Active suspension of automobile engine
A technology for automotive engines and active mounts, which is applied to power plants, vehicle components, jet propulsion devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing low-frequency and large-value vibrations of engine powertrains, poor adaptability, etc., and achieve low mounts Dynamic stiffness, high active power efficiency, and strong adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
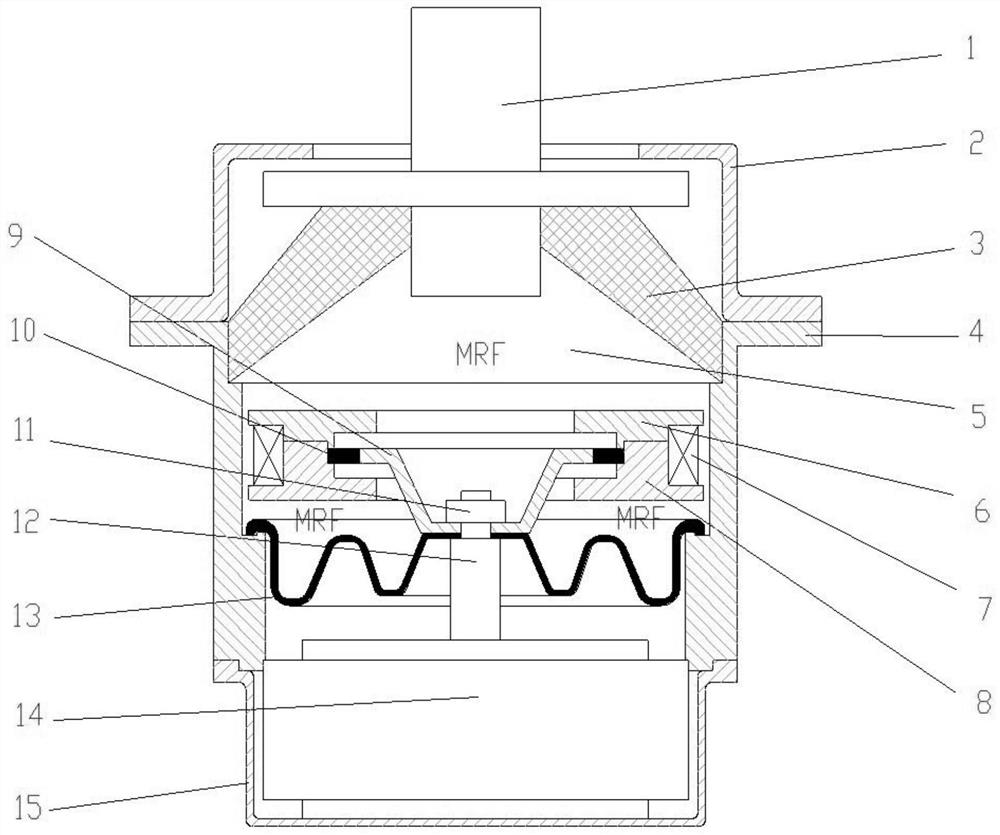
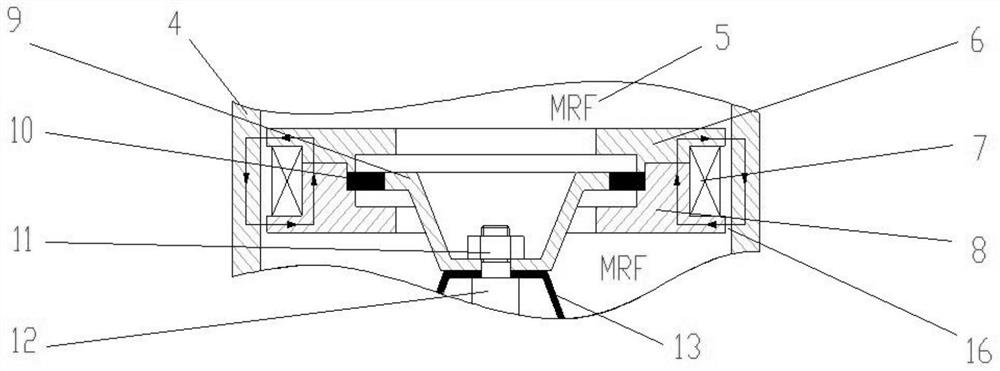
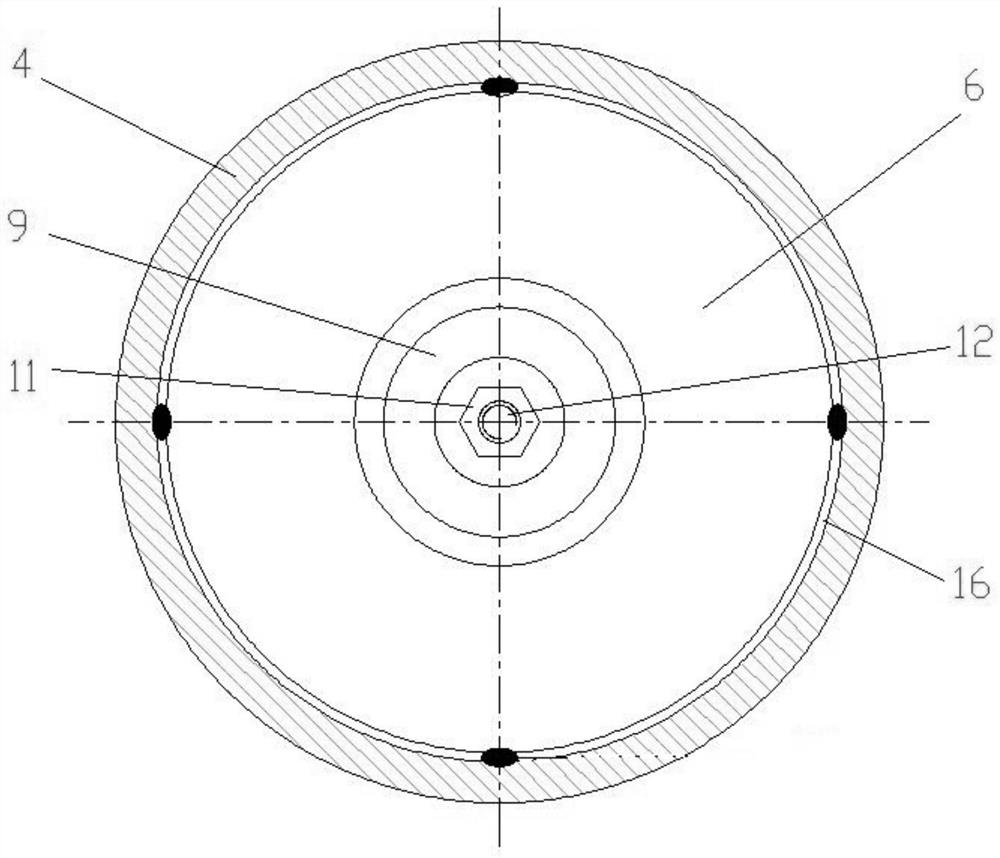
[0030] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the automobile engine active mount of this embodiment specifically includes an engine connection section 1, a mount upper shell 2, a rubber main spring 3, a mount middle shell 4, a magnetorheological fluid 5 (MRF), a first bracket 6, Coil 7, second bracket 8, decoupling disk 9, rubber diaphragm 10, nut 11, actuator output rod 12, suspension base film 13, actuator 14, suspension lower shell 15, channel 16.
[0031] In this embodiment, the connecting section 1 of the engine is connected with the power assembly of the engine by bolt connection, and the connecting section 1 of the engine is made of light aluminum alloy. The suspension upper case 2 is used to protect the rubber main spring 3, and the upper part of the suspension upper case 2 can limit the large upward displacement of the engine connecting section 1, so as to avoid the large tensile stress of the rubber main spring 3 and the suspension middle case 4. Disengagement, s...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the main difference is: as Figure 4 with Figure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, the controllable fluid is the electrorheological fluid 21 , and the fluid control member is an electrode capable of controlling the shear yield strength of the electrorheological fluid 21 in the channel 16 . In this embodiment, the electrorheological fluid 21 (ERF) is used to replace the magnetorheological fluid 5 in Embodiment 1, that is, the first liquid chamber and the second liquid chamber are filled with the electrorheological fluid 21 .
[0050] Since the electrorheological fluid 21 needs an electric field to be controlled, and the structure generated by the electric field is different from the structure generated by the magnetic field, the structure of the corresponding fluid channel 16 in the suspension also needs to be changed.
[0051] In this embodiment, the channel 16 is an annular electrorheological fluid channel 19, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the main difference is that: in this embodiment, the first liquid chamber is also filled with hydraulic oil rubber capsules, the hydraulic oil rubber capsules are located at a position away from the channel 16, and the hydraulic oil rubber capsules Isolated from controlled fluids.
[0056] In this embodiment, magnetorheological fluid 5 is only used in the magnetorheologically controllable damping channel, while traditional hydraulic oil is used in other parts. This reduces the cost of the suspension and reduces the weight of the active suspension. Put ordinary hydraulic oil in the rubber capsule, and then place the rubber capsule filled with hydraulic oil in the suspended first liquid chamber (that is, the upper liquid chamber), and the hydraulic oil rubber capsule fills a part of the first liquid chamber (that is, the upper liquid chamber). liquid chamber), so that the amount of magnetorheological fluid 5 can be r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com