Meteorological parameter fine scale conversion method based on deep bimodal
A meteorological parameter and dual-mode technology, applied in the field of refinement, can solve the problems of inapplicability of super-resolution technology, smooth interpolation space, difficult to reflect, etc., to improve learning efficiency and generalization, and strong model optimization ability , the effect of high training accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
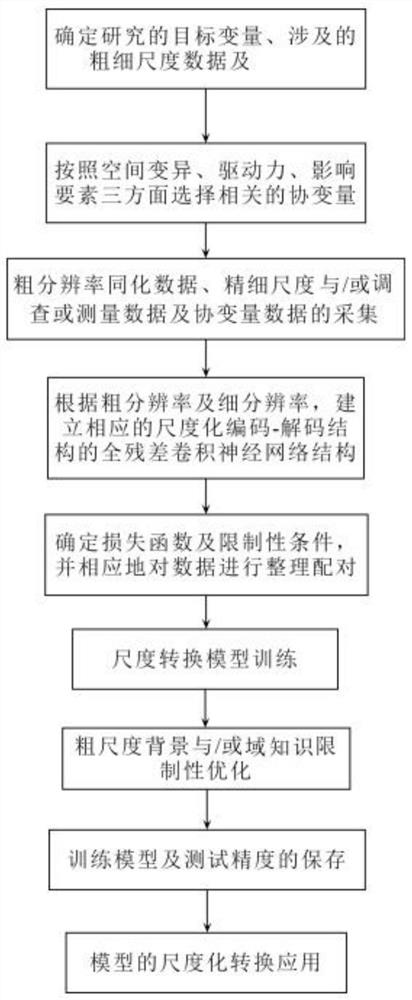
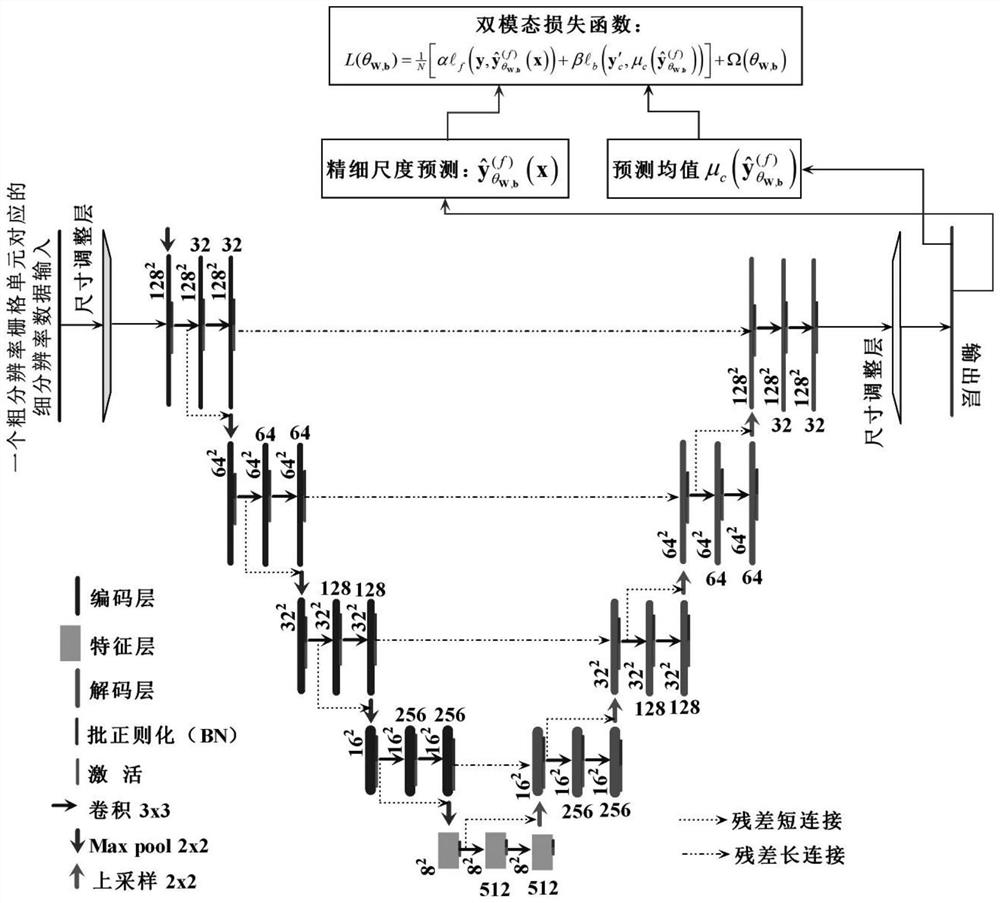
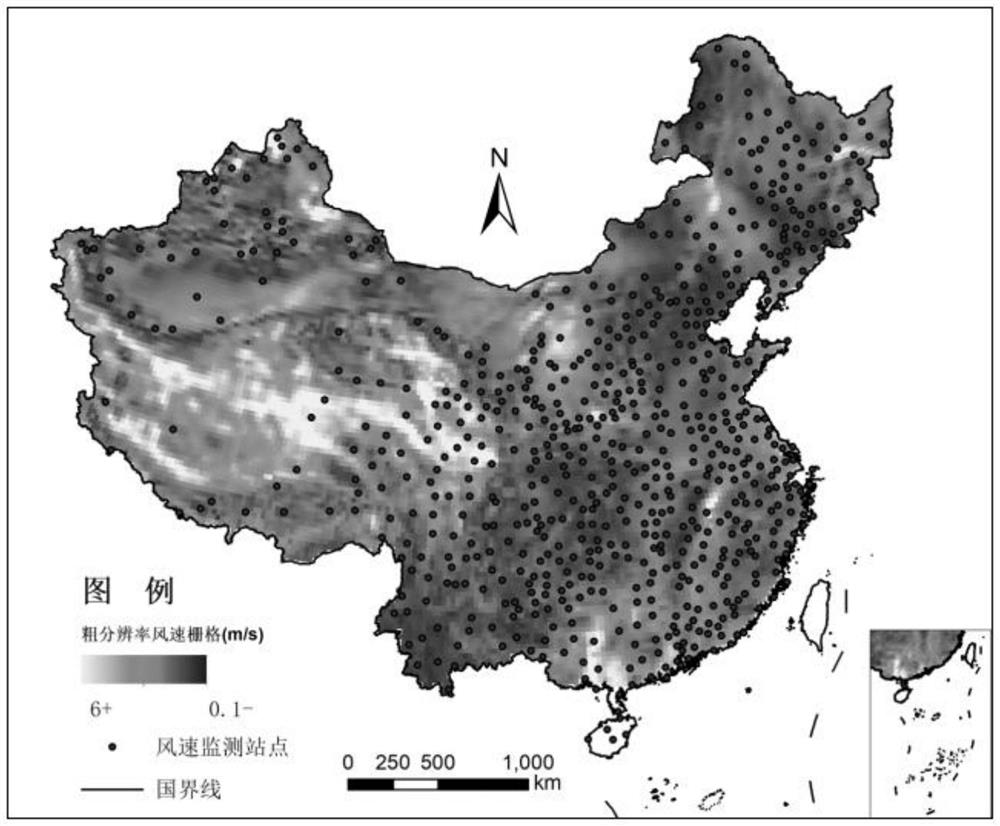
[0127] In this example, the wind speed in the meteorological reanalysis data is fine-scale transformed and transformed into modeling. The research area covers mainland China, and the research time period is the data of 2018 days. The target spatial resolution of the study is 1x1km 2 .
[0128] Step S1: figure 1 Shown the workflow of the present invention, the first step: determine that research target variable is surface wind speed, and unit of measurement is m / s (being meter / second), has adopted the global land surface meteorological data assimilation system (Global LandDataAssimilation System, GLDAS) The wind speed data of the same period has a spatial resolution of 0.25° (longitude) x 0.25° (latitude). The study found that there is a lack of high-resolution wind speed data on the ground, so the wind speed data from the ground meteorological stations are used as the actual measurement data. , the study determined that 1x1km 2 As the spatial fine resolution of the target, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com