M2 group-based candidate causal mutation site gene localization method
A mutation site and gene positioning technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics and biology, can solve time-consuming and labor-intensive problems, save time, help locate causal mutations, and remove background mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0037] Soybean was used as the plant material for the experiment below.
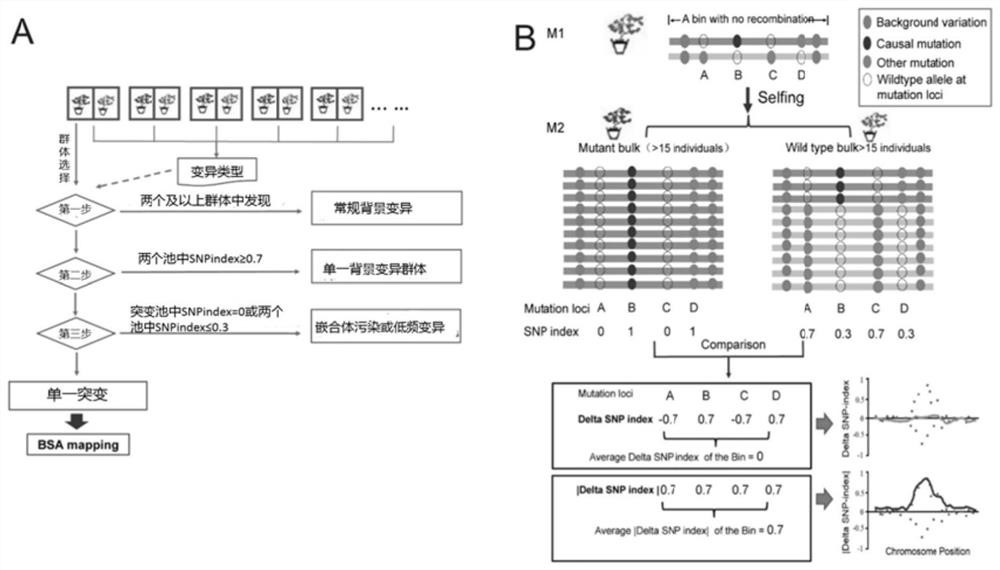
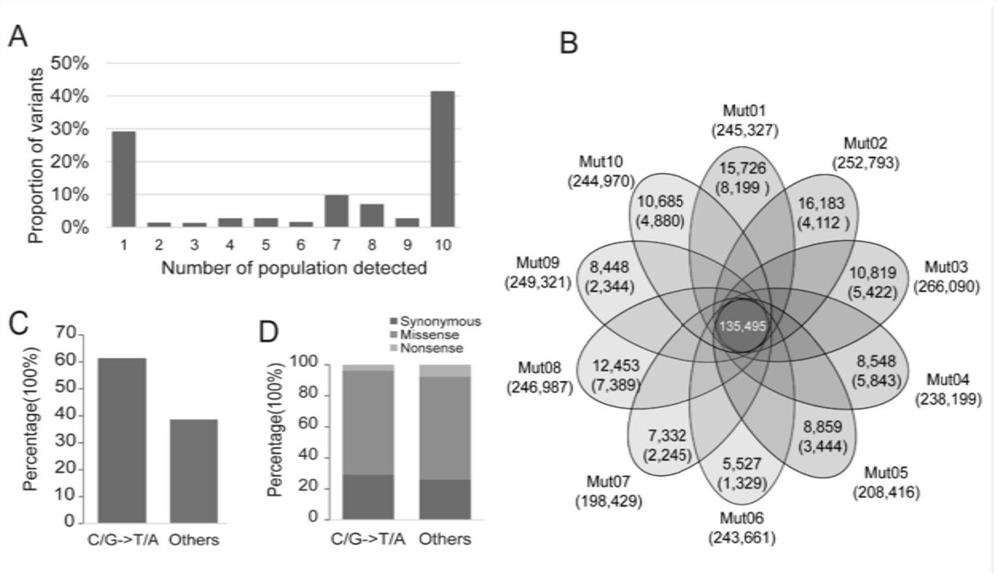
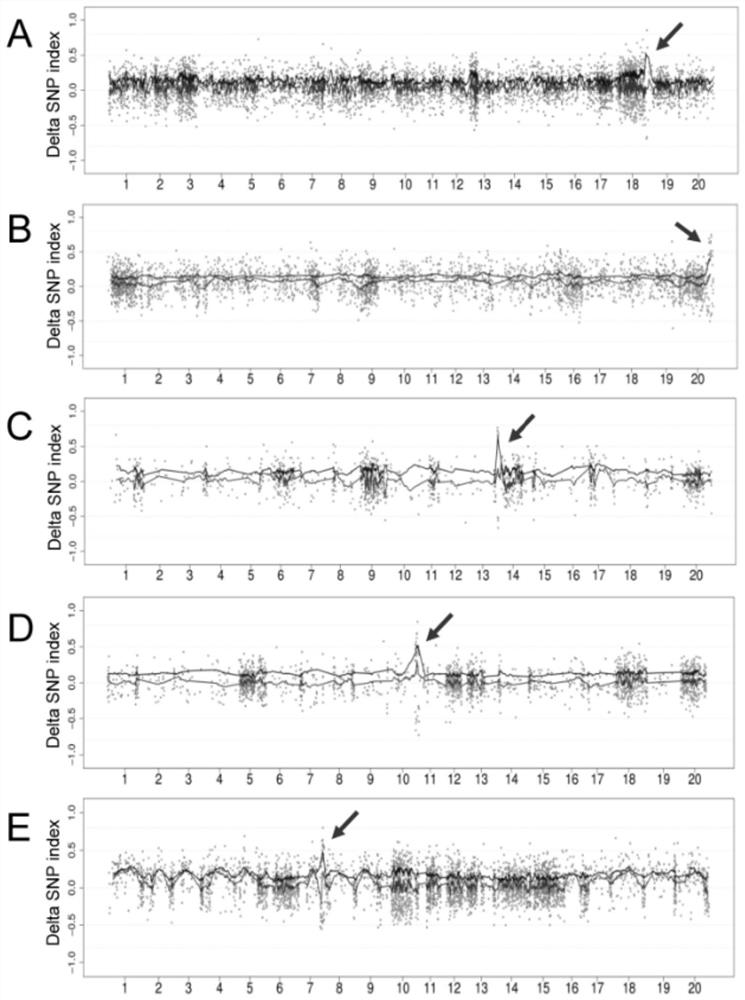
[0038] figure 1 The principle of M2-seq is illustrated. figure 1 A overview of the mutation filtering process. In the present invention, two DNA pools (wild-type pool and mutant-type pool) were respectively constructed in each M2 population, and DNAs from 15 individuals with wild-type and mutant phenotypes were respectively mixed in equal amounts. High-depth (>30X) whole-genome sequencing was performed on each DNA pool. M2-seq consists of two key processes: (i) removal of interfering variants; (ii) mapping of genomic regions harboring causal mutations.
[0039] In order to eliminate the false positive variation that represents the genetic polymorphism or sequencing / alignment error between the wild-type ancestor of the mutant and the reference genome sequence, the present invention designs a variation filtering process with the data of multiple M2 populations, as shown below ( figure 1A). In step 1,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com