Sampling and identifying method for micro-plastics in dust in workplace and application thereof
An identification method and technology for microplastics, applied in sampling, sampling devices, analysis materials, etc., can solve the problem of failure to clarify the degree of pollution of micro-nano plastics in shape and size, insufficient identification of chemical components, and inability to analyze exposure risk exposure of micro-nano plastics. job issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) Fixed-point sampling of dust in the job post:
[0042] Choose a glass fiber filter membrane (Φ40mm) as the dust-measuring filter membrane. After weighing, put it into the sampling head, and then place the dust sampler connected to the sampling head at the detection point, and carry out a sampling flow rate of 25L / min on the injection molding posts respectively. For dust sampling, the sampling time is set to 30min or 90min.
[0043] (2) Calculation of dust concentration at the job post:
[0044] Weigh the filter membrane again after sampling, and calculate the dust concentration in the air according to the following formula, in mg / m 3 express:
[0045]
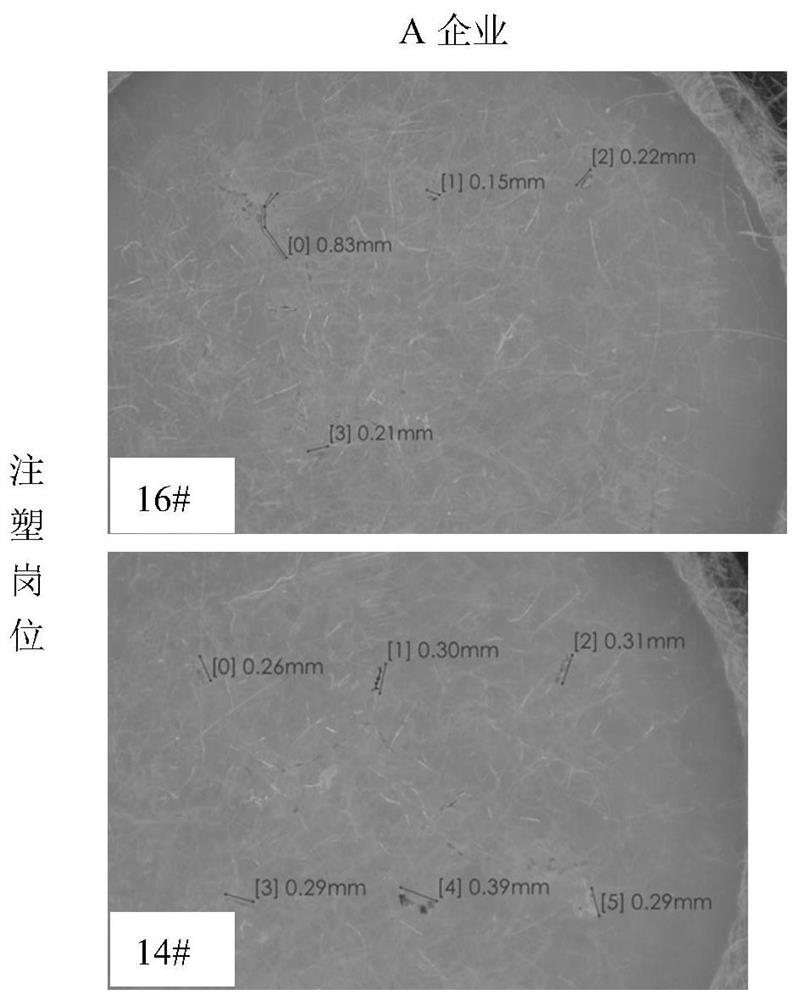
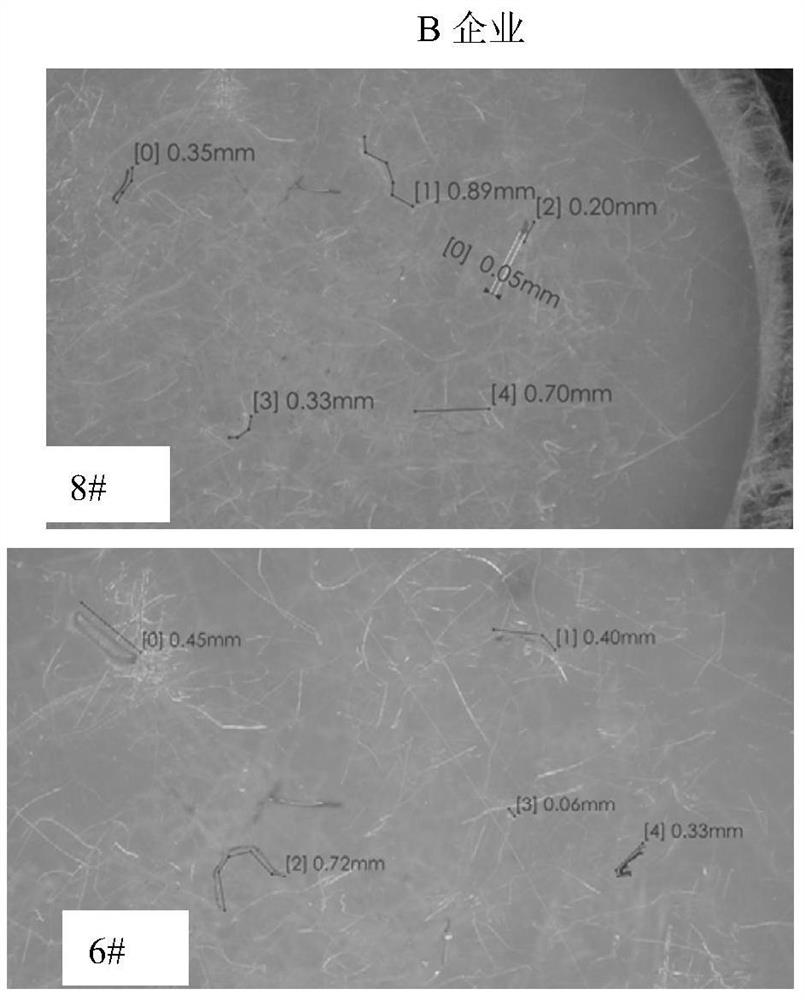
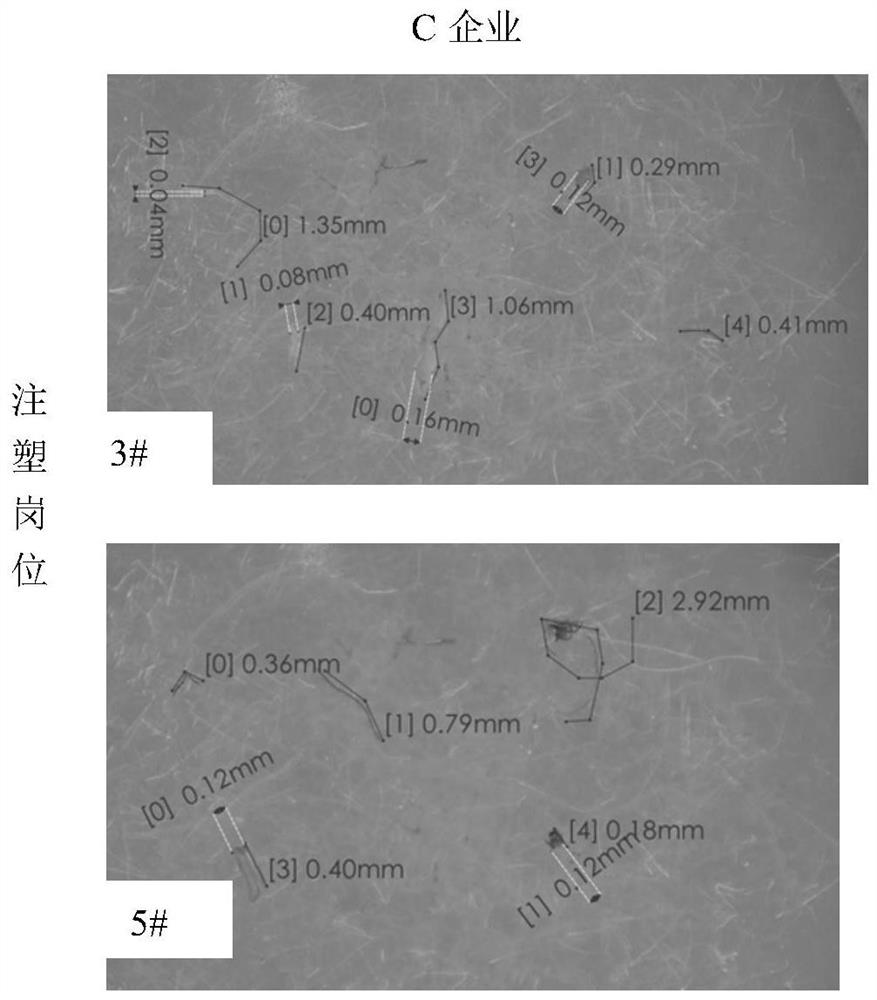
[0046] (3) Observation of the quantity and shape and size of suspected microplastics in the dust of the workplace:
[0047] (1) Quantity detection of suspected microplastics:
[0048] Place the filter membrane under an optical microscope to observe whether there are suspected microplastics on the filter membrane...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com