A Method for Evaluating the Competitive Adsorption of Polystyrene Microspheres and Humic Acid in Sand Filtration
A technology of polystyrene microspheres and competitive adsorption, which is applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, filtration separation, etc., and can solve problems such as unclear degree of competitive adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
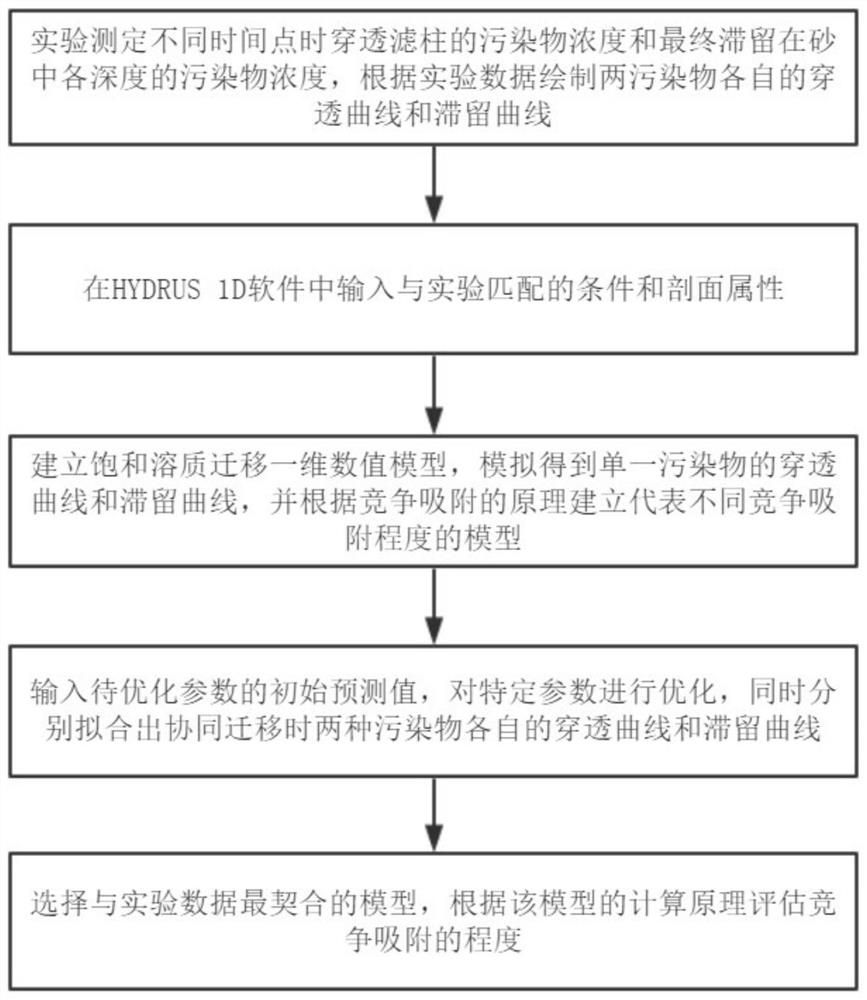
[0052] S1: carry out a tracer experiment. 100mM background salt solution (KCl solution) was injected into the sand filter column, and different time points were measured
[0055]
[0056]
[0060]
Embodiment 2
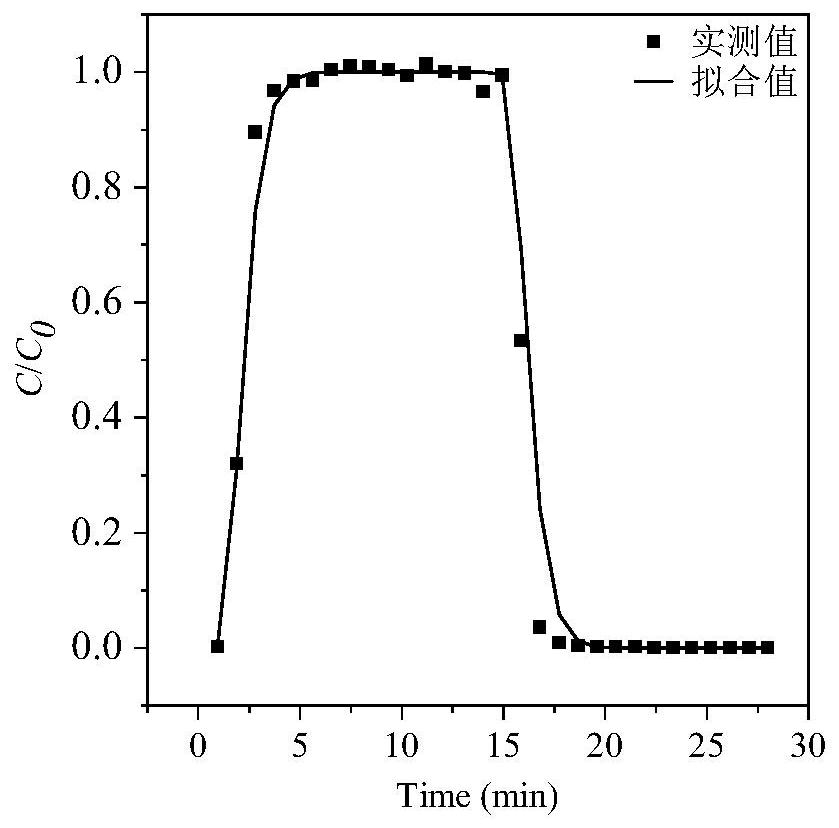
[0063] S1: carry out a single pollutant migration experiment. Separate migrations of polystyrene microspheres and humic acid were carried out separately
[0066]
[0067]
[0068]
Embodiment 3
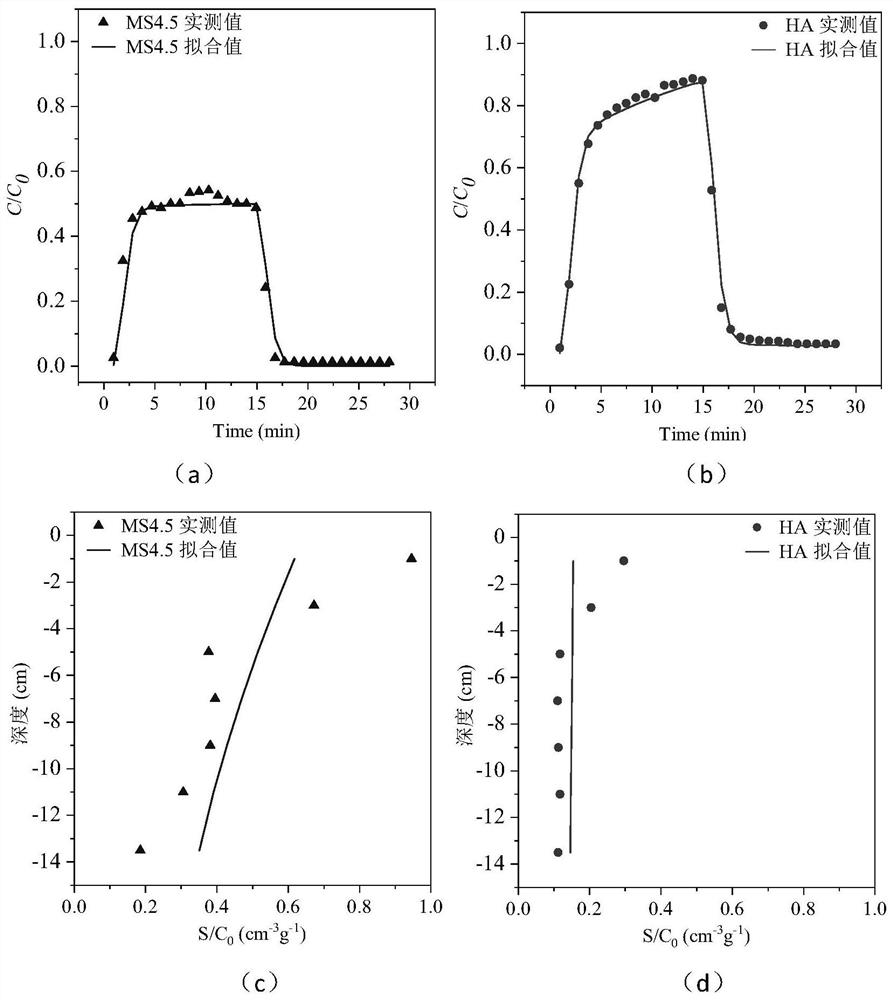
[0072] S1: carry out the co-migration experiment of two pollutants. 4.5μm polystyrene microspheres (MS4.5) and corrosive
[0075]
[0076]
[0077]
[0078]
[0079]
[0080]
[0082] S4: for M1, set Г
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com