A Millimeter Wave Beam Alignment Method Based on Sparse Coding
A sparse coding, millimeter-wave technology, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, space transmit diversity, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as long scan time, lower gain, difficulty in obtaining millimeter-wave channel information, etc., and achieve low computational complexity , the effect of reducing the number of scans
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0061] This example includes the following steps:
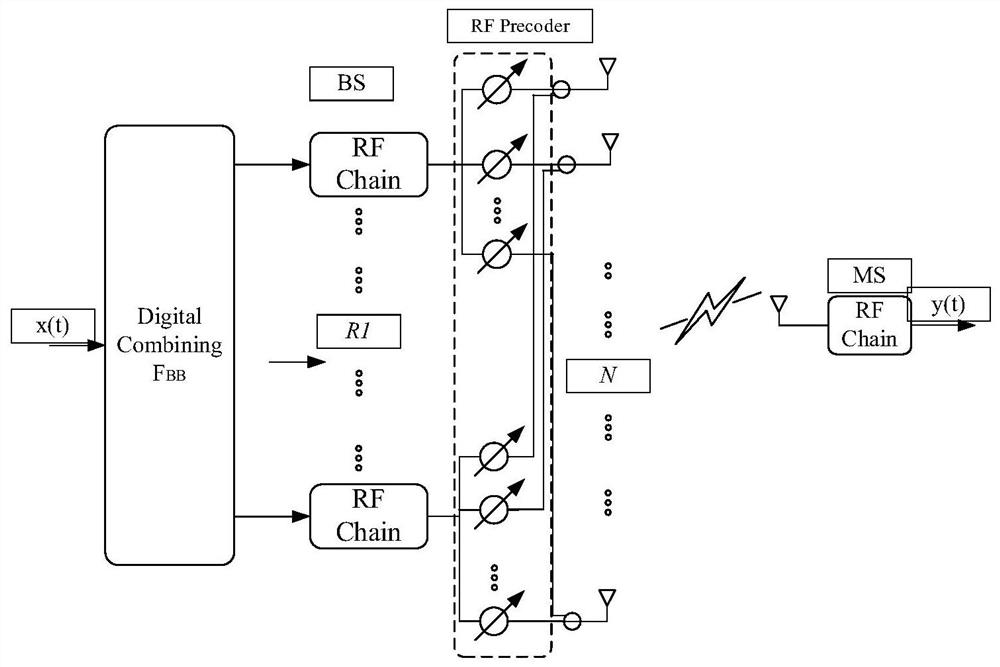
[0062] S1: In the first stage, the BS sends T pilot signals to estimate the time-varying channel, and at the same time, the BS uses a multi-beam receiving matrix to receive. Specifically, at time t, the BS sends the pilot vector Receiver uses Received, both vectors satisfy the following conditions
[0063] f(t)=F RF (t)F BB (t)=F BS ψ(t)
[0064] w(t)=W RF (t)W BB (t)=F MS (t)v(t)
[0065] S2: Separately intercept the T pieces of data received by the i-th radio frequency link and process them separately as follows
[0066]
[0067] S3: Divide the measurement matrix ψ into two parts and design separately as follows
[0068] ψ=G⊙S
[0069] where ⊙ represents a row tensor operation, where G is a sparse pattern matrix, and S is a node identification matrix.
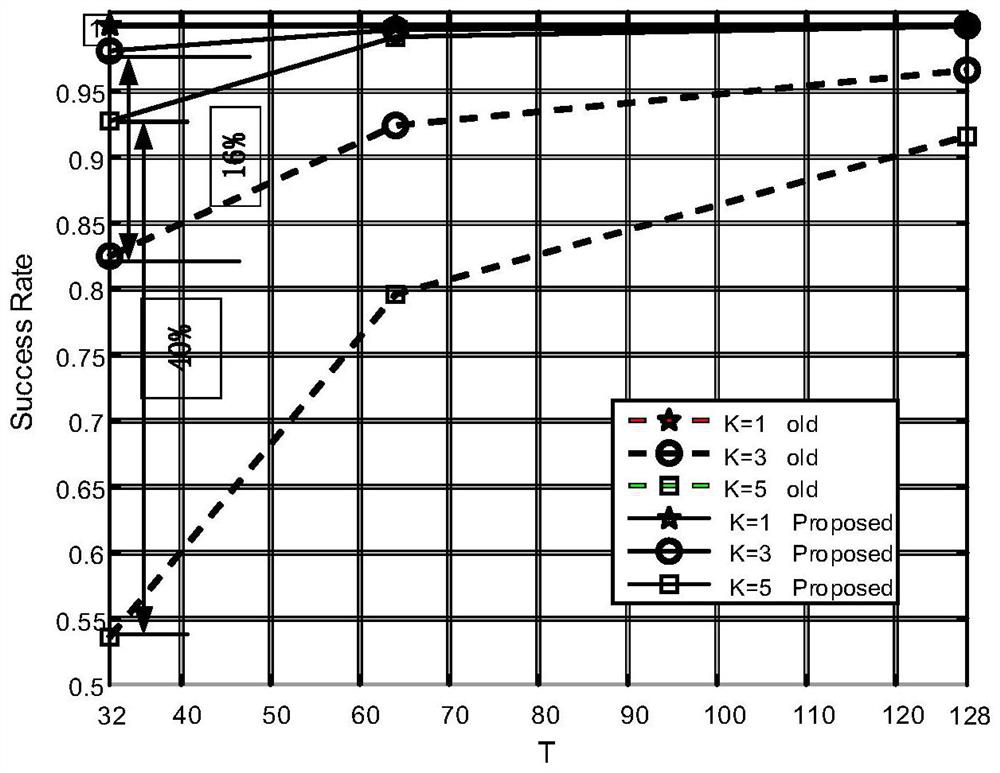
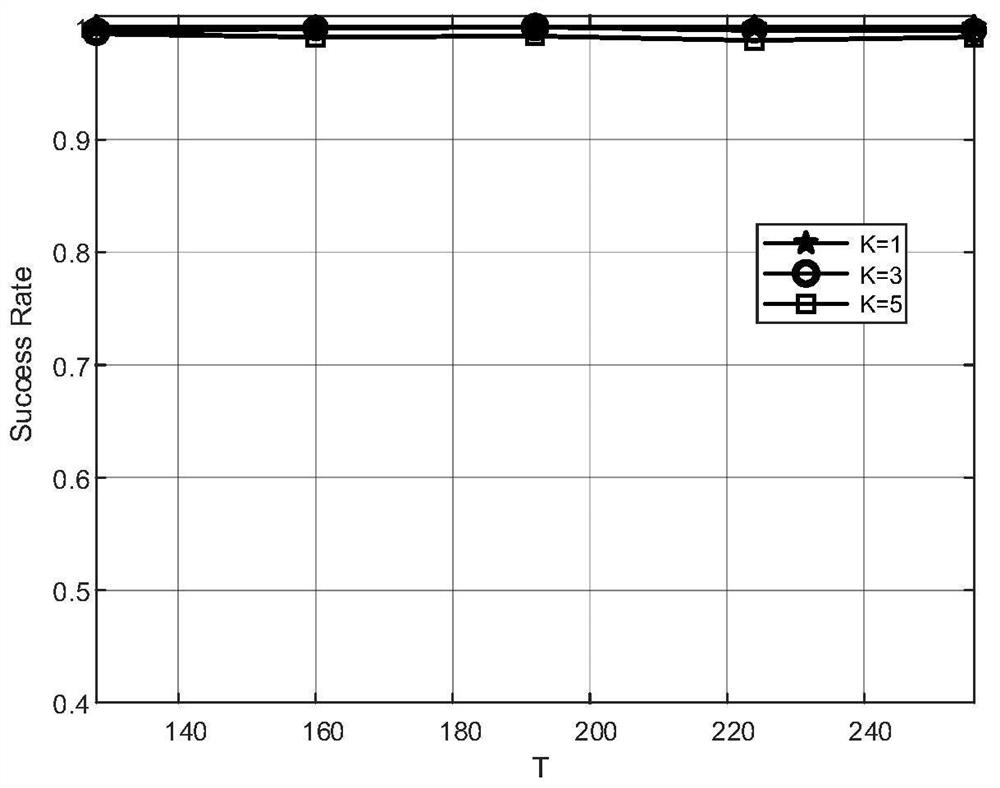
[0070] zero-ton: Define a check node as zero-ton when its multi-beam detection (the connecting line of the node on the right of the figure) does not reach ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com