Image pickup optical lens optical lens
An optical lens and lens technology, applied in the field of optical lenses, can solve the problems of unreasonable setting of long focal length, ultra-thinning, focal power, lens spacing and lens shape, etc., and achieve the effect of excellent optical characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
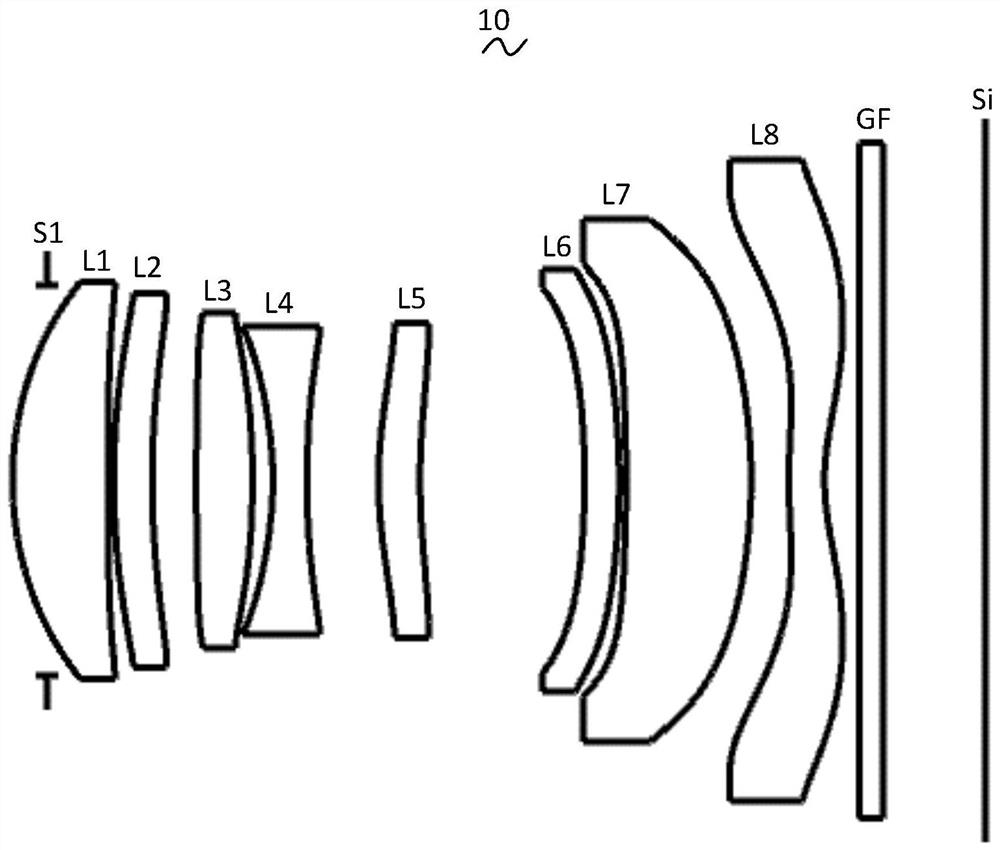
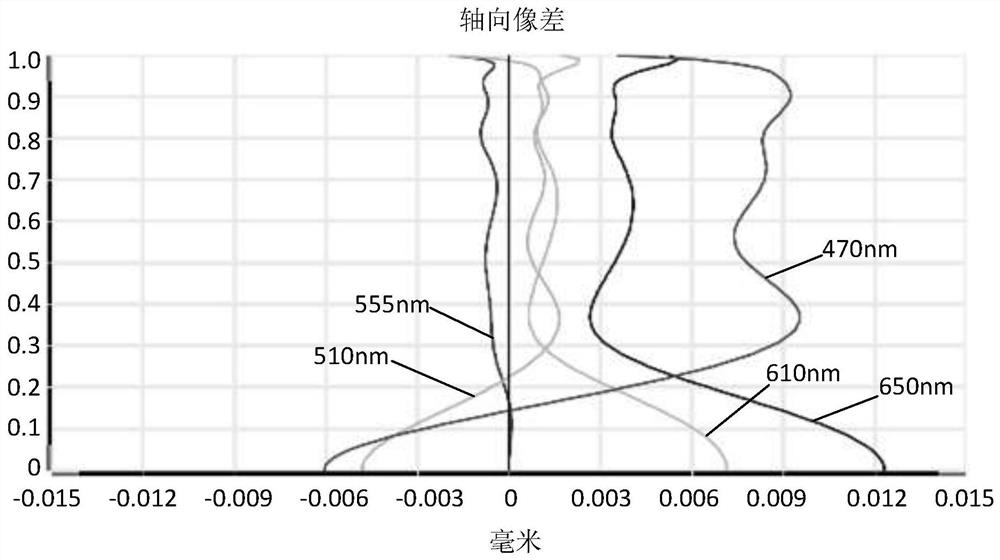
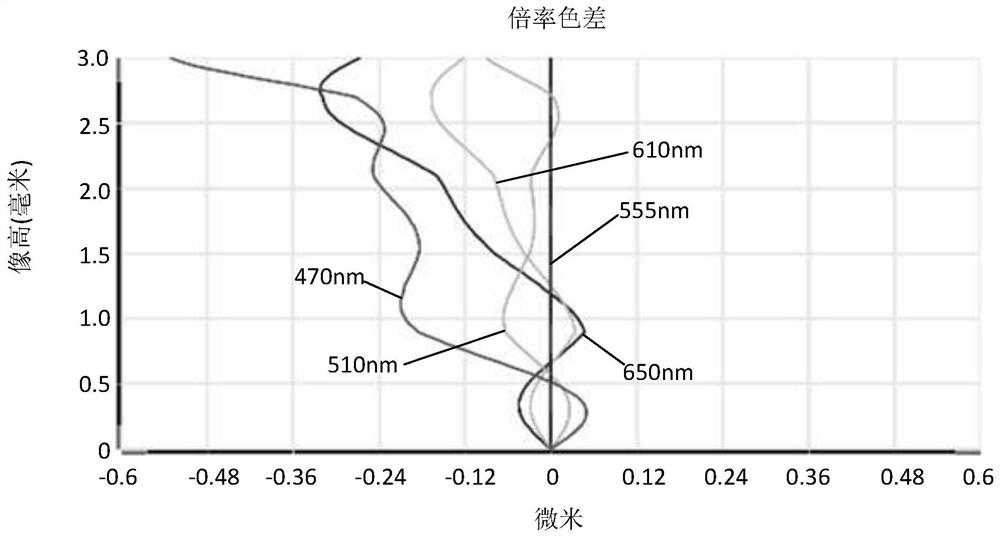
[0034] Referring to the accompanying drawings, the present invention provides an imaging optical lens 10 . figure 1 Shown is a schematic structural view of the imaging optical lens 10 according to the first embodiment of the present invention, and the imaging optical lens 10 includes eight lenses. Specifically, the left side is the object side, and the right side is the image side, and the imaging optical lens 10 includes in sequence from the object side to the image side: an aperture S1, a first lens L1, a second lens L2, a third lens L3, and a fourth lens L4, fifth lens L5, sixth lens L6, seventh lens L7, and eighth lens L8. An optical element such as an optical filter (filter) GF may be disposed between the eighth lens L8 and the image plane Si.
[0035] In this embodiment, the first lens L1 has positive refractive power, the second lens L2 has positive refractive power, the third lens L3 has positive refractive power, the fourth lens L4 has negative refractive power, and ...
no. 2 approach
[0168] Figure 5 Shown is a schematic structural view of the imaging optical lens 20 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The second embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, and the meanings of the symbols are the same as those of the first embodiment. Only the differences are listed below.
[0169] In this embodiment, the third lens L3 has a negative refractive power, the image side of the first lens L1 is a convex surface on the paraxial axis, the image side of the second lens L2 is a convex surface on the paraxial axis, and the object side of the third lens L3 is convex. Concave in the near axis.
[0170] Table 5 and Table 6 show design data of the imaging optical lens 20 according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0171] 【table 5】
[0172]
[0173]
[0174] Table 6 shows the aspheric surface data of each lens in the imaging optical lens 20 according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[01...
no. 3 approach
[0188] Figure 9 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of the imaging optical lens 30 of the third embodiment of the present invention. The third embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, and the meanings of symbols are the same as those of the first embodiment. Only the differences are listed below.
[0189] In this embodiment, the third lens L3 has a negative refractive power, the image side of the first lens L1 is a convex surface on the paraxial axis, the image side of the second lens L2 is a convex surface on the paraxial axis, and the object side of the third lens L3 is convex. Concave in the near axis.
[0190] Table 9 and Table 10 show design data of the imaging optical lens 30 according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0191] 【Table 9】
[0192]
[0193] Table 10 shows the aspheric surface data of each lens in the imaging optical lens 30 of the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0194] 【Table 10】
[0195]
[0196...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com