A kind of cystine cholesterol gelling factor and its preparation method
A cystine cholesterol, gel factor technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, fluorescence/phosphorescence, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of the rational design of the gel factor structure, the difficulty of precise control of the morphology and performance, and achieve enhanced non-toxicity. Covalent bond force, unique structure, low price effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040]Example 1: Synthesis of a cystine-cholesterol gelling factor with a "butterfly" molecular structure, the synthesis route of the cystine-cholesterol gelling factor is as follows:
[0041]
[0042] (1) Synthesis of N-1-naphthylethylenediamine (Formula 1): Dissolve N-1-naphthylethylenediamine hydrochloride (600mg, 2.31mmol) in water, add NaOH solid (185mg, 4.62mmol ), stirred at room temperature for 2h. The aqueous phase was extracted three times with ethyl acetate, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and rotary evaporated to obtain N-1-naphthylethylenediamine yellow oily liquid.
[0043] (2) Synthesis of tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc)-protected cystine (Formula 2): Dissolve cystine (500mg, 2.08mmol) in water, add Et under ice-cooling 3 N and Boc 2 O stirring, the temperature naturally rises to room temperature and reacts for 4h, and TLC monitors that the reaction is complete. The reaction solution was spin-dried, and the residu...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Gel performance of cystine cholesterol gelling factor in different solvents
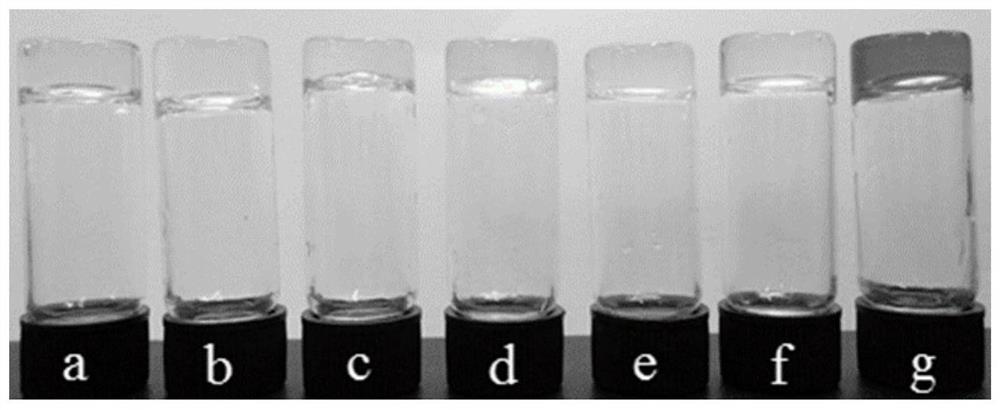
[0050] In order to study the gelation ability of cystine-cholesterol gelling factor, a certain amount of cystine-cholesterol gelling factor was weighed, respectively added to different solvents (benzene solvents, n-propanol, cyclohexane, etc.), ultrasonically heated , after cooling to room temperature and standing for a period of time, observe its gel performance. The results are shown in Table 1:
[0051] Table 1 The gelation ability of cystine cholesterol gelling factor in different solvents
[0052]
[0053] Among them, TG is a transparent gel; OG is an opaque gel; I is insoluble during the heating process; P is dissolved first and then gradually precipitated; S is still in a solution state after cooling to room temperature. Measured 19 kinds of solvents respectively, and found that the gel factor can form gels in almost all benzene solvents such as benzene, toluene, chlorob...
Embodiment 3
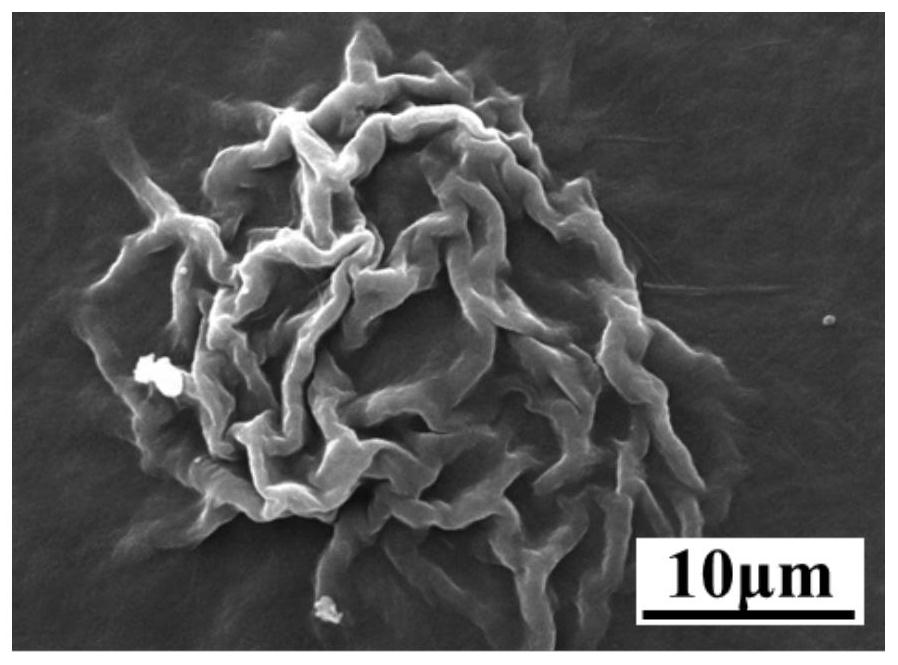
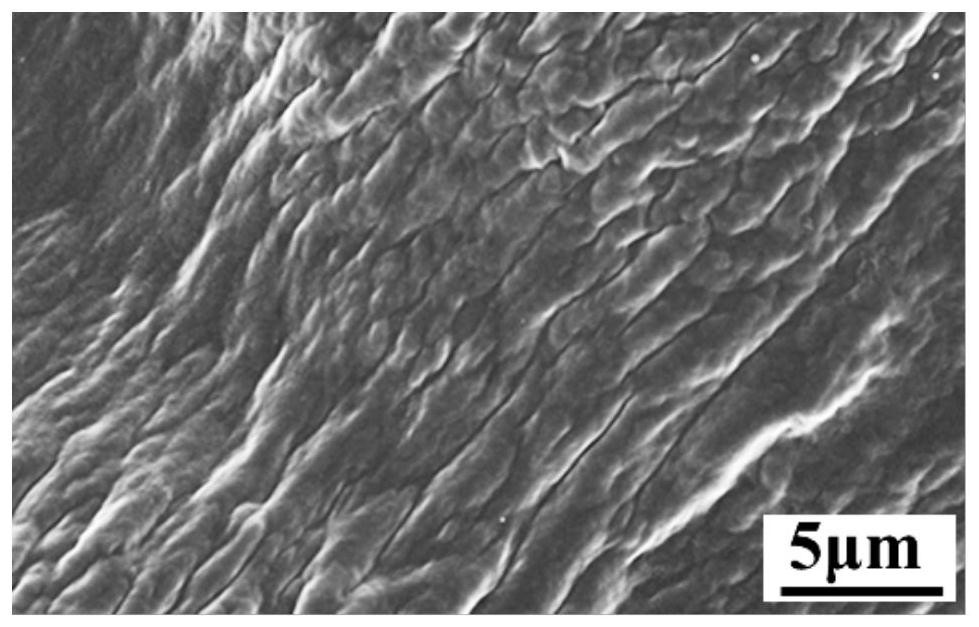
[0054] Example 3: Microscopic morphology of gel formed by cystine-cholesterol gelling factor in different solvents
[0055] The morphology of the gel formed in each system was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and it was found that the microscopic morphology of the gel formed by the cystine-cholesterol gelling factor was very different in different solvents. The gel formed by cystine-cholesterol gelling factor in o-xylene and m-xylene can be seen that thick fibers with a diameter of 2-3 μm are intertwined and stacked ( figure 2 , image 3 ); in the gel formed in n-propanol, molecules aggregate to form a fibrous network structure, and fibers with a diameter of about 30nm are interlaced to form cavities of 50-100nm size ( Figure 4 ). These fibers are intertwined with each other, trapping the solvent in them to restrict the flow, forming a gel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com