Coupled image lattice-based recoverable heterogeneous network cascade failure method and device, and storage medium
A heterogeneous network and cascading failure technology, which is applied in the field of transportation network, can solve the problems such as the degree of interpretation of the reality of the model needs to be strengthened, the correlation is not considered enough, and it is difficult to accurately reflect the real situation. The effect of strong explanatory power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
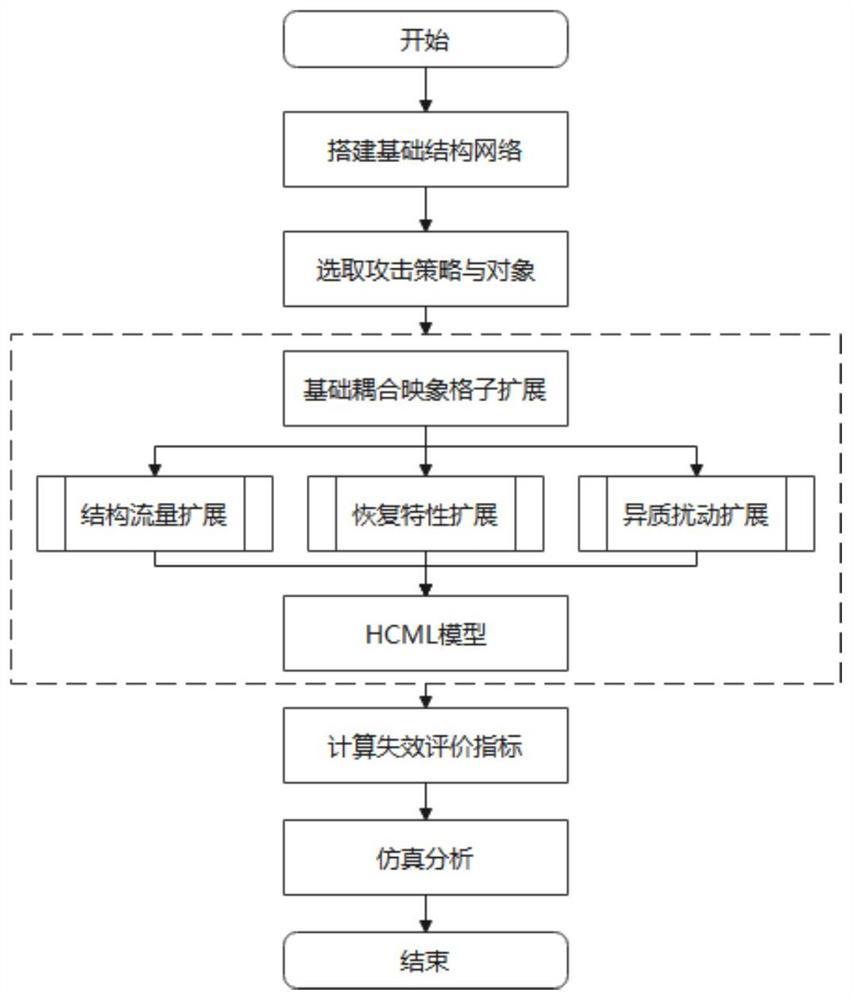
[0070] A cascading failure method for recoverable heterogeneous networks based on coupled mapping lattices, specifically in accordance with the following steps:
[0071] S1: Select the rail network data of Xi’an: consider the subway station as a node of the subway network, connect the front and rear stations of the same line, and abstract the urban rail transit network into a weighted and undirected network in view of the two-way mobility of traffic. There are currently 8 subway lines and 150 stations in the selected urban public transportation. The network topology is as follows: image 3 shown.
[0072] S2: There are two types of coupling strength at any node, ε 1 Indicates the structural coupling strength, ε 2 Indicates the flow coupling strength, and the corresponding values of the coupling strength of all nodes are consistent, that is, the structural coupling strength of all nodes ε 1 The same, the flow coupling strength ε of all nodes 2 Similarly, as an important v...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Based on the rail transit network framework selected in Example 1, select 4 types of nodes with a node degree of 1-4 in the network, and substitute them into the HCML model to carry out deliberate single-point attacks, ε 1 =ε 2 = 0.4, considering the topological elements and traffic elements as the top two elements of the network, this embodiment assigns the same weight to the two types of elements that meet the constraint conditions; within 100 time steps, the relationship between the network failure scale G and the iteration time t is calculated , the simulation results are as Figure 5 shown. The results show that nodes with a large attack node degree have a significant impact on the overall failure degree of the network than nodes with a small attack node degree. It shows that the Dadu node is attacked, that is, the node with the strong recovery ability set in the model fails first (at the beginning of the attack, the first step gives the Dadu node an attack beyon...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Based on the environment set in Example 2, select the same attack, and apply the non-resilience coupling map lattice (N-CML) model, low resilience (L-HCML) model and high resilience (H-HCML) model to measure and calculate respectively Network failure scale, the experimental results are as follows Figure 6 shown. N-CML means a CML model that does not consider recovery, that is, formula (5) that does not include the H item; L-HCML means a low resilience (Low) HCML model, that is, h in formula (5) 0 The value range is (1,5), here 4 is taken; H-HCML represents the HCML model with high resilience (High), that is, h in formula (5) 0 The value range is [5,10), and 8 is used here. The results show that the time for the L-HCML and H-HCML models to reach the global collapse situation is much shorter than that of the CML model. When the basic recovery ability of the model is improved h 0 When the value is , the invulnerability of the network increases significantly and can be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com