Prediction and characterization of dlbcl cell of origin subtypes
A technology of B cells and cells, applied in the field of prediction and characterization of cell subtypes of DLBCL origin, which can solve problems such as different histories of precursor cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0047] Example 1: Sample
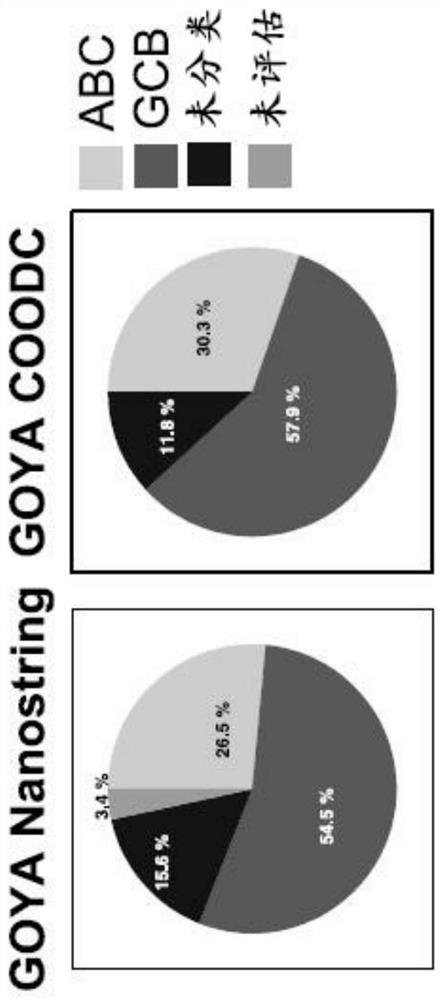
[0048] Clinical and genomic data are available from patients treated in the following trials: GOYA clinical trial (NCT01287741; R-CHOP and G-CHOP) (Vitolo, U. et al., Obinutuzumab or Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone in PreviouslyUntreated Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 35, 3529-3537 (2017)), and the MAIN clinical trial (NCT00486759; R-CHOP+ / -Bevacizumab) (Seymour, J.F. et al., R-CHOP with or without bevacizumab in patients with previously untreated diffuse large B Cell lymphoma: final MAIN study outcomes. Haematologica 99, 1343-1349 (2014)). The protocols of the original trials were approved by local or national ethics committees according to the laws of the respective countries, and the studies were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Activated B-cell (ABC) / germinal center B-cell (GCB) / unclassified DLBCL prognostic subtypes were determined by Nanostring as...
example 2
[0049] Example 2: DNA Sequencing
[0050] use The DNA component of the platform sequenced all samples and included targeted DNA sequencing of approximately 465 genes as described in: He, J. et al., Integrated genomicDNA / RNA profiling of hematologic malignancies in the clinical setting . Blood 127, 3004-3014 (2016). In addition to validated short variants, copy number alterations (advanced amplifications and deep deletions), rearrangements, tumor mutational burden (TMB), and microsatellite instability (MSI) status, studies using only platform signatures were utilized , including chromosome arm-level copy number and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) metrics.
example 3
[0051] Example 3: Machine Learning
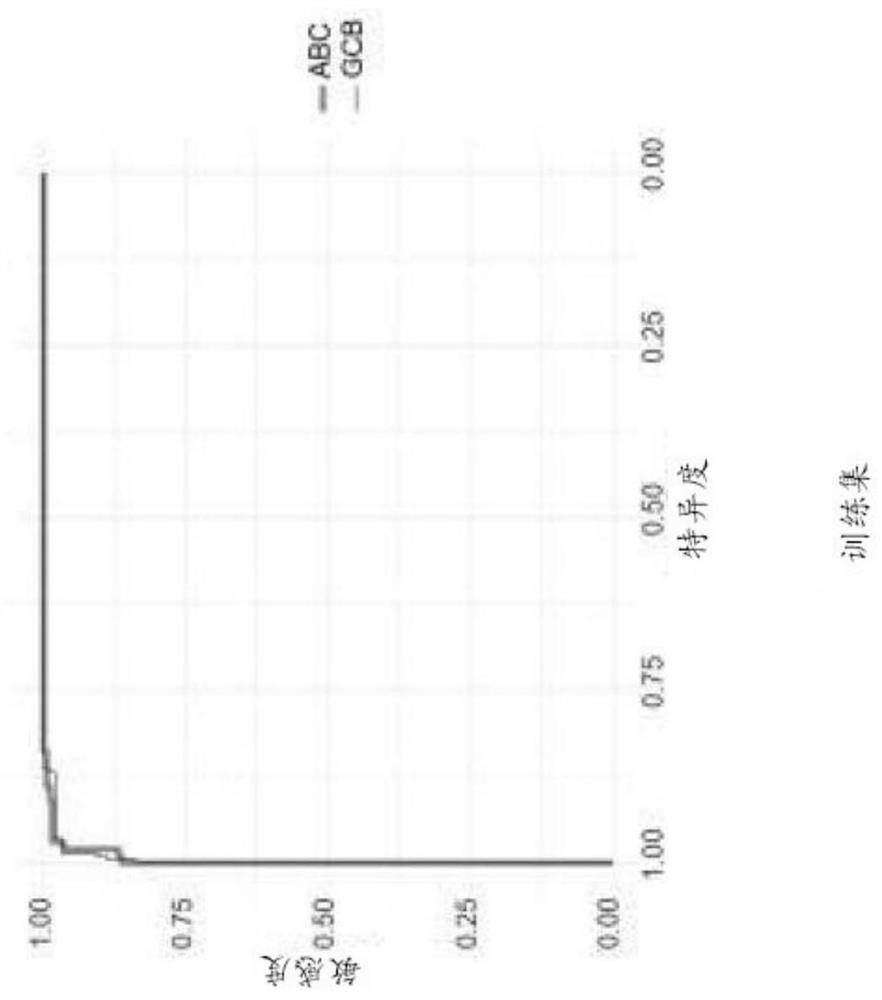
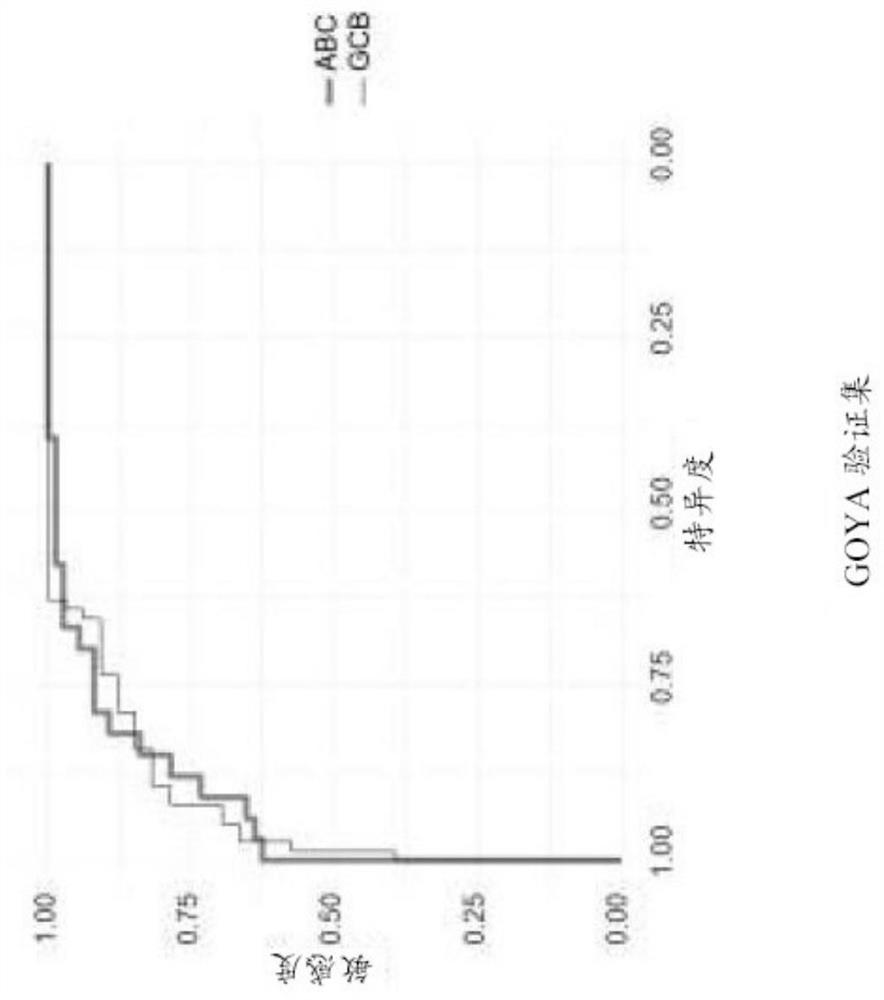
[0052]The COODC model was developed using penalized Lasso regression using 25-fold internal cross-validation implemented from the glmnet package (version 2.0-10) in R version 3.3.2 and using RStudio version 1.0.136. The 482 GOYA samples with Nanostring data were divided into training set (70% of samples) and validation set (30% of samples). The initial training set is further refined by removing Nanostring unclassified samples so that the training focuses on ABC or GCB detection. 296 samples are used for the final training set, while 139 samples are used for the validation set. 592 features are used in the model. z-scores continuous features to maintain a consistent scale between continuous and binary features. The final COODC model includes 74 non-zero features (Table 1). The per-sample probabilities extracted from the model are used to determine ideal cutoffs. Generate ROC curve ( Figure 1A and 1B ), and choose the "best" cutoff ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com