Task unloading and resource allocation method in uncertain network environment
A technology of resource allocation and network environment, applied in the field of task offloading and resource allocation, which can solve the problems of high energy consumption, unrealistically predicted value of task queuing waiting time, and lack of computing resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
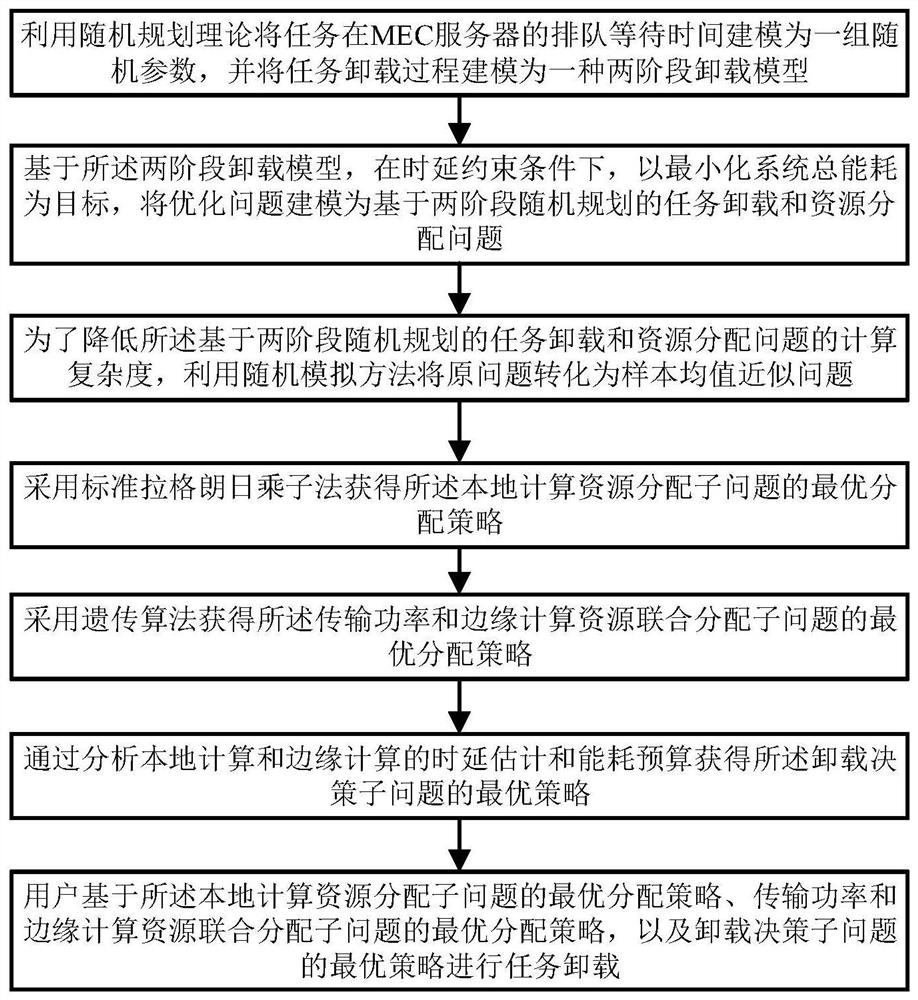
[0058] This embodiment provides a specific implementation of task offloading and resource allocation problem modeling based on two-stage stochastic programming.
[0059] Due to the randomness of task arrival and the time-varying nature of the MEC server task queue, it is unrealistic to obtain an accurate prediction of the task queue waiting time. In this embodiment, the uncertainty analysis of the queuing waiting time is firstly performed, and then the optimization problem is modeled as a two-stage stochastic programming based Task offloading and resource allocation issues, specifically:
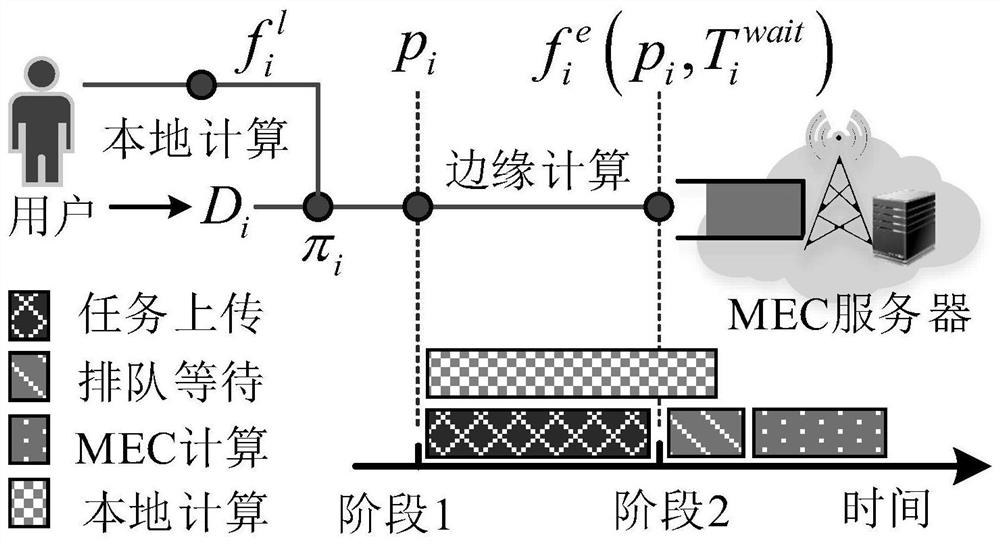
[0060] (1) Uncertainty analysis of waiting time in queue
[0061] In order to deal with the uncertainty of MEC server queuing time, the present invention uses stochastic programming theory to model the uncertain queuing time as a set of random parameters described by probability distribution. Without loss of generality, assuming that the waiting time of MEC servers obeys an exponential dis...
Embodiment 2
[0076] In this embodiment, in order to reduce the computational complexity of the two-stage stochastic programming problem proposed in Embodiment 1, the expected value model in problem P1 is transformed into a MINLP problem based on sample mean approximation. Next, the MINLP problem is decoupled into three sub-problems: allocation of local computing resources, joint allocation of transmission power and edge computing resources, and offloading decision-making, including:
[0077] (1) Transform the expected value model in problem P1 into a MINLP problem based on sample mean approximation
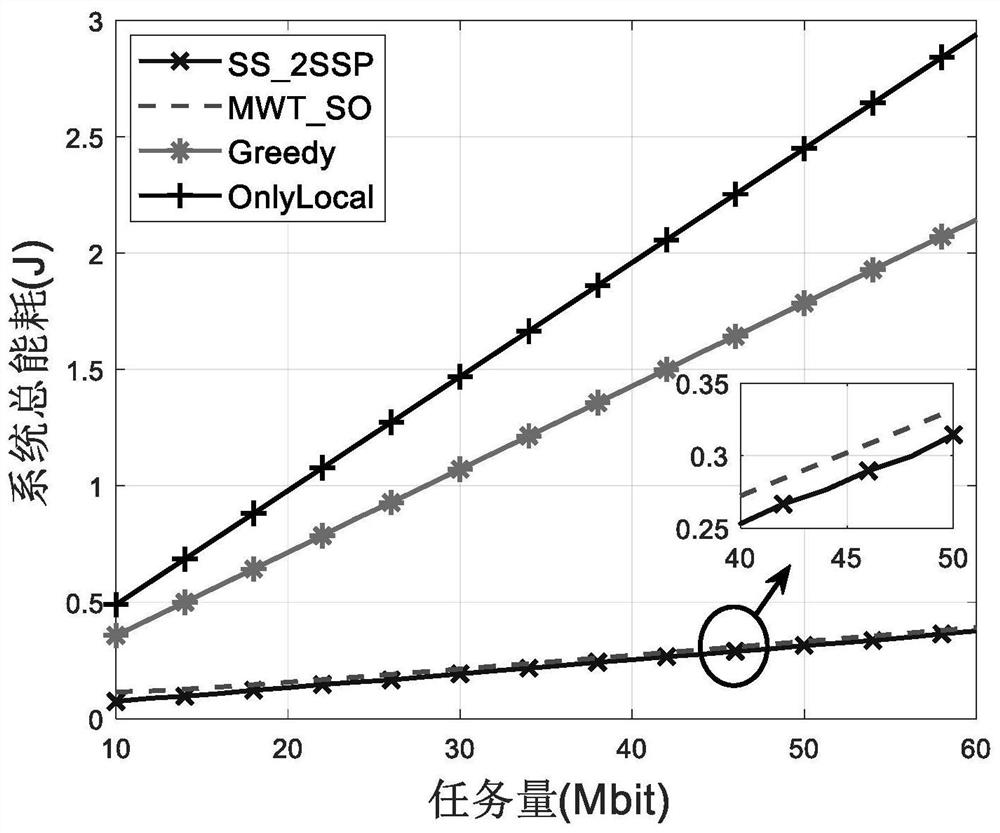
[0078] The invention considers the problem of task unloading and resource allocation optimization under the uncertain environment of MEC server queuing waiting time, and models the optimization problem as a two-stage random programming problem. However, solving two-stage stochastic programming problems usually faces the challenge of "curse of dimensionality", which will lead to high computatio...
Embodiment 3
[0099] This embodiment proposes the specific implementation of using the genetic algorithm to obtain the global optimal solution of the P2-2 problem, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0100] 1) encoding
[0101] In the two-stage unloading model, the main goal is to determine the transmission power of the first-stage task. Therefore, the present invention encodes each feasible transmission power in a floating-point vector, and each floating-point vector represents a chromosome, and the dimension of the floating-point vector is the same as The dimensions of the solution vectors are the same.
[0102] 2) Initial population
[0103] Define M to represent the population size, and the initialization process randomly generates M chromosomes. Randomly generate a point from the feasible domain of the user's transmission power, and check whether it satisfies the constraint condition, if it is satisfied, it is regarded as a chromosome, otherwise, a random point is rege...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com