Reed-solomon decoder employing new polynomial arrangement architecture and decoding method therefor
A polynomial, decoder technology, applied in the field of error correction decoding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
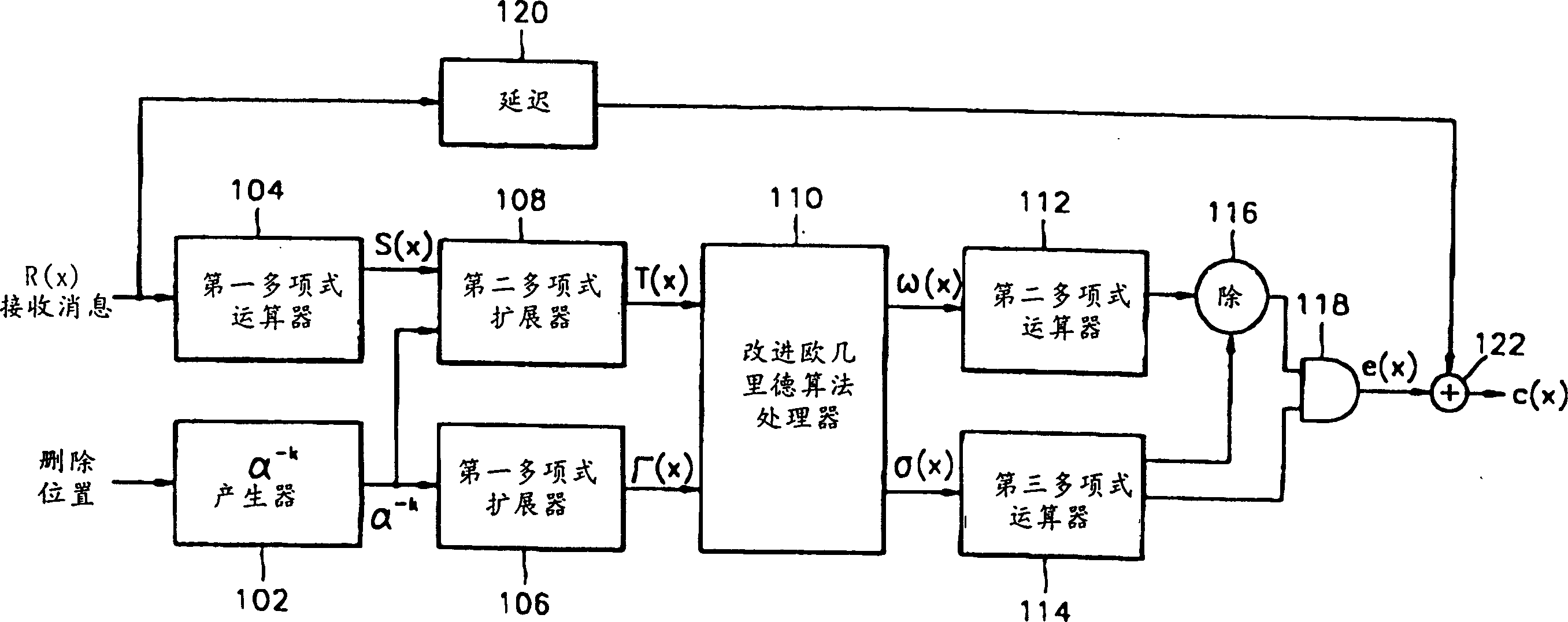
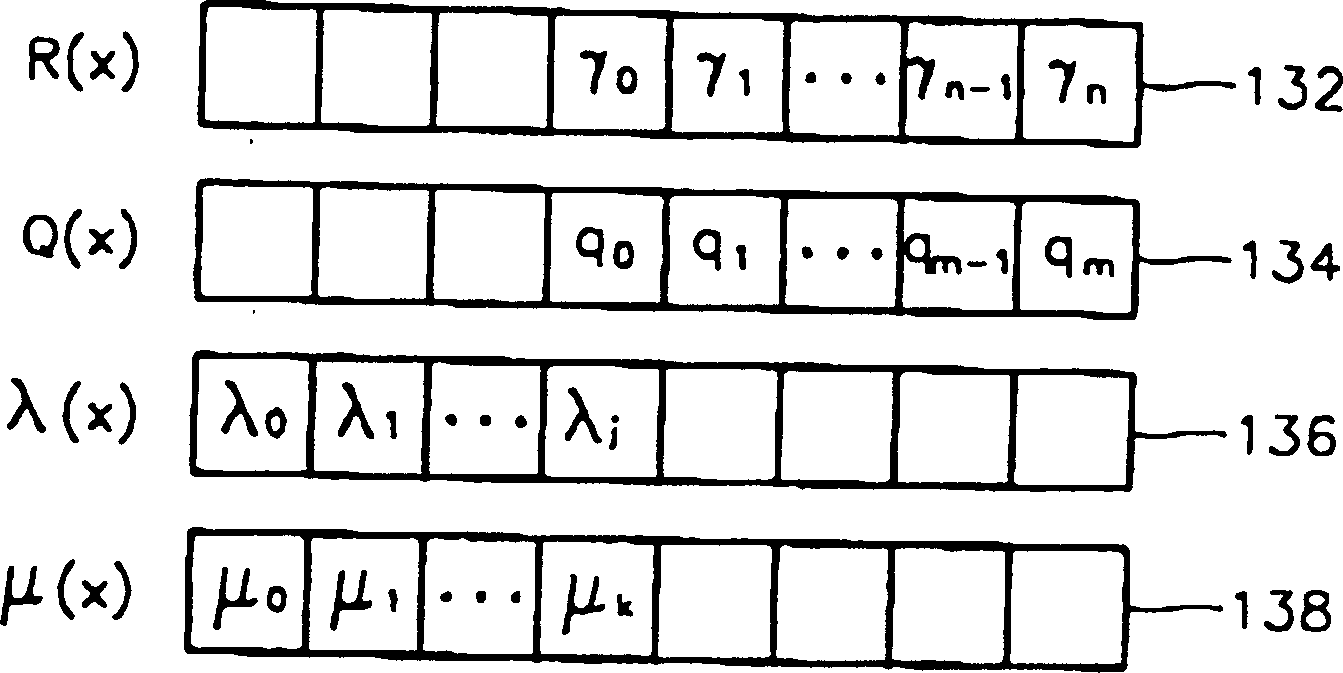
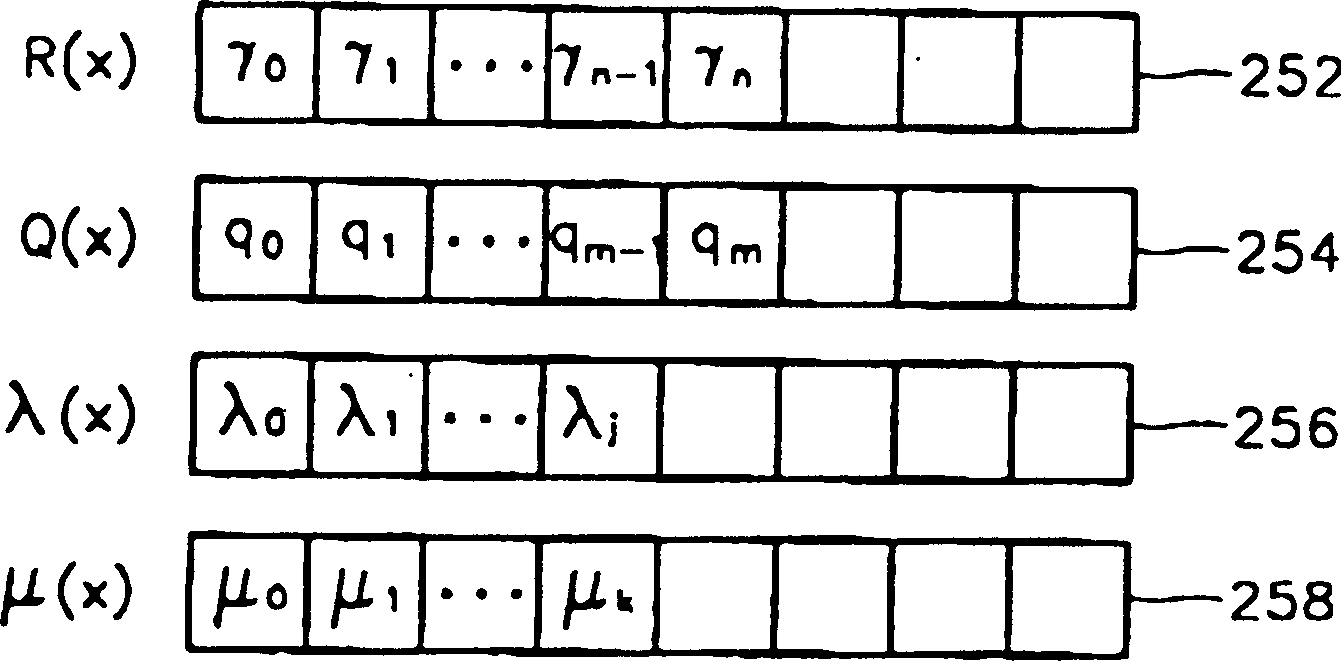
[0037] image 3 is a block diagram of the RS decoder of the present invention. alpha -i The generator 202 uses the input initial deletion position information to generate the root α of the initial error location polynomial -i , and corresponding to the newly deleted information α -i is an iteration control signal (ss) that identifies the start of each iteration operation, and outputs the generated iteration control signal (ss) to the improved Euclidean algorithm operator 210 . The first polynomial expander 206 utilizes α -i α generated by generator 202 -i Extend the initial error localization polynomial Γ(x).
[0038] The first polynomial operator 204 calculates the syndrome value of the received data, and constructs the syndrome polynomial S(x). Equation 13 is a syndrome polynomial of order 2t-1 with coefficients for the calculated syndrome values. 〖Equation 13〗
[0039] S(x)=S 0 +S 1 x+S 2 x 2 +…+S 2t-1 x 2t-1
[0040] The second polynomial expander 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com