Aav viral vectors and uses thereof
A virus vector, intrathecal administration technology, applied in the field of virus particle composition, can solve problems such as lengthy induction period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0139] The rAAV viral vectors disclosed herein can be prepared according to methods of preparation and purification known in the art. In some embodiments, the purpose of the purification method is to remove contaminants from the host cells and chemicals added during collection of the viral vector. In some embodiments, the methods disclosed in PCT / US2018 / 058744, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety, are used. In some embodiments, these methods use about 1×10 13 vg / mL and 1×10 15 Between vg / mL, such as about 1-8×10 13 Concentrations between vg / mL yield rAAV viral vectors. In some embodiments, these methods use about 1.0×10 13 vg-9.9×10 14 Doses (eg, unit doses) of vg yield rAAV viral vectors. In some embodiments, these methods use about 1.0×10 13 vg-5.0×10 14 Doses (eg, unit doses) of vg yield rAAV viral vectors. In some embodiments, these methods use about 5.0×10 13 vg-3.0×10 14 Doses (eg, unit doses) of vg yield rAAV viral vectors. In some embo...
example
[0172] preclinical evaluation
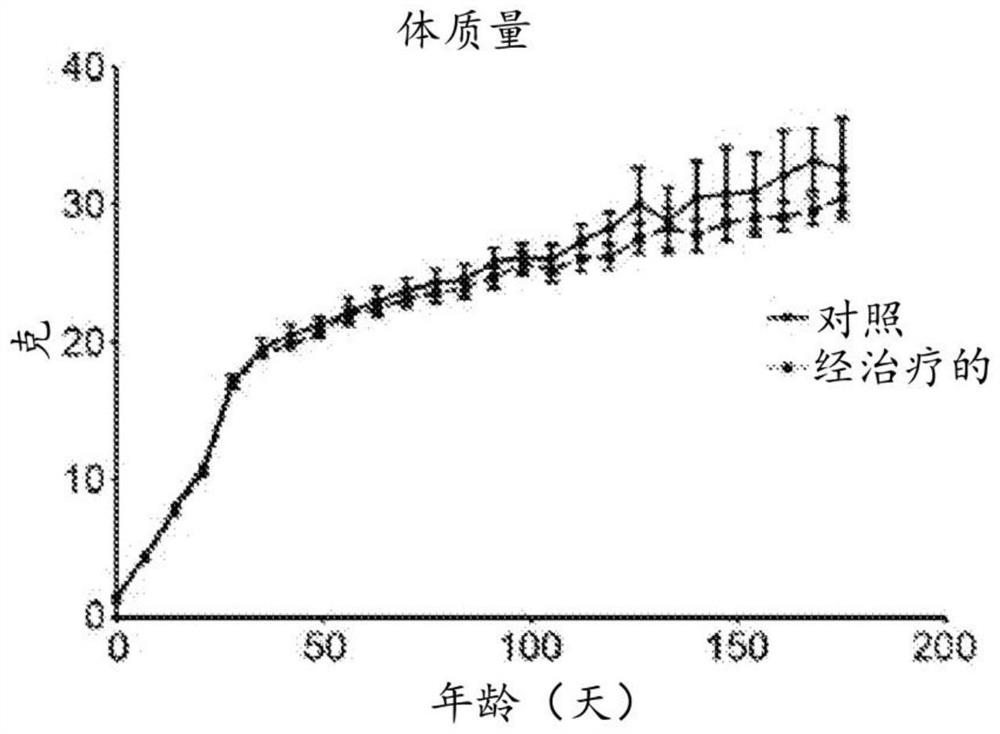
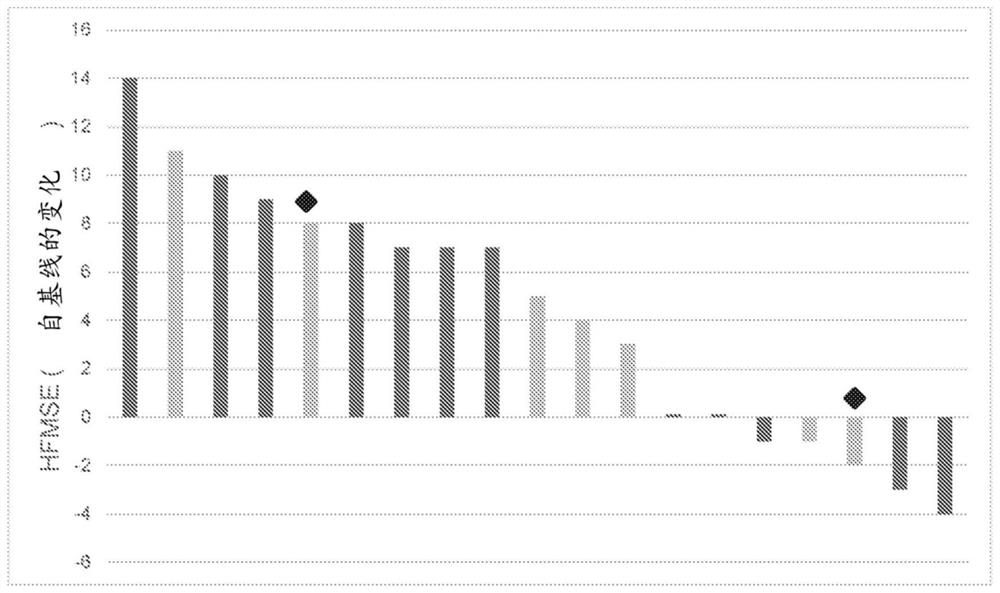
[0173] The SMNΔ7 mouse is a suitable model for studying gene transfer. Butchbach et al., "Abnormal motorphenotype in the SMNΔ7 mouse model of spinal muscular atrophy [SMNΔ7 mouse spinal muscular atrophy model abnormal motor phenotype]" Neurobiology of disease [disease of neurobiology], 27 (2): 207 -19. 5 x 10 of scAAV9.CB.SMN 11 Injection of individual viral genomes into the facial vein of 1-day-old mice rescued the SMNΔ7 mouse model. Foust et al., "Rescue of the spinal muscular atrophy phenotypein a mouse model by early postnatal delivery of SMN," Nature biotechnology, 28(3):271-4. Approximately 42 ± 2% of lumbar spinal motoneurons were transduced in scAAV9.CB.SMN-treated mice. SMN levels were also increased in the brain, spinal cord and muscle of scAAV9.CB.SMN-treated animals compared to untreated SMA mice (albeit lower than WT controls). The ability of scAAV9.CB.SMN- or scAAV9.CB.GFP-treated SMA animals to return to normal posture was a...
example 1
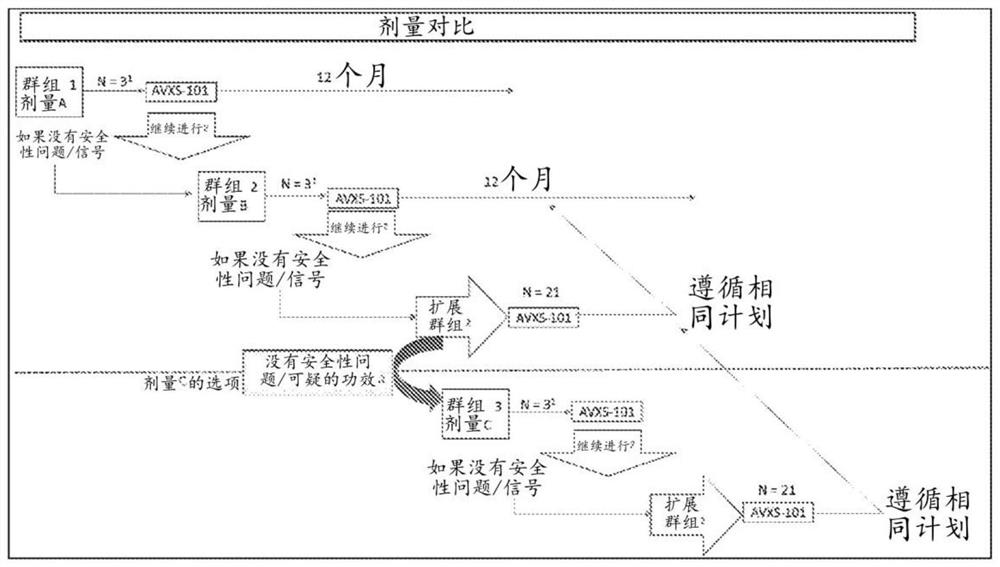
[0186] Example 1 - Clinical Trial Protocol
[0187] Phase 1, open-label, single-dose clinical trial in infants and children with a genetic diagnosis of SMA, biallelic deletion of SMN1, and 3 copies of SMN2 (no genetic modifiers), at Able to sit but not stand or walk on study entry. Patients received up to three (3) potentially therapeutic doses of AVXS-101 in the dose comparison safety study, as described below. Patients were divided into two groups, age ≥6 months and 6 months and 24 and <60 months were enrolled.
[0188] The first group enrolled three (3) patients aged ≥6 months and 13 Administration of vg of AVXS-101 (dose A). There was an interval of at least four (4) weeks between dosing for each patient within the cohort. Investigators reported to the Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) all AEs of grade III or higher that were likely, probable, or definitively related to the study reagents within 48 hours before proceeding with enrollment. After enrolling the first th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com