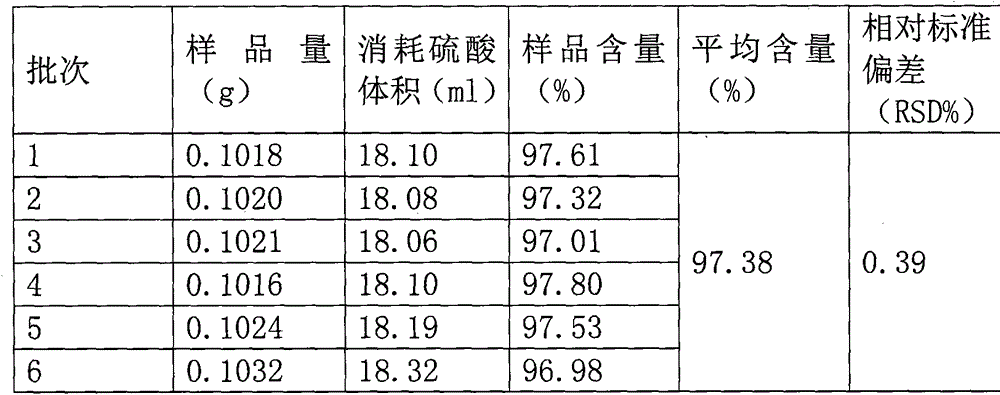
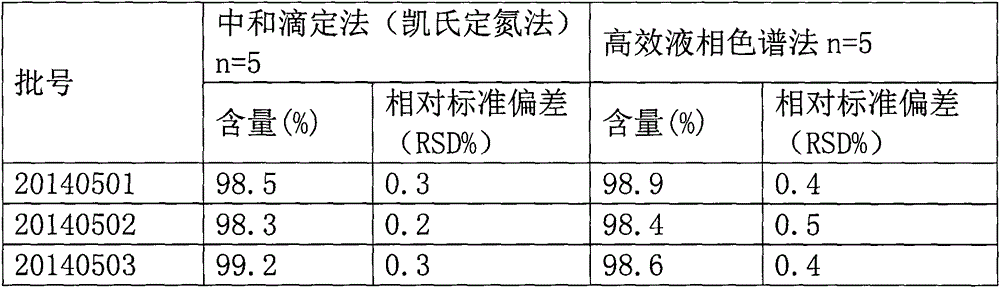
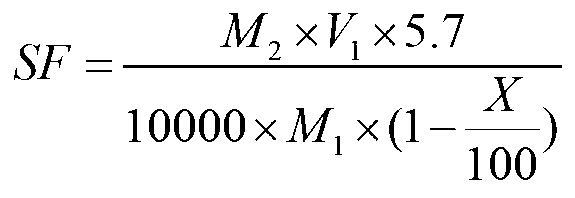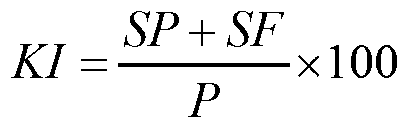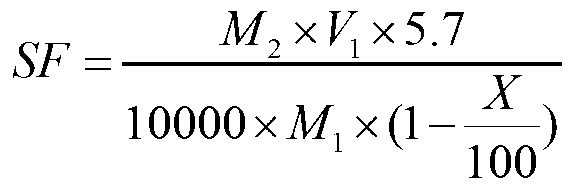Patents
Literature
55 results about "Kjeldahl method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Kjeldahl method or Kjeldahl digestion ([ˈkʰɛltæːˀl]) in analytical chemistry is a method for the quantitative determination of nitrogen contained in organic substances plus the nitrogen contained in the inorganic compounds ammonia and ammonium (NH₃/NH₄⁺). Without modification, other forms of inorganic nitrogen, for instance nitrate, are not included in this measurement. This method was developed by Johan Kjeldahl in 1883.
Method for conveniently and quickly determining nitrogen content of plant material
InactiveCN103411965AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsDistillationEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a method for determining element content, in particular to a method for conveniently and quickly determining the nitrogen content of plant material. Aiming at that the plant material is high in organic carbon content and nitrogen mainly exists in an organic nitrogen form, the method provided by the invention combines the conceptions of concentrated sulfuric acid digestion, hydrogen peroxide decolorization, Nessler's agent coloration and standard curve comparison, eliminates three steps of alkalified distillation, boric acid absorption and acidometric titration in the kjeldah method, and is used for determining the nitrogen content of the plant material with the combination of a Nessler's agent spectrophotometric method, the operation is simple, instruments are simple, the agent is easy to obtain, the determination of the nitrogen content of the plant material is enabled to be convenient and fast, moreover, the security is high, the results are accurate, the agent is saved, environmental protection is achieved, and remarkable social and economic benefits are obtained.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for conveniently and rapidly determining total nitrogen content in organic material
InactiveCN102680640AEasy to measureAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationDistillationTotal nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for determining element content of substances, in particular to a method for conveniently and rapidly determining total nitrogen content in an organic material including the content of the organic nitrogen and the content of inorganic nitrogen. The method mainly adopts a concept for combining the digestion with sulfuric acid and titration of ammonia ion with formaldehyde, so that the three steps of alkalization distillation, absorption with boric acid and acid titration in a kjeldahl determination method can be omitted, and equipment, instruments and chemical reagent used in the method are ordinary, so that the determination of the total nitrogen content in the organic material becomes convenient and rapid, and remarkable economic benefit and social benefit can be realized.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Formula and preparation method of composite peanut protein powder
The invention belongs to the field of peanut protein deep processing, and provides a formula of composite peanut protein powder. The formula is characterized by consisting of low-temperature cold-pressed semi-defatted peanut protein powder, mung bean flour, millet flour, peanut shell water-soluble dietary fiber and xylitol. The invention also provides a method for preparing the composite protein powder, which comprises the following steps of: weighing raw materials; mixing; soaking in aqueous solution; grinding into pulp by using a colloid grinder; preparing solution; homogenizing at high pressure; and performing freeze drying. The composite peanut protein powder prepared by the method has high protein content of over 40 percent through a Kjeldahl method, comprehensive and balanced nutrients, and can be drunk after being made by boiling water. Therefore, the composite peanut protein powder has the advantages of high protein content, easy solubility in boiling water, suitability for different groups, simple and easy operation of production process, suitability for industrial production and good economical and social benefits.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Production method of humus for organic environment-friendly gardening
ActiveCN102276315APromote growthLeaf color light greenBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationNerium oleanderCamellia oleifera
The invention relates to a method for producing organic environment-friendly horticultural humus, and discloses a method for producing organic ecotype insecticidal and environment-friendly horticultural humus. The method comprises the following steps of: adding 10kg of oleander chip into each 1,000g of camellia shell and stirring to prepare a material, determining the content of total carbon in the material by a potassium dichromate volumetric method, and determining the content of total nitrogen by a micro Kjeldahl method; calculating the content of pure nitrogen which is required to be added on the basis of the carbon nitrogen ratio of (25-30):1; and adding 1kg of fermentation strains and 3kg of pure nitrogen, stirring uniformly, regulating and controlling composting time to 20 to 60 days to fulfill the production aims of garden surface coverage and soilless culture substrates, and oven-drying or air-drying until the water content is less than 30 percent. The process is simple, the source of raw materials is stable, and the humus is cheap in price and meets environmental protection requirements. By the method, the problem of the pollution of the partial forestry waste is solved,and a recycling and added-value utilization way is also explored for forestry waste.
Owner:虹越花卉股份有限公司
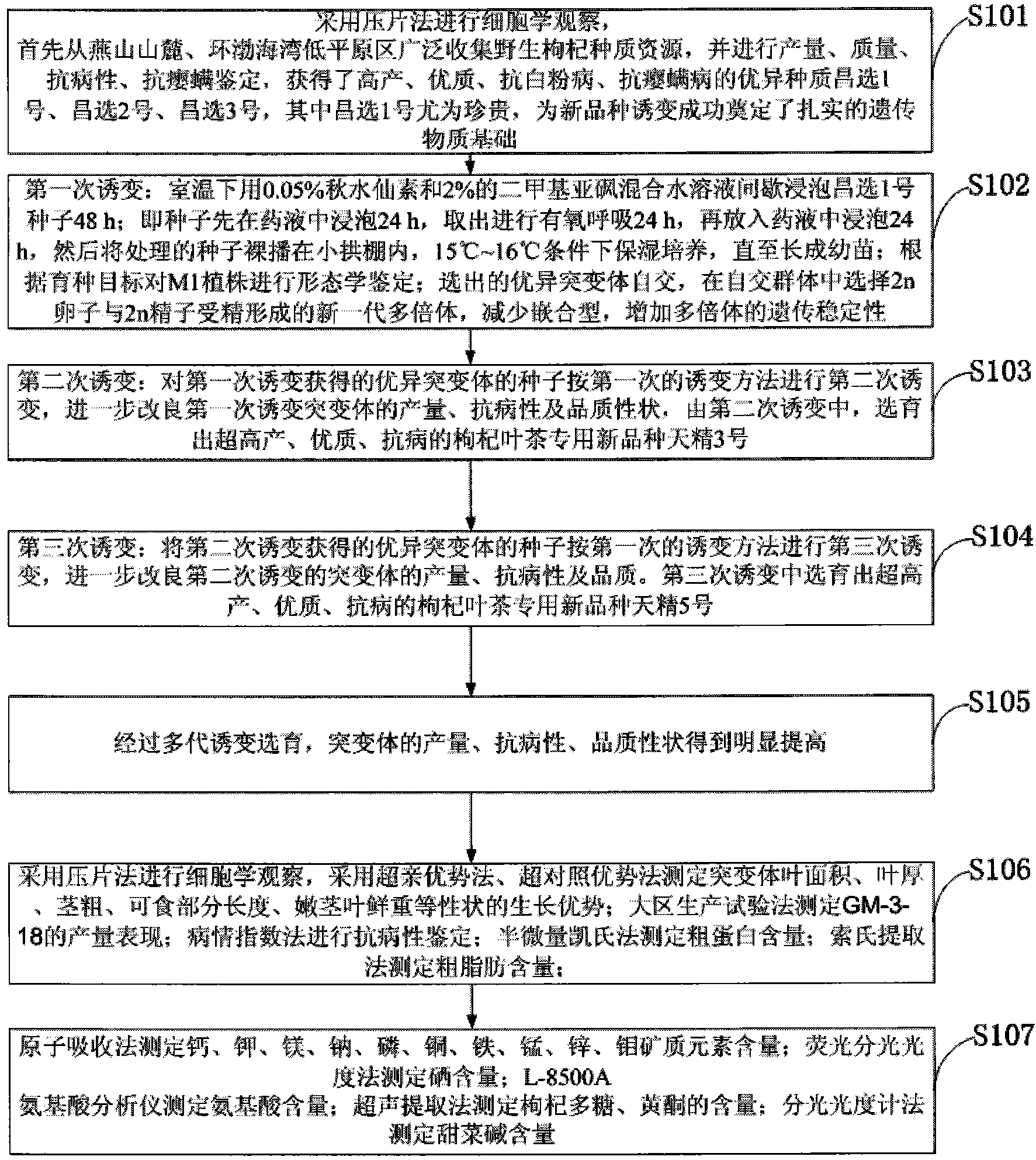
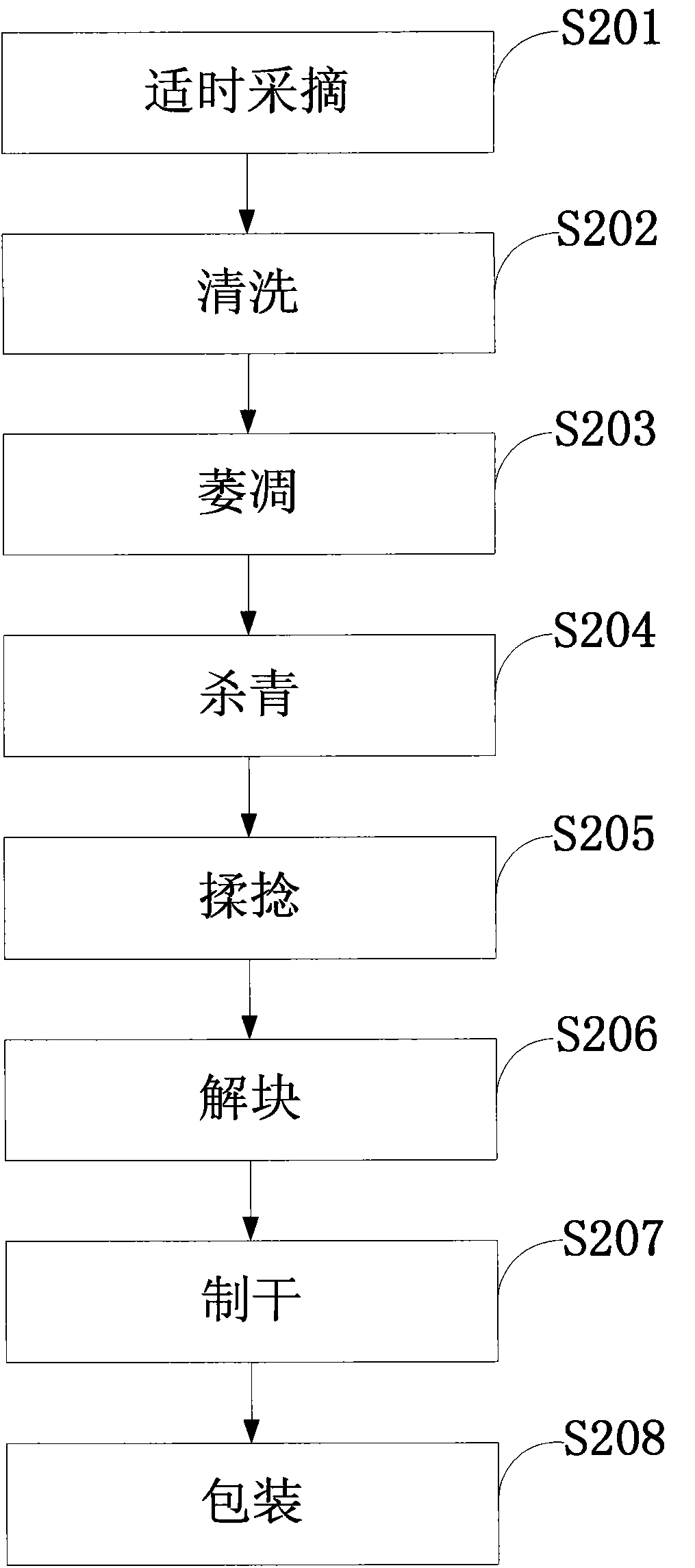
Breeding method and preparation method of new variety of health-care boxthorn leaf tea
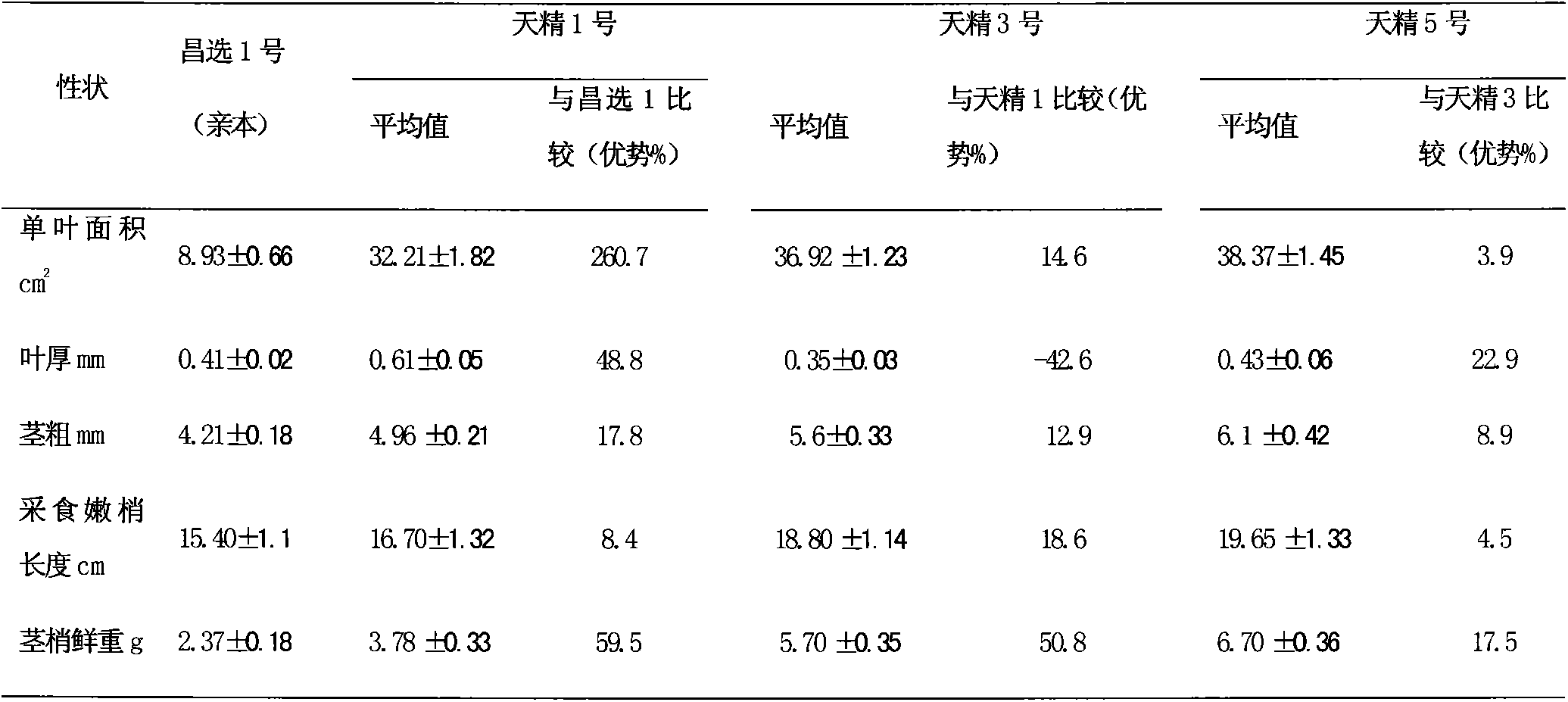
InactiveCN103749289AIncrease productionImprove disease resistanceTea substituesPlant genotype modificationDiseaseBetaine
The invention discloses a breeding method and a preparation method of a new variety of health-care boxthorn leaf tea. A squashing technique is adopted for cytological observation; an over-parent heterosis method and an over-contrast dominant method are utilized to determine the growth advantages of the leaf area, the leaf thickness and the stem diameter of a mutant, the length of an edible part and the fresh weight of tender stems and leaves; a region production testing method is adopted to determine the yield performance of the new variety; a disease index method is used for identification of disease resistance; a semimicro kjeldahl method is adopted to determine the content of crude protein; a Soxhlet extraction method is utilized to determine the content of crude fat; an atomic absorption method is used for determining the contents of calcium, potassium, magnesium, sodium, phosphorus, copper, iron and the like; a fluorescence spectrophotometry is adopted to determine the content of selenium; an L-8500A amino acid analyzer is adopted to determine the content of amino acid; an ultrasonic extraction method is utilized to determine the contents of lycium barbarum polysaccharide and flavone; a spectrophotometer is used for determining the content of glycine betaine; the bred multiploid new variety has strong growth vigor, stable hereditary, super high yield, strong root rot resistance, high nutrition and good medicine quality, and the produced boxthorn leaf tea has high quality.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for detecting basic protein content of milk
InactiveCN102866152AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorComponent separationCentrifugationMyelin basic protein
The invention relates to a method for detecting the basic protein content of milk, and provides a method for determining basic protein substances in the milk, in particular for the determination of milk basic proteins. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) removing caseins and fats in an acid regulation centrifugation way; 2) adsorbing the caseins by using cationic resin; 3) collecting eluent; and 4) determining the proteins by utilizing a micro Kjeldahl method. The invention also provides a method for collecting the milk basic proteins by utilizing chromatography equipment instead of manual collection.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA MENGNIU DAIRY IND (GRP) CO LTD
Method for rapidly monitoring solubility of beer wheat malt protein
ActiveCN103278470AImprove processing efficiencyImprove processing qualityColor/spectral properties measurementsMalt GrainSoluble nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for rapidly monitoring the solubility of protein in a preparation process of beer wheat malt. The method can be used for judging the wheat malt library value according to the measurement results of water-soluble protein content and FAN content in green wheat malt, and aims at rapidly and accurately judging the solubility of green wheat malt protein. A conventional wheat malt library value measurement method mainly refers to the standard of QB / T1686 beer wheat malt. A standard method comprises the steps of drying green wheat malt into finished wheat malt, carrying out EBC saccharification and then respectively measuring the content of soluble nitrogen and the total nitrogen of wheat malt in a kjeldahl method. The standard method is more in steps, complicated in operation, long in time consumption (about 30h) and high in cost. The method, which can judge the solubility of the wheat malt protein according to the water-soluble protein content and the FAN content in the green wheat malt, has the total time consumption of shorter than 3h, can rapidly and accurately judge the wheat malt library value, reasonably control the germinating time and accurately judge the finished wheat malt library value, and is capable of saving the analysis time and improving the processing efficiency and quality of wheat malt.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting protein from cereal fine powder
InactiveCN101434979AHigh extraction rateHigh purityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationDry basisPrecipitation
The invention provides a method for extracting protein from grain finemeal, which comprises the steps: firstly saccharification is carried out to the grain finemeal, and then the protein residue after saccharification is separated and purified by the alkaline extraction and acid precipitation method for obtaining high-purity protein. The saccharification process solves the technical problems that some grain protein is combined with starch tightly and is not easy for being separated, and the extraction of protein is difficult; the alkaline extraction and acid precipitation process effectively improves the extraction rate and purity of grain protein; and the saccharification liquid can be used for other usages, thereby saving the resources to the largest extent. The protein extracted by the invention can be analyzed and determined with kjeldahl method-GB / T 5009.5 and is not less than 80 percent when being counted by crude protein content (NX6.25 dry basis), and the yield thereof is 6-10 percent.
Owner:甘肃奇正实业(集团)有限公司
Method for analysis and determination by measuring content of amino acids and proteins in food and feed
The invention discloses a method for analysis and determination by measuring the content of amino acids and proteins in food and feed. The content of proteins is measured by a kjeldah method and the content of various free and hydrolytic amino acids and the total content of amino acids are measured by an amino acid analyzer; a lot of samples are analyzed fundamentally to form a database and a judgment system; and each measured result is analyzed and compared with system data to judge whether fake proteins are adulterated in the food and the feed. By the method, a precise judgment can be made that components of non-proteins or fake proteins are adulterated in the sample only if one or more of the following measured data is abnormal: content of non-proteins, content of free amino acids, content of characteristic amino acids, percentage between the total content of amino acids and the proteins, the ratio of each component of the amino acids to the total content of the amino acids and the like, so that the quality safety of the food and the feed are ensured.
Owner:GUANGDONG FOOD IND INST
Novel method for measuring Kjeldahl nitrogen
InactiveCN102103105AReduce consumptionShorten the timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial resistancePhysical chemistryNitrogen measurement
The invention belongs to the technical field of Kjeldahl nitrogen measurement methods, and in particular relates to a novel method for measuring Kjeldahl nitrogen. The novel method for measuring Kjeldahl nitrogen achieves the purposes of measuring nitrogen content in a measured object by the following steps of: digesting the measured object according to a conventional Kjeldahl method to obtain a digestion solution, adding water to dilute the digestion solution and adding alkaline to obtain an alkaline digestion solution, heating and blowing off the digestion solution with gas, absorbing the blown-off gas with an absorption solution, and measuring the difference value between the electrical conductivities before and after the absorption by a conductivity meter.
Owner:济南精密科学仪器仪表有限公司
Rapid protein detection kit as well as detection method and application using same
InactiveCN105486682ASolubilizedWith sensitizationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorProtein detectionNational standard
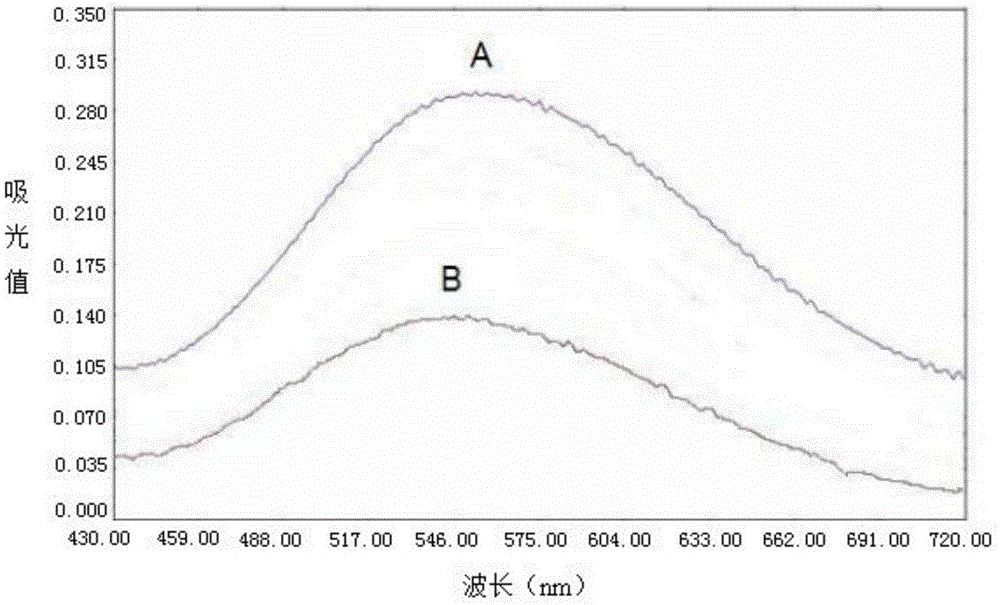
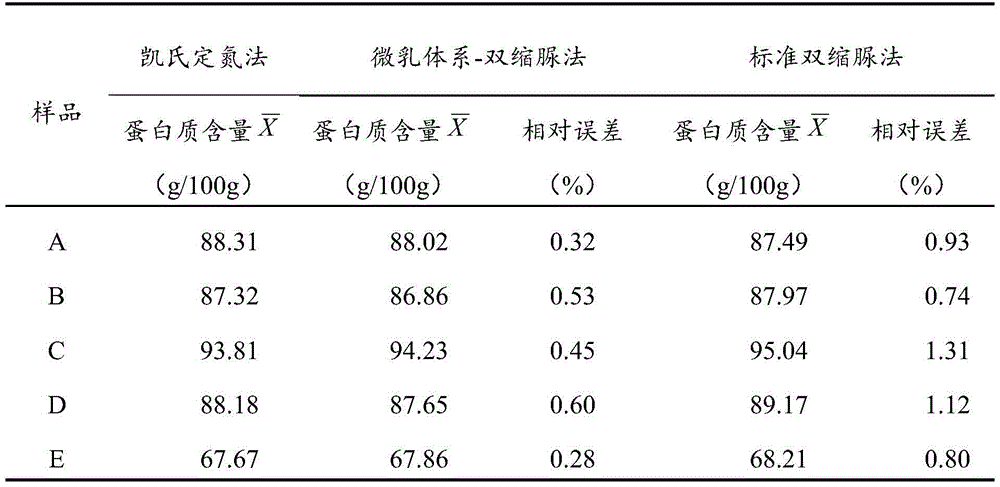
The invention discloses a rapid protein detection kit as well as a detection method and an application using the same. The detection kit comprises a biuret reagent, a surfactant and a cosurfactant. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, through addition of the surfactant and the cosurfactant in the biuret reagent, the prepared microemulsion has the characteristics of solubilization and sensibilization, the improved biuret method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simplicity in operation, less interferents and good repeatability. The detection sensitivity of the detection method disclosed by the invention on protein is 6-11 times that of the traditional method. The detection method can be applied to detection of a trace protein sample, and the relative error of the detection method is between 0.28% and 0.60% as compared with that of an national standard kjeldahl determination method. The detection method disclosed by the invention has good precision and accuracy.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for determining content of organic amine
InactiveCN106546694ALow costEasy to operateChemical analysis using catalysisChemical analysis using titrationDistillationRepeatability
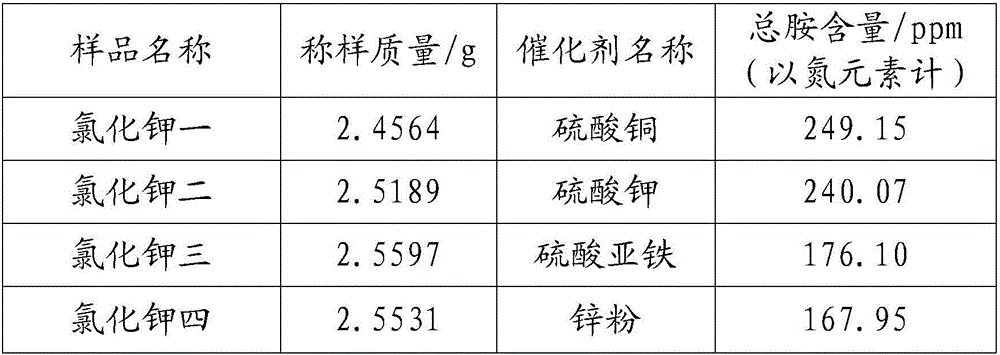
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of organic amine. The method comprises the following steps: step 1: determining content w2 of inorganic amine in a sample to be detected by adopting a distillation titration method; step 2: determining content w1 of total amine in the sample to be detected by adopting a Kjeldahl method; and step 3: calculating the content of the organic amine in the sample to be detected, wherein content w3 of the organic amine in the sample to be detected is equal to (w1-w2), and sequences of the step 1 and the step 2 can be exchanged or the step 1 and the step 2 can be carried out simultaneously. Compared with a traditional gas chromatography for determining the content of the organic amine, the method for determining the content of the organic amine has the advantages of relatively low cost and relatively simple operation. Meanwhile, the method also has the advantages of relatively high precision, accurate determination result, good repeatability, environment friendliness and the like, and can be applied to conventional analysis and quality control of the content of the organic amine.
Owner:ЦИНХАЙ СОЛТ ЛЕЙК ИНДАСТРИ ГРУП КО ЛТД
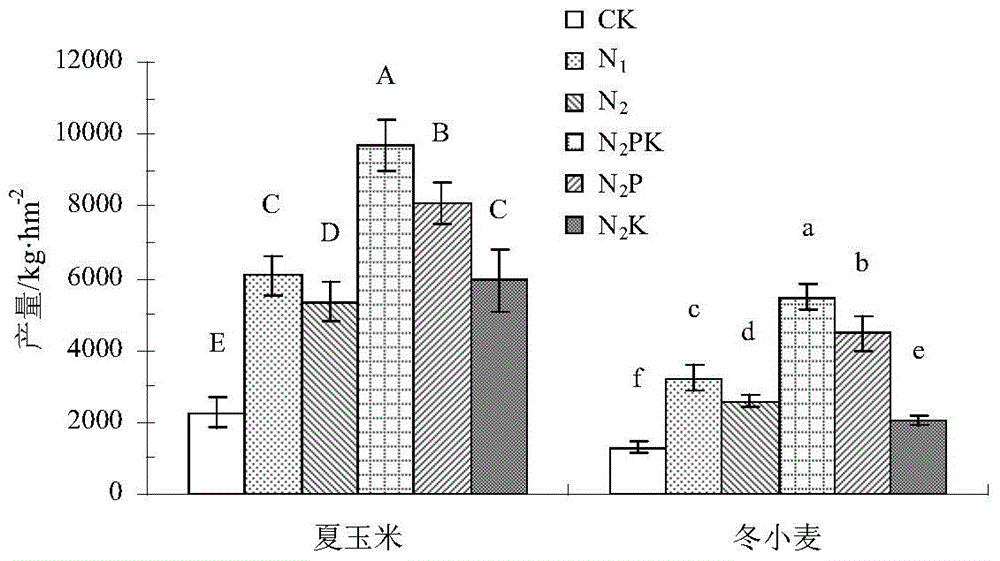
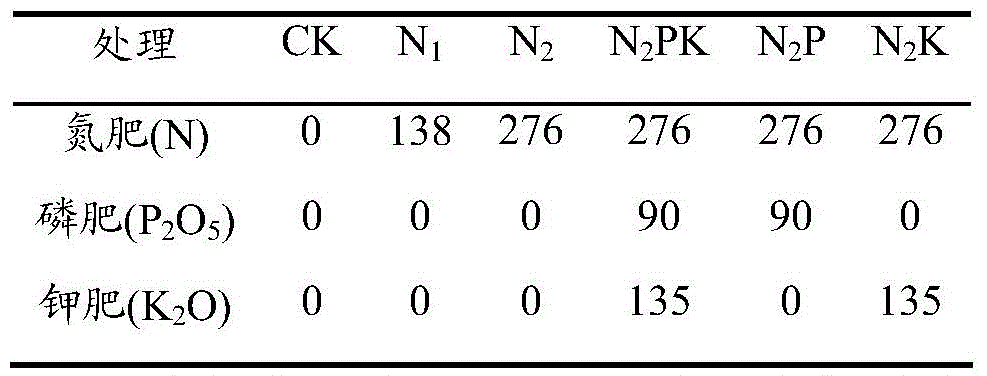
Method for influencing moisture soil nitrogen mineralization characteristics and crop yield by long-term positioned fertilization
The invention provides a method for influencing moisture soil nitrogen mineralization characteristics and crop yield by long-term positioned fertilization. By means of in-situ field and anion-cation exchange resin process, the influence of long-term application of nitrogen fertilizer and supportive phosphorus potassium fertilizer upon non-calcareous moisture soil nitrogen in-situ field mineralization characteristics, crop nitrogen absorption and crop yield is studied, and a relation of the influence with crop nitrogen absorption and crop yield is studied; total nitrogen of soil and plants is measured by Kjeldahl determination, NO3<->-N and NH4<+>-N in soil and ion exchange resin bags are extracted with KCl solution, and after filtering, determinations are made respectively by means of dual-wavelength ultraviolet spectrometry and Nessler's reagent colorimetry. Theoretical basis is provided for the sustainable development of a soil nitrogen nutrition bank, controlling of soil nitrogen supply in this area and achievement of high crop yield.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for determining nitrogen content
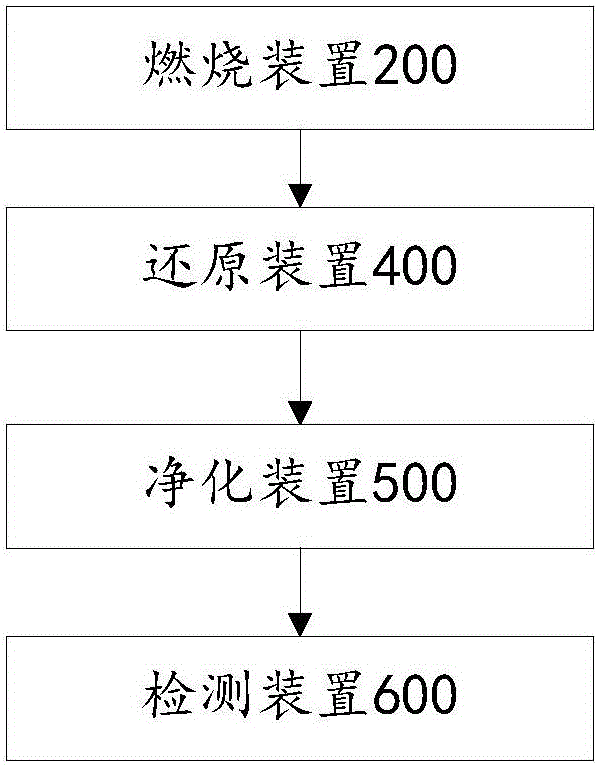
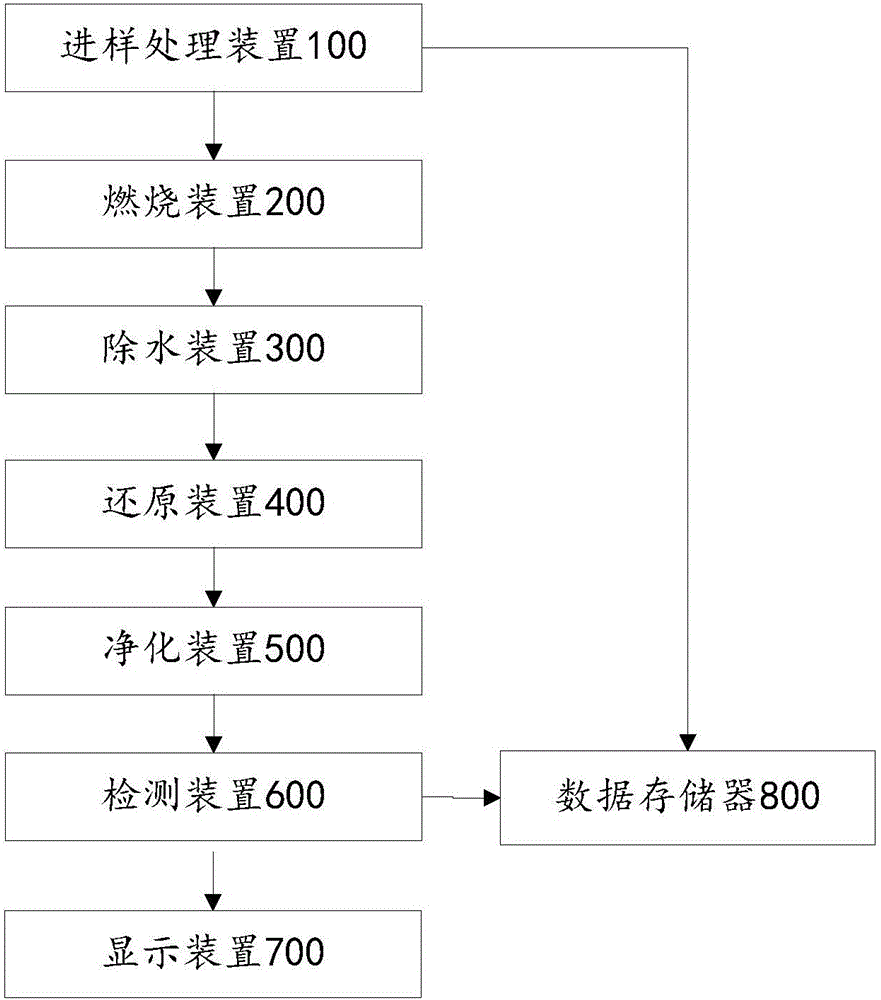
The invention provides a method for determining the nitrogen content, and belongs to the technical field of detection. The method comprises the following steps: combusting a sample to be determined by using a combustion device to generate a mixed gas; reducing the mixed gas through a reducing device; purifying the reduced mixed gas through a purifying device o remove impurities in order to obtain residual gas, wherein the impurities comprise at least one of water, carbon dioxide and halogens; and detecting the nitrogen content of the residual gas through a detecting device. The technical defects of use of corrosive acid and alkali, complicated operating steps, long time consumption and severe environment pollution, caused by adopting a Kjeldahl determination technology in traditional methods, are solved in the invention.
Owner:DINGTAI HUIBEI BIOCHEM INSTR MFG
Method for detecting protein content in regenerated protein fiber
InactiveCN108205045AShort test cycleShorten digestion timeChemical analysis using titrationPreparing sample for investigationProtein insertionConversion coefficients
The invention discloses a method for detecting protein content in regenerated protein fiber. The method includes weighing a certain amount of regenerated protein fiber baked to constant weight, into adigestive tube, adding a certain amount of copper sulfate, potassium sulfate and concentrated sulfuric acid, then digesting the mixture in a constant temperature digestion furnace for a period, and then performing test on a Kjeldahl analyzer after cooling. The protein content can be obtained by performing converting according to the set protein conversion coefficient. The method overcomes the shortcomings of complicated operation and long test period of the existing Kjeldahl method and the sodium hypochlorite method, and has the advantages of short test period, wide application range, high efficiency, simple operation and good repeatability.
Owner:广东省江门市质量计量监督检测所
Method for preparing thallus protein extractum from bacterial residue of amino acid fermentation liquor
PendingCN110423691AIncreased yield of enzymatic hydrolysisGood effectMicroorganism lysisFermentationSlurryHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for preparing thallus protein extractum from bacterial residue of amino acid fermentation liquor. The method comprises the following steps of: filtering amino acid fermentation liquor with a ceramic membrane, taking a concentrated slurry fungus residue solution, and measuring the protein content by a Kjeldahl determination method; adjusting the pH value of the concentrated slurry fungus residue solution to 7.0-8.5 by using alkali, carrying out high-temperature high-pressure treatment, and adding protease for enzymolysis; after the enzymolysis reaction is finished, preserving heat, adding activated carbon, and performing decolorizing and filtering to obtain a decolorized liquid; and preparing the extractum: concentrating the decolorized liquid under reducedpressure to obtain the thallus protein extractum. The method subjects amino acid fermentation thalli to high-temperature high-pressure wall breaking, enzymolysis, filtration and concentration so as to obtain the extractum with a micromolecule bioactive peptide (namely, oligopeptide) content exceeding 90%, thereby greatly improving the added value, wherein the market price of the thallus crude protein is about 2500 thousand yuan per ton, and the market price of the extractum is about 20-30 thousand yuan per ton.
Owner:宜昌三峡普诺丁生物制药有限公司
Method for detecting nitrogen content
ActiveCN105572121AAvoid accumulationEnsure clarityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhenolphthaleinDistillation
The invention relates to a method for detecting the element content of a material and in particular relates to a method for detecting the nitrogen content of a compound fertilizer, belonging to the field of analytical chemistry. The method for detecting the nitrogen content comprises the following steps: drying the compound fertilizer till constant weight, drying the compound fertilizer till constant weight again after grinding and sieving the compound fertilizer, weighing required amount of compound fertilizer and digesting the compound fertilizer with sulfuric acid, neutralizing the remaining sulfuric acid with sodium hydroxide after digestion is completed, adding dipropylene glycol and dimethyl sulfoxide, using phenolphthalein as an indicator and titrating ammonium ions by utilizing a sodium hydroxide solution. The method has the beneficial effects that the method is simple and feasible and has the advantages that the three steps including alkalization distillation, boron absorption and acidometric titration are omitted compared with a kjeldahl method; besides, the required equipment and instruments, chemicals and reagents are articles commonly used in laboratories, so that the method has obvious economic benefits.
Owner:GUIZHOU RES INST OF CHEM IND
Composite fertilizer nitrogen content detection method
ActiveCN105548458AAvoid accumulationEnsure clarityChemical analysis using titrationDistillationDigestion
The invention relates to a substance content detection method and especially relates to a composite fertilizer nitrogen content detection method and belongs to the field of analytical chemistry. The composite fertilizer nitrogen content detection method comprises drying composite fertilizer until constant weight, crushing the composite fertilizer, carrying out sieving, carrying out drying until constant weight, weighing a desired amount of the composite fertilizer powder, carrying out digestion on the composite fertilizer powder through sulfuric acid, neutralizing the residual sulfuric acid through sodium hydroxide after digestion, adding ethanol and dimethyl sulfoxide into the solution, and carrying out ammonium ion titration through a sodium hydroxide solution in the presence of a phenolphtalein indicator. The method is simple and easy. Compared with the Kjeldahl determination method, the method provided through the invention is free of alkalization distillation, boron absorption and acid titration processes. The method utilizes laboratorial common apparatuses and reagents and has obvious economic benefits.
Owner:GUIZHOU RES INST OF CHEM IND
Method for quantitatively detecting content of protein in protein viscose
InactiveCN104020075AReduce pollutionGood test reproducibilityWeighing by removing componentWater bathsBottle
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting the content of protein in protein viscose. The method comprises the following steps: (1) arranging a test sample in a measuring bottle, and transferring the dried test sample to a constant weight into a conical flask with a stopper; (2) diluting a well-calibrated sodium hypochlorite stock solution to given concentration, arranging the diluted sodium hypochlorite stock solution into the conical flask with the stopper, covering a bottle cover, oscillating the moistened test sample, and arranging the test sample into a constant-temperature oscillation water-bath pot and oscillating at a given temperature; transferring residues into a glass sand core crucible with known drying mass, and washing the residues by utilizing the sodium hypochlorite sodium solution, tertiary water and dilute acetic acid respectively; (3) calculating the content of the protein according to the reduced mass of the protein viscose test sample before and after being processed by sodium hypochlorite. By adopting the method, the weaknesses that the test period is long, the danger in operation is high, toxic and harmful gas is likely to generate, and the like in the classical kjeldah method for measuring the content of the protein can be overcome. The method has the advantages of good test reproducibility, simplicity in operation, accuracy conforming to the analysis requirement, slight environmental pollution and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEAVING SCIENCE RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +1
Determination method for detecting true protein content by using salting-out method and application of determination method
ActiveCN112924448AImprove stabilityEasy to detectMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationPhysical chemistryFilter paper
The invention discloses a determination method for detecting true protein content through a salting-out method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) weighing a sample, placing the sample in a container, adding a proper amount of water, heating to boiling, and then transferring into a water bath at 80 DEG C for 30 minutes; 2) taking out from the water bath, immediately and slowly adding sodium hydroxide, then adding copper sulfate, standing and aging to obtain a test solution; 3) filtering the test solution after standing, and washing the precipitate for several times; 4) fully drying the precipitate and the filter paper, putting the precipitate and the filter paper into a nitrogen determination and elimination tube, firstly adding 15mL of sulfuric acid, standing, slowly heating and pre-digesting, then taking down and cooling, then adding sulfuric acid, anhydrous sodium sulfate and copper sulfate again, heating to 420 DEG C, digesting to be clear, and obtaining a to-be-tested sample; and 5) determining nitrogen of the to-be-detected sample by using a Kjeldahl method to obtain the content of true protein in the sample. According to the method, the result of detecting the true protein content in the feed or a dairy product by using the salting-out method is more accurate, and the repeatability and the stability of the detection result are improved.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Colored nutritive formula organic rice and making method thereof
The invention discloses colored nutritive formula organic rice. The colored nutritive formula organic rice contains the following raw materials in percentage by weight of the organic rice: 50% of organic brown rice, 10% of organic black rice, 10% of organic red rice, 10% of organic green rice, 10% of organic purple rice and 10% of organic yellow rice. The invention further discloses a making method of the colored nutritive formula organic rice. The making method comprises the following steps of taking materials, performing preliminary cleaning, removing stones, performing husking, performing rice milling, performing classification, performing polishing, compounding colored organic rice, separately measuring the water content, the amylose content, the crude protein content and the crude fatcontent of raw material rice by a 105 DEG C constant mass method, an iodine combination colorimetric method, a kjeldahl method and a Soxhlet extractor method, selecting the materials including the organic brown rice, the organic red rice, the organic yellow rice, the organic green rice, the organic purple rice and the organic black rice, of which the water mass content is 13-16%, the amylose masscontent is 18-22%, the crude protein mass content is smaller than or equal to 10% and the crude fat mass content is smaller than or equal to 0.45%, compounding mixed colored organic rice, and performing mixing in a quantitative manner, so that the organic rice can integrate various nutrients.
Owner:广东坤辉农业技术开发有限公司
Method for extracting livetin and oil from larimichthys crocea eggs at the same time
ActiveCN108976295AIncrease profitFully develop and utilizePeptide preparation methodsFatty-oils/fats productionFreeze-dryingTotal protein
The invention discloses a method for extracting livetin and oil from larimichthys crocea eggs at the same time. The method comprises the steps of larimichthys crocea egg freeze-dried powder preparation, freeze-dried powder dissolution, primary extraction, precipitation dissolution, secondary extraction, mixing and dialysis. According to the method for extracting the livetin and the oil from the larimichthys crocea eggs at the same time, a sodium chloride solution is adopted for digestion at a room temperature, and through centrifugation, the livetin and the oil are separated according to different tensity so that the oil and protein can be recovered at the same time; the livetin recovery rate is up to 76-82%, a kjeldah method is used for detecting the protein purity which is up to 80% or above, and through mass spectrum identification, the livetin content accounts for more than 99% of the total protein content; the oil recovery rate reaches 22-23%, and the oil purity is reaches 90% orabove; the emulsibility of the larimichthys crocea egg livetin prepared through the method is significantly improved compared with that of the freeze-dried powder and is significantly better than thatof soy isolate protein, so that the method has important significance in larimichthys crocea egg deep-processing.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Method for producing organic environment-friendly horticultural humus
ActiveCN102276315BPromote growthLeaf color light greenBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationNerium oleanderCamellia oleifera
Owner:虹越花卉股份有限公司
Method for rapidly determining nitrogen contents of different organs of plant
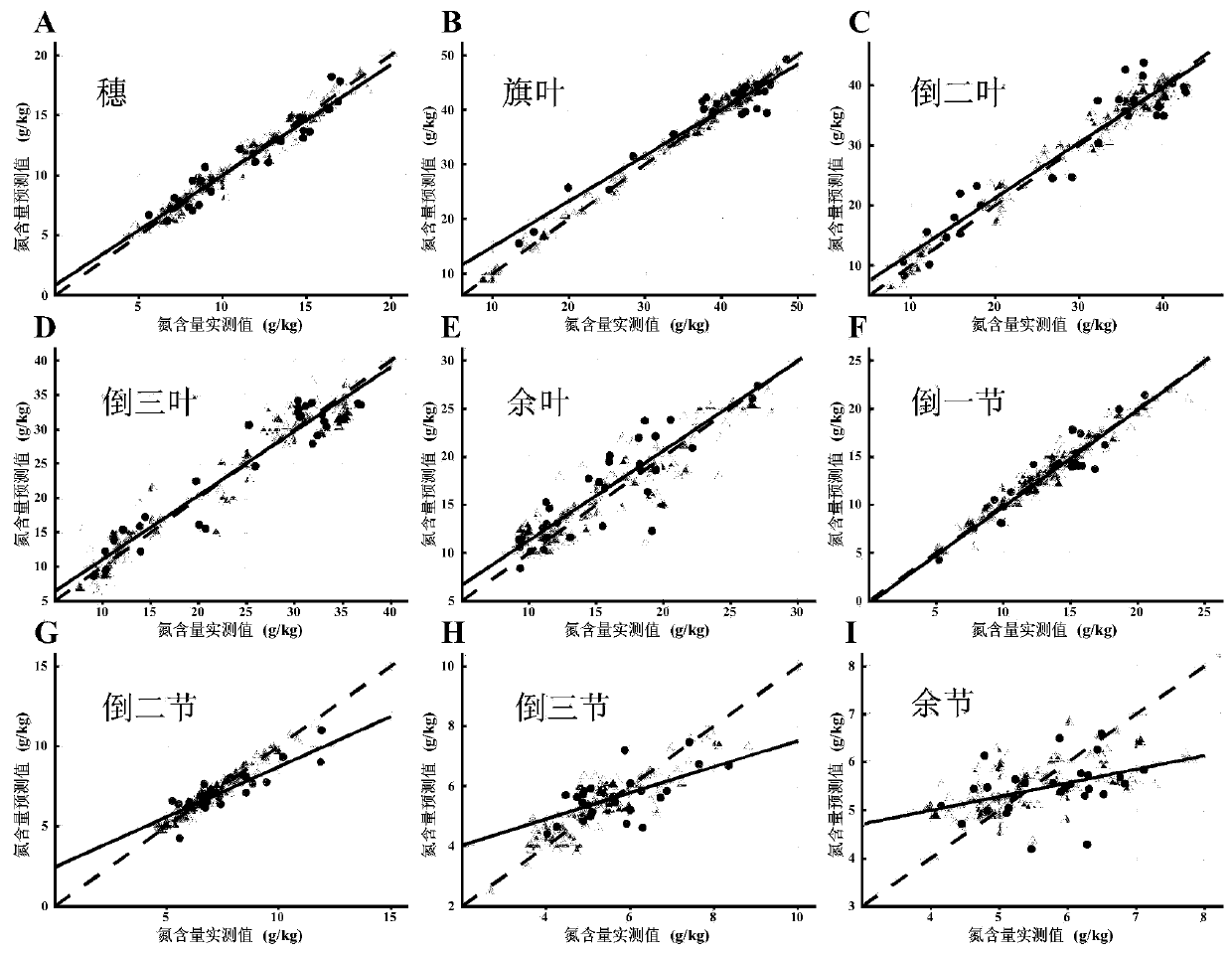
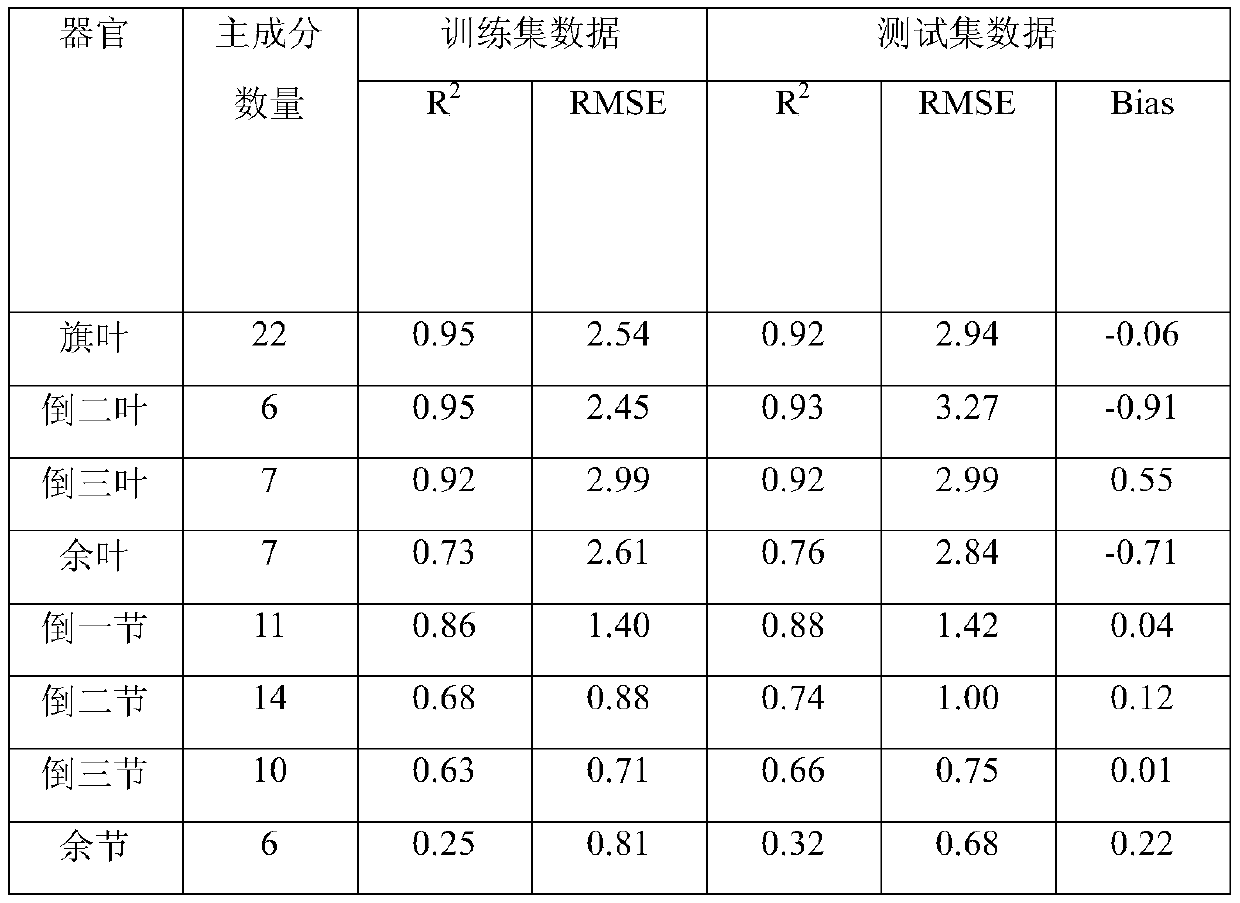
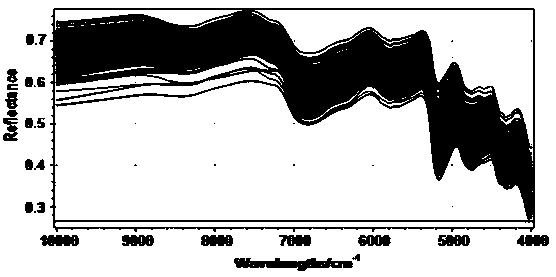
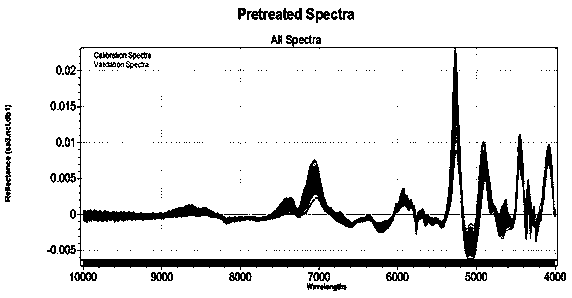
InactiveCN111426645AEfficient determinationEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPlantletReflectivity
The invention discloses a method for determining the nitrogen contents of different organs of a plant. The method comprises the following steps of taking a plant sample, separating according to organs, drying the sample, grinding and sieving, acquiring a reflectivity spectrum of the powder sample by using a hyperspectral camera, meanwhile, determining the nitrogen content in the sample by adoptinga Kjeldahl determination method, and establishing a spectral prediction model of the nitrogen content. According to the method, different organs of the wheat plant are subjected to nitrogen content determination, and an organ-specific nitrogen content prediction model is established, so that research on nitrogen transfer among the organs can be carried out in a targeted manner. According to the method, the spectral camera is used for acquiring reflectivity spectral data, so that the requirement on the sample amount is low, multiple groups of samples can be simultaneously collected, and the detection flux is improved. According to the method, prediction model construction is carried out by adopting an unprocessed original spectrum, and model construction is carried out by adopting an opensource algorithm, so that the spectrum analysis threshold is simplified, and the spectrum technology can be better applied to the technical field of agriculture.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for measuring crude protein content in Phalaris arundinacea by using near infrared spectrum
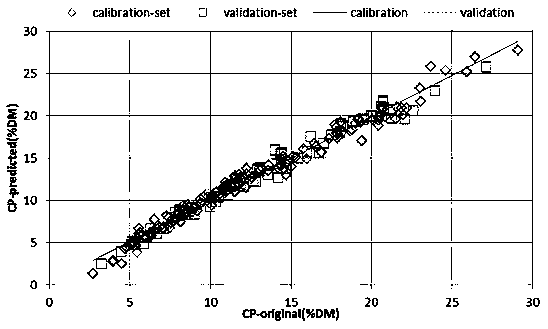
InactiveCN110044841AImprove stabilityGood reproducibilityMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredAnimal Foraging
The invention relates to the field of measurement of pasture quality, and in particular relates to a method for measuring crude protein content in Phalaris arundinacea by using near infrared spectrum.The method comprises the following steps of 1, widely collecting representative Phalaris arundinacea samples; 2, collecting near infrared spectrum data of modeled samples; 3, measuring the crude protein content in the samples by using a kjeldahl determination method; 4, building a calibration model; 5 verifying the calibration model; and 6, measuring the Phalaris arundinacea samples to be measured. The measurement method is easy to acquire samples and convenient to measure; continuous and unlimited analysis can be performed after the model is built, the time for being on the machine only needs 16s, the test period is shortened, the analysis efficiency is greatly improved, the measurement result is good in reproducibility and high in stability, meanwhile no chemical reagent is used, no pollution and damage are generated. The method can be used for quickly measuring the plenty of material, and has the wide application prospect in the aspects of Phalaris arundinacea quality assessment, quality breeding, daily ration configuration and forage product circulation.
Owner:SICHUAN ACAD OF GRASSLAND SCI
Method for rapidly monitoring solubility of beer wheat malt protein
ActiveCN103278470BImprove processing efficiencyImprove processing qualityColor/spectral properties measurementsMalt GrainSoluble nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for rapidly monitoring the solubility of protein in a preparation process of beer wheat malt. The method can be used for judging the wheat malt library value according to the measurement results of water-soluble protein content and FAN content in green wheat malt, and aims at rapidly and accurately judging the solubility of green wheat malt protein. A conventional wheat malt library value measurement method mainly refers to the standard of QB / T1686 beer wheat malt. A standard method comprises the steps of drying green wheat malt into finished wheat malt, carrying out EBC saccharification and then respectively measuring the content of soluble nitrogen and the total nitrogen of wheat malt in a kjeldahl method. The standard method is more in steps, complicated in operation, long in time consumption (about 30h) and high in cost. The method, which can judge the solubility of the wheat malt protein according to the water-soluble protein content and the FAN content in the green wheat malt, has the total time consumption of shorter than 3h, can rapidly and accurately judge the wheat malt library value, reasonably control the germinating time and accurately judge the finished wheat malt library value, and is capable of saving the analysis time and improving the processing efficiency and quality of wheat malt.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for simply and conveniently measuring content of non-protein nitrogenous substance in milk product
InactiveCN103575686AEasy to operateStrong resistance to reagent interferenceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical analysis using titrationTotal nitrogenAmount of substance
The invention discloses a method for simply and conveniently measuring the content of a non-protein nitrogenous substance in a milk product. According to the method, casein serves as a standard substance; a kjeldahl method and a colorimetric method are used for measuring simultaneously; a correction coefficient is calculated; a calculated result of the colorimetric method can be converted into total nitrogen of the kjeldahl method. When a sample is measured, the two methods are used for measuring simultaneously, and the result of the colorimetric method is converted into a result of the kjeldahl method, and deducted from total nitrogen of the kjeldahl method, so that the content of the non-protein nitrogenous substance in the milk product can be obtained. A colored sample is decolorized and then measured by the method, and milk powder can be diluted and then measured by the method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Economical method for quickly screening high-protein variety of paddy rice
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic breeding and innovation of germplasm resources, and provides an economical novel method for quickly screening high-protein variety of paddy rice. The method comprises the following steps of: comparing by taking the paddy rice variety which is tested by a Kjeldahl method to have the protein content of about 8-9% as medium-protein content, randomly selecting one grain of polished rice from each variety to be tested, dipping in distilled water in a 1.5ml small centrifuge tube for 3 hours, breaking the polished rice to be naturally fractured by hands, dyeing by acridine orange (0.02%, v / v) for 10 minutes under the condition of keeping out of the sun, and washing by the distilled water for 1 minute. The Nikon ECLIPSE 90i laser scanning confocal microscope is used for observing, excitation light is 488nm, emitted light is 575nm-605nm, and NIH Image 1.6.2 software is used for analyzing an image. The transverse facial cleft of the polished rice is higher in protein content compared with the coarse surface, the higher the roughness is, the higher the protein content is, and otherwise the protein content is lower. The method can be used for quickly screening the high-protein variety of the paddy rice by few samples for the subsequent genetic breeding, so that the quality of the paddy rice can be improved.
Owner:天津天隆农业科技有限公司
Method for detecting content of mildronate intermediate 3-(2,2,2-trimethylhydrazine) methyl propionate methylsulfate
InactiveCN104155292AEasy to operateThe measurement result is preciseMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDistillationDigestion
The invention provides an analytical method for measuring the content of mildronate intermediate 3-(2,2,2-trimethylhydrazine) methyl propionate methylsulfate by use of nonaqueous titration, and relates to an analytical method for measuring the content of a mildronate crude drug intermediate. The analytical method is characterized in that kjeldahl determination is adopted and nitrogen in a C7H17N2O2SO4-CH3 monomer is measured by use of a neutral titration method after digestion, and therefore, the purpose of measuring the main content of the intermediate can be achieved. The analytical method comprises the following specific measurement steps: putting a test sample into a Kjeldahl flask, adding water for dissolving, adding a sodium hydroxide test solution, heating for distillation, guiding the distillate into a boric acid solution, taking methyl red-bromocresol green as an indicating liquid, titrating by use of an inorganic acid titrant until the terminal point that the solution turns to grey purple from blue-green, and then calculating the content of C7H17N2O2SO4-CH3 according to the dosage of the titrant. The detection result obtained by the method is capable of achieving basically consistent effects with an HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection result. The method is simple and quick, precise in measurement result and high in accuracy, and can be applied to conventional analysis and quality control of the mildronate crude drug intermediate 3-(2,2,2-trimethylhydrazine) methyl propionate methylsulfate.
Owner:DONGLI NANTONG CHEM +1
Method of judging fertilizing amount by utilizing citrus leaf nutrients
InactiveCN110050555AReduce adverse effectsReduce blindness in fertilizationFertilising methodsSample plotShoot
The invention discloses a method of judging fertilizing amount by utilizing citrus leaf nutrients. The method comprises the following steps: 1, setting a plurality of sample plots in a citrus garden plot to be tested; 2, selecting leaves on the top of spring vegetative shoots of a current year and mixing the leaves into a leaf sample; 3, removing dirt and petioles, carrying out enzyme deactivationunder the condition of 100 DEG C, and placing in a constant temperature oven with the temperature of 75 DEG C for baking for 24 hours; 4, crushing and sieving the sample, adding concentrated sulfuricacid and hydrogen peroxide, and carrying out boiling elimination at 300 DEG C; 5, measuring N by adopting kjeldahl determination, measuring P by adopting a molybdenum-antimony anti-colorimetric method, and measuring K by adopting an atomic absorption method; if N is 2.40-2.70%, P is 0.12-0.16%, K is 1.00-1.40%, P / N is 0.050-0.059, and K / N is 0.416-0.519, a citrus tree is balanced in nutrition. The method of judging fertilizing amount by utilizing the citrus leaf nutrients can judge deficiency of nutritive elements and balance conditions of the various nutrients, and reduce adverse effects ofblind fertilization on soil.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com