A series reconfigurable variable stiffness robot joint structure based on permanent magnet spring
A technology of robot joints and permanent magnet springs, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient load capacity of variable stiffness joints, complex structure of variable stiffness devices, and increased joint mass and inertia. Human-computer interaction safety, simple structure, and the effect of reducing joint energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
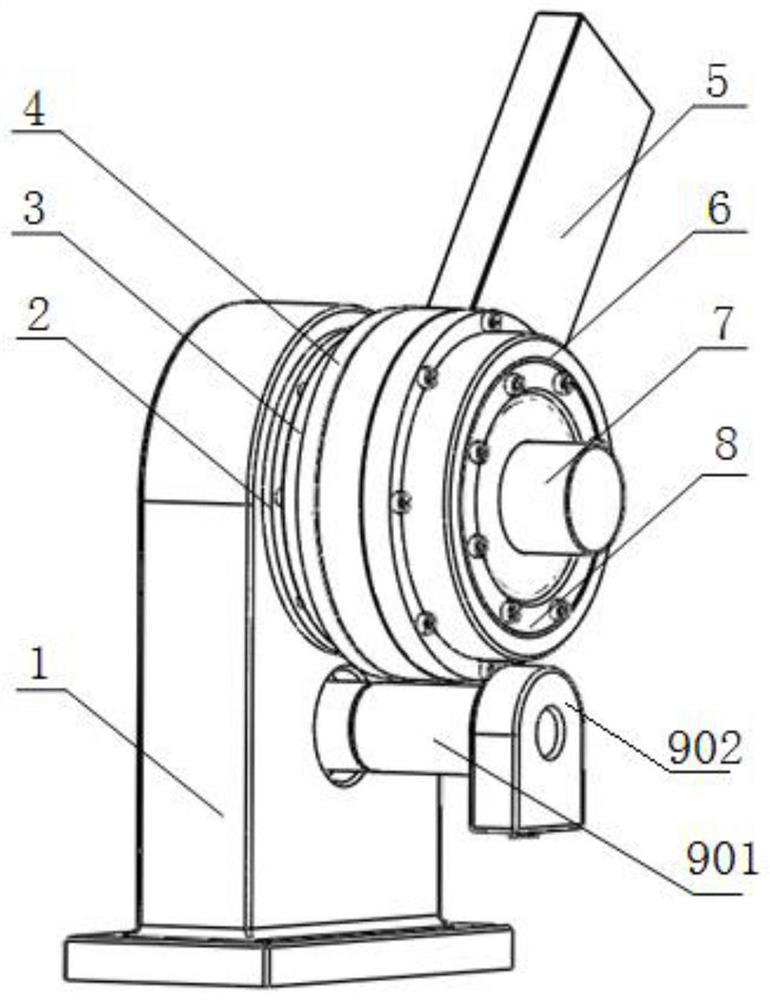
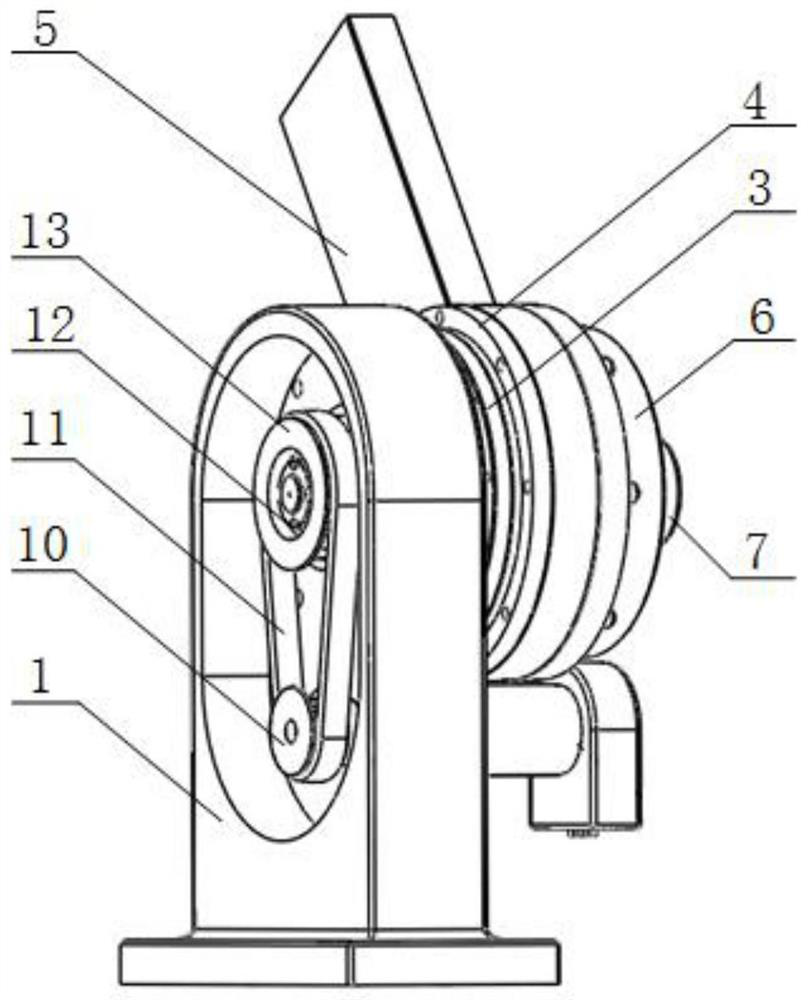
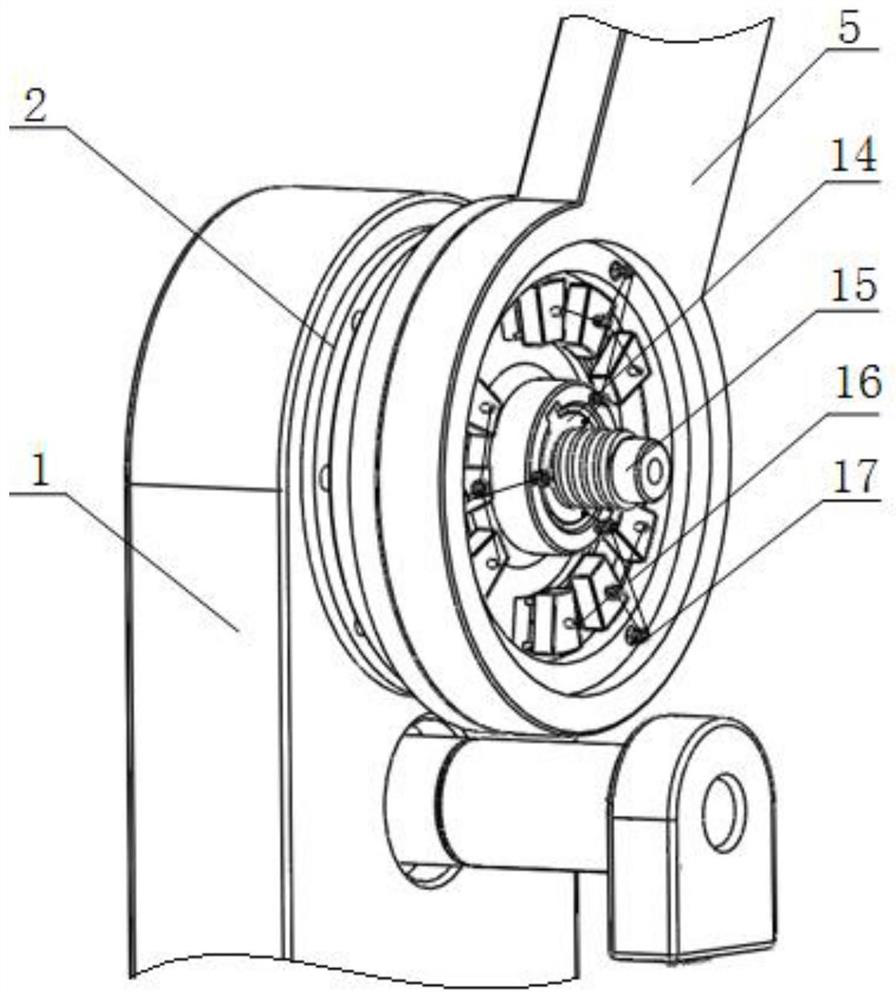
[0023] like Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, a series reconfigurable variable stiffness robot joint structure based on permanent magnet spring includes a base 1, a rope 16, and a variable stiffness motor 7; one end of the vertical base of the base 1 is processed into a waist-shaped blind hole, The other end is machined with an upper through hole and a lower through hole that communicate with the waist-shaped blind hole. A rotating shaft I is installed in the lower through hole through a bearing. One end of the rotating shaft I is sequentially connected with a reducer 901 and a position servo motor 902, and the bottom of the reducer 901 is connected. One end is fixedly installed on the upper surface of the base 1, and the other end is located in the waist-shaped blind hole and is partially installed with a small pulley 10; The sub-bearing I2 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com