Method for modifying mussel protein through high-pressure homogenization treatment
A technology of high-pressure homogenization and mussels, which is applied in the direction of food homogenization, textured treatment, animal protein processing, etc., can solve the problem of less research on shellfish protein, achieve changes in structural and functional properties, and improve functional properties , high efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
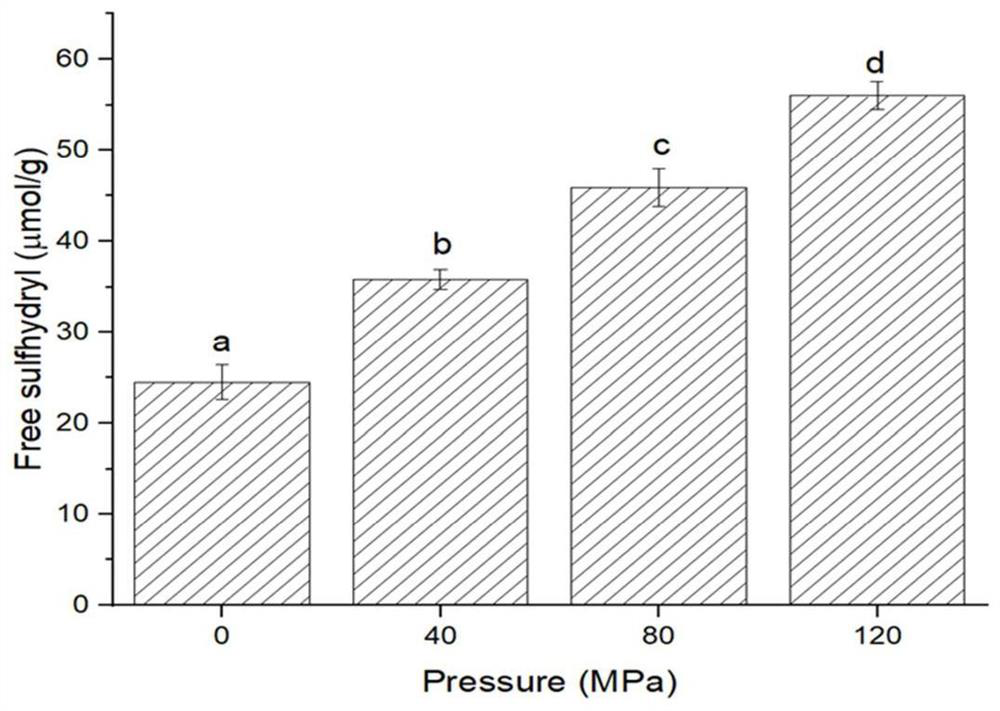
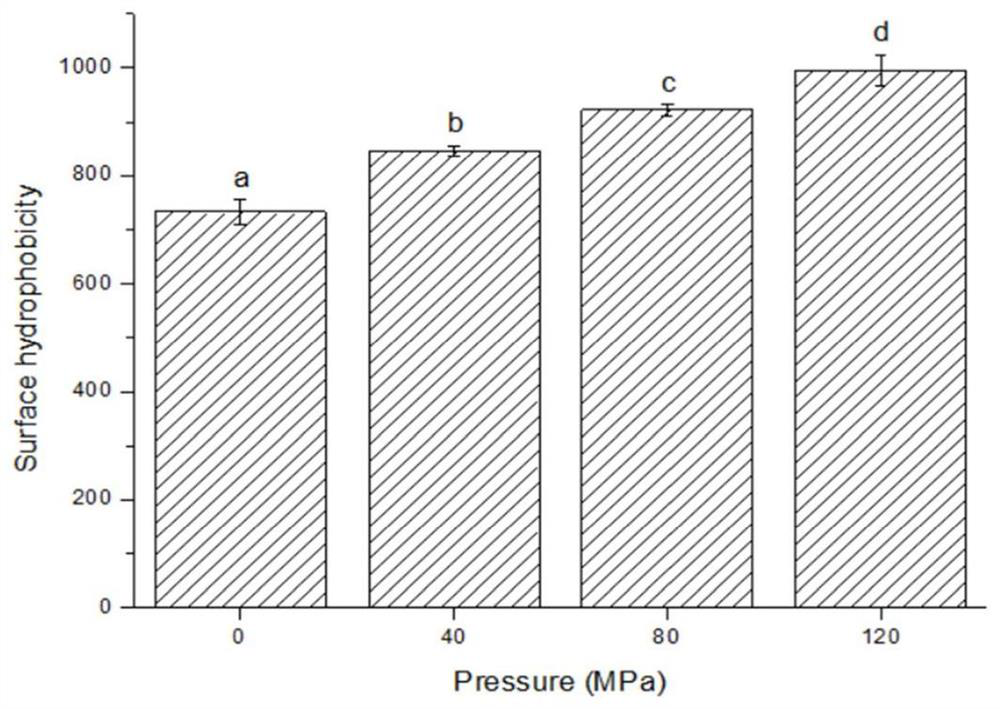
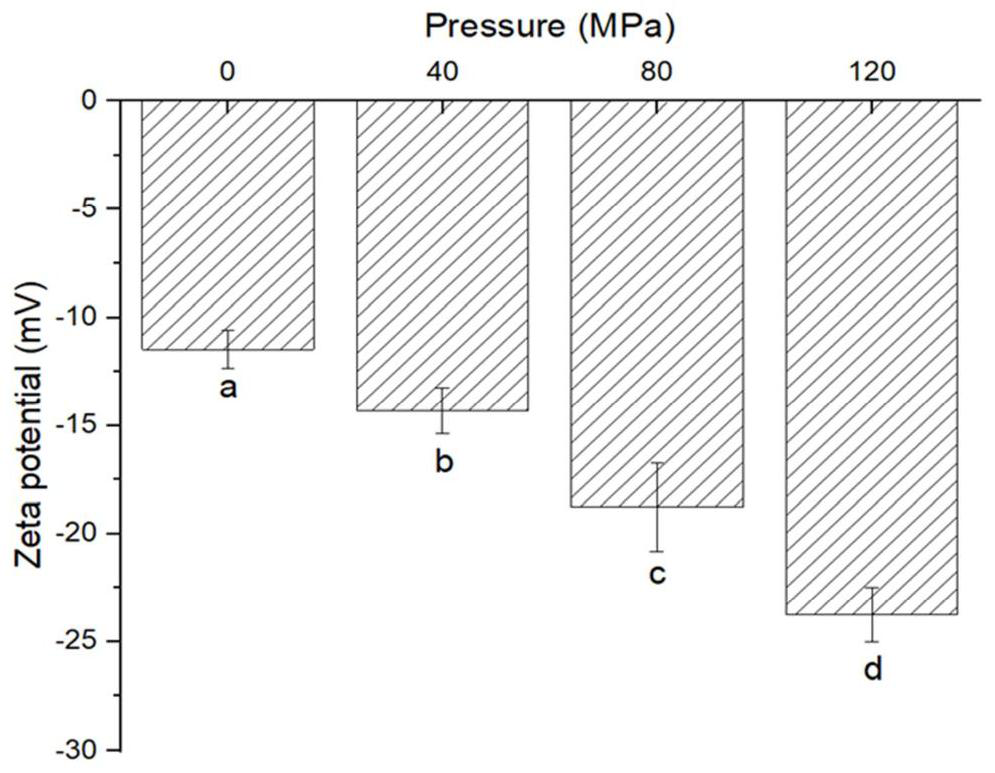
[0021] Extraction of mussel protein: Fresh mussels purchased in the local market were shelled and meat was removed, 500 g of mussel tissue homogenate was dissolved in 1 L of deionized water, and the pH was adjusted to 10.0 with 2.0 mol / L NaOH. Stir continuously at room temperature for 2 hours, centrifuge at 10,000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C, and take the supernatant. Adjust the pH to 5.5 with 2.0 mol / L HCl, centrifuge at 13800 g for 20 minutes, and collect the precipitate. The precipitate was dispersed in deionized water and adjusted to pH = 7.0 with 2.0 mol / L NaOH. The dispersion with a final concentration of 1% (w / v) was stored at 4° C., and the protein content of the mussel was measured by the Kjeldahl method to be 824.7±9.3 mg / g.
[0022] High-pressure homogenization: Mussel protein was subjected to high-pressure homogenization using a Panda Plus 2000 homogenizer. The mussel protein (10 mg / mL) was treated with HPH of 0 MPa and repeated three times. The initial temperature ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Extraction of mussel protein: Fresh mussels purchased in the local market were shelled and meat was removed, 500 g of mussel tissue homogenate was dissolved in 1 L of deionized water, and the pH was adjusted to 10.0 with 2.0 mol / L NaOH. Stir continuously at room temperature for 2 hours, centrifuge at 10,000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C, and take the supernatant. Adjust the pH to 5.5 with 2.0 mol / L HCl, centrifuge at 13800 g for 20 minutes, and collect the precipitate. The precipitate was dispersed in deionized water and adjusted to pH = 7.0 with 2.0 mol / L NaOH. The dispersion with a final concentration of 1% (w / v) was stored at 4° C., and the protein content of the mussel was measured by the Kjeldahl method to be 824.7±9.3 mg / g.
[0025] High-pressure homogenization: Mussel protein was subjected to high-pressure homogenization using a Panda Plus 2000 homogenizer. The mussel protein dispersion (10 mg / mL) was treated at a HPH of 40 MPa and repeated three times. The initial ...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Extraction of mussel protein: Fresh mussels purchased in the local market were shelled and meat was removed, 500 g of mussel tissue homogenate was dissolved in 1 L of deionized water, and the pH was adjusted to 10.0 with 2.0 mol / L NaOH. Stir continuously at room temperature for 2 hours, centrifuge at 10,000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C, and take the supernatant. Adjust the pH to 5.5 with 2.0mol / L HCl, centrifuge at 13800g for 20 minutes, and take the precipitate. The precipitate was dispersed in deionized water and adjusted to pH = 7.0 with 2.0 mol / L NaOH. The dispersion with a final concentration of 1% (w / v) was stored at 4° C., and the protein content of the mussel was measured by the Kjeldahl method to be 824.7±9.3 mg / g.
[0028] High-pressure homogenization: Mussel protein was subjected to high-pressure homogenization using a Panda Plus 2000 homogenizer. Mussel protein (10 mg / mL) was treated at a HPH of 80 MPa and repeated three times. The initial temperature was 4°C....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com