Distributed active and reactive optimal control method for wind power plant
An optimal control and wind farm technology, applied in wind power generation, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to obtain the optimal power reference value and guarantee the optimal operation, and achieve optimal active power and reactive power. Reference, reactive capacity maximization, effect of improving scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
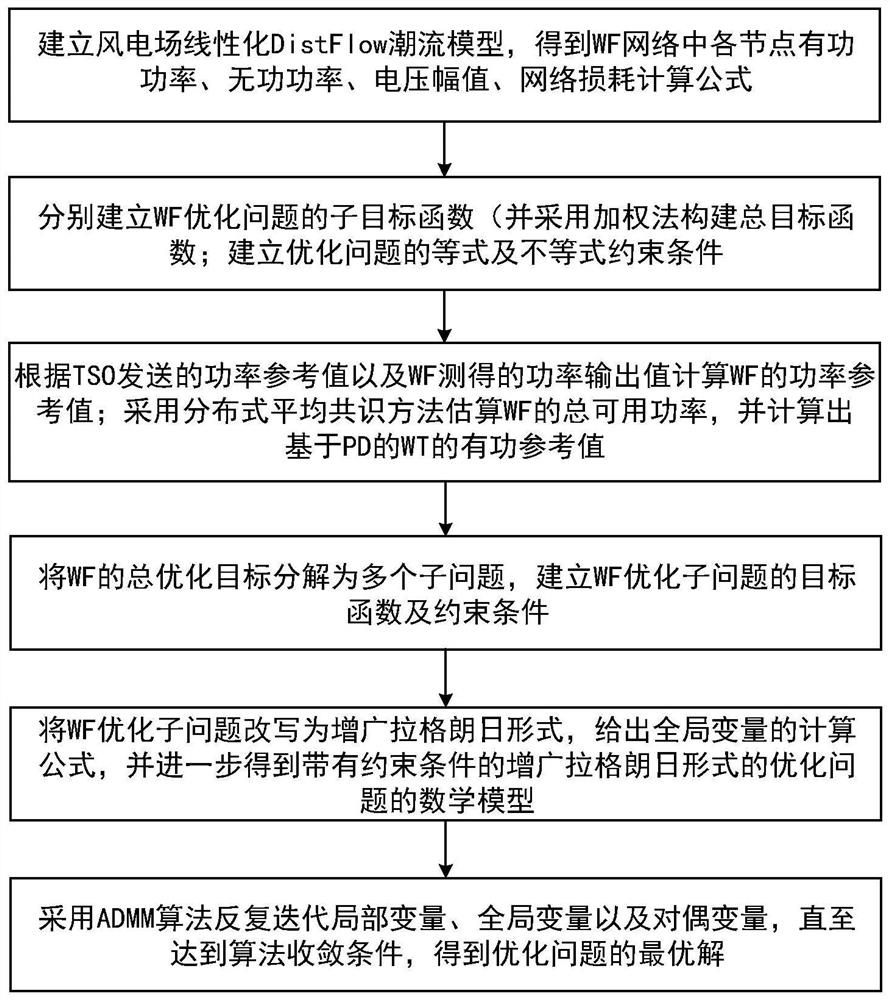
[0080] In order to understand the above-mentioned purpose, features and advantages of the present invention more clearly, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments of the present application and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other.
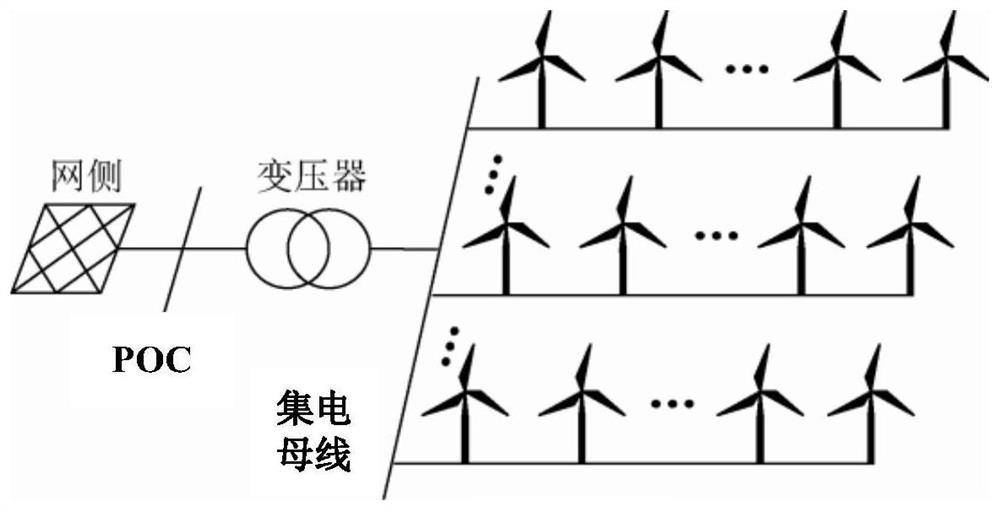
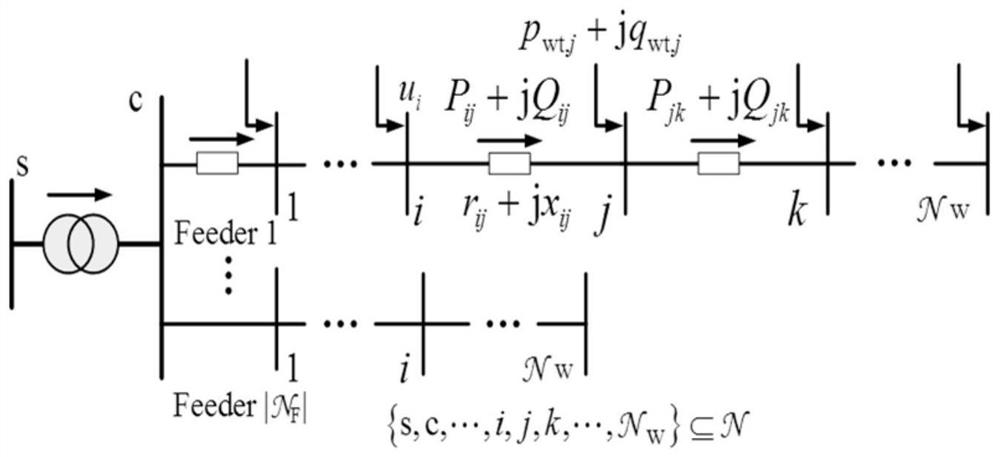
[0081] figure 1 It is a typical structural configuration of a wind farm, which includes wind turbines, medium-voltage feeders for each wind generator, collector buses connecting each feeder, step-up transformers, high-voltage cables, and slack busbars for grid connection points. The wind farm is connected to an external grid through a step-up transformer and a high-voltage cable, and the electric energy generated by the wind generator is collected by a medium-voltage feeder connected to the wind generator. Each collector bus is connected to multiple wind turb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com