microspheres
[0029] PLLA was dissolved in dichloromethane, gelatin and polyvinyl alcohol PVA were dissolved in deionized water to make solutions with final concentrations of 2wt%, 7.5wt%, and 1wt% respectively; 1g gelatin and PVA mixed solution was added to 3g PLLA solution , ultrasonically mixed (power 10%, ultrasonic 2s, interval 1s), as an emulsion.
[0030] The microfluidic device for preparing microspheres is a coaxial needle with dual channels, the inner and outer diameters are (0.26mmi.dx0.51mm o.d, 0.84mm i.d x1.27 mm o.d, 25G / 18G), and the end of the needle is connected to PVC tubing for collection; a syringe loaded with emulsion as the discontinuous phase, connected to the inner diameter of the device; a continuous phase of 1% PVA solution, connected to the outer diameter of the device, and the flow rate of the two was set at 20:1 to make it continuous Run until the emulsion is used up; collect the mi...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3 Preparation of antagonist-functionalized poly-L-lactic acid porous microspheres
[0032] Ultrasonically disperse the L-polylactic acid porous microspheres prepared in Example 2 into 5 mL of MES (pH=6.0) buffer, add 40 mg of EDC and 60 mg of NHS respectively, ultrasonicate for 15 s, react at 37°C for 15 min, centrifuge and discard the supernatant solution; the antagonist-loaded BSA nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 were dispersed in 10 mL of deionized water, the centrifuged EDC-activated microspheres were added to it, and ultrasonically mixed; reacted overnight at 37°C, and finally centrifuged again. The antagonist-functionalized L-polylactic acid porous microspheres were obtained by repeated washing three times with deionized water.
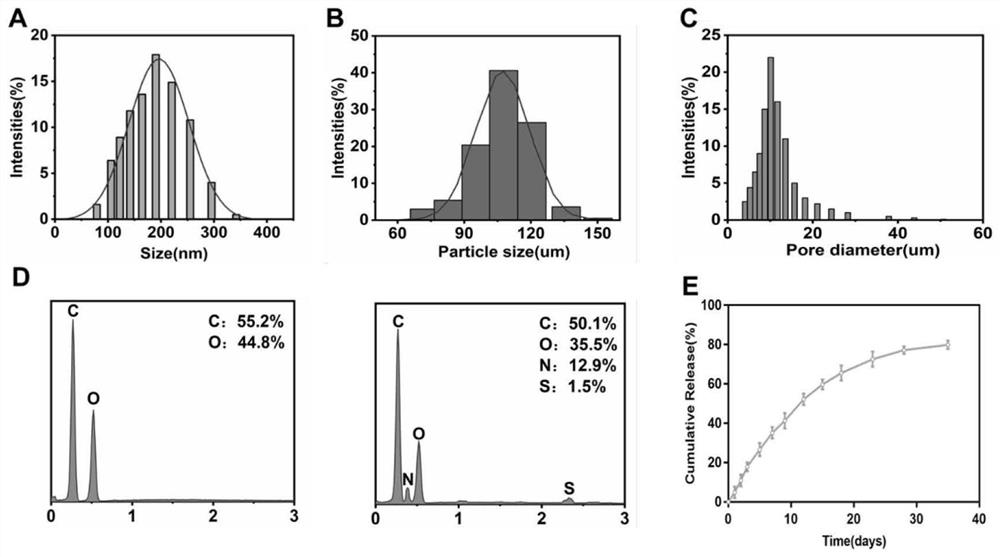
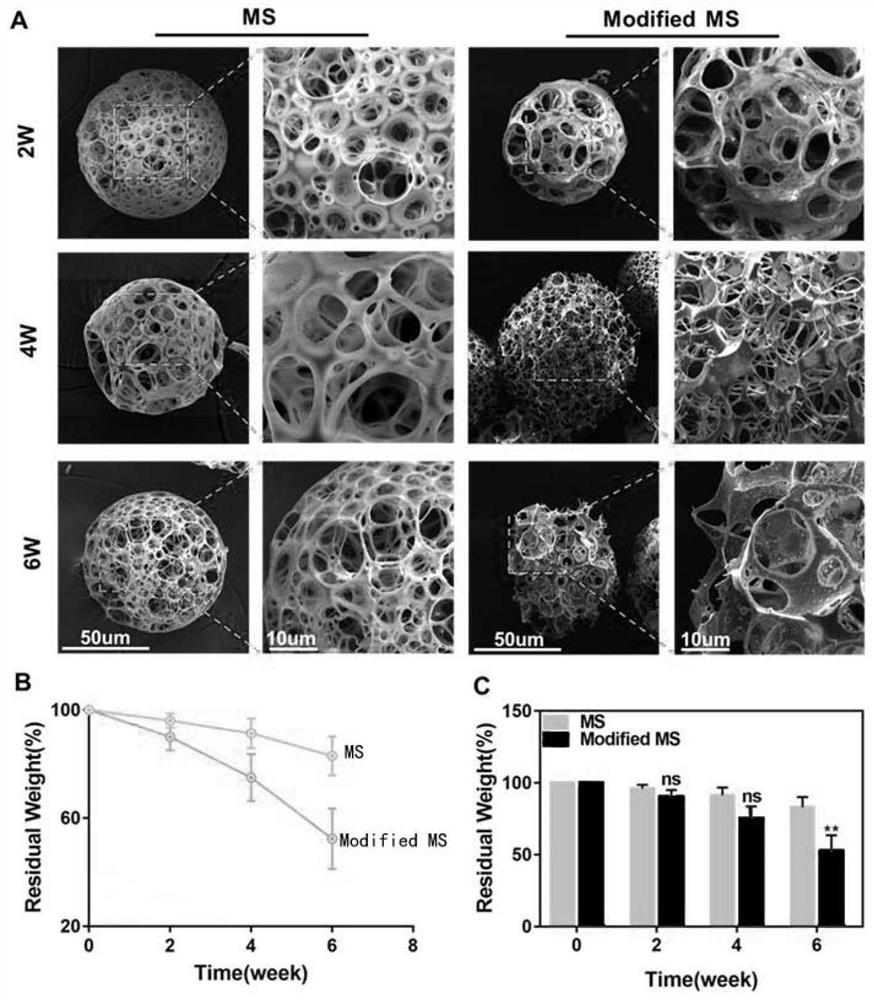
[0033] figure 1 A and B are the flow charts for the preparation of the microspheres of the present invention, figure 1 In A, the PLLA microspheres were treated with alkaline solution to expose the surface carboxyl groups, fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com