Monocular depth estimation method based on electro-hydraulic focusable lens, corresponding camera and storage medium
A depth estimation and electro-hydraulic technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve the problems of complex monocular camera structure, high initial cost, high price, etc., and achieve the effect of simple and practical establishment process, low cost, and simple method and algorithm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
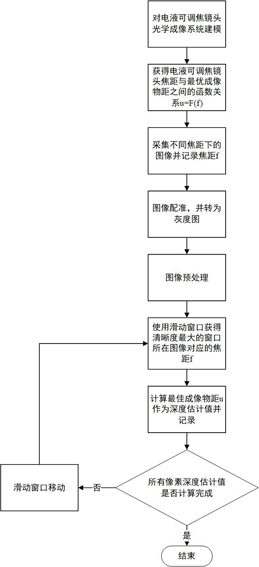
[0046] see figure 1 , a monocular depth estimation method based on an electro-hydraulic adjustable focus lens, comprising the following steps:
[0047] S1: Use Zemax software to establish the optical imaging system model of the electro-hydraulic zoom lens, and set the radius, thickness, curvature, material and other information of the electro-hydraulic zoom lens used in the Zemax software.
[0048] S2: Establish the functional relationship between the focal length of the electro-hydraulic adjustable focus lens and the optimal imaging object distance. The specific establishment process is:
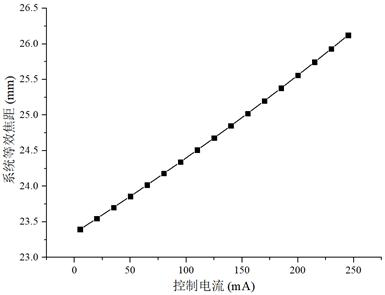
[0049] A: see figure 2 , using the optical imaging system model modeled in step S1, the relationship between the control current and the focal length of the electro-hydraulic adjustable focus lens can be obtained:
[0050] f=αI+β (1)
[0051] Among them, f is the focal length, I is the control current, and α and β are coefficients obtained by curve fitting;
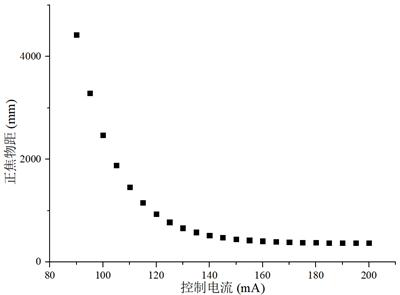
[0052] B: see image 3 , ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] A monocular depth estimation method based on an electro-hydraulic adjustable focus lens, the only difference from Embodiment 1 is that the sliding window slides with a step size λ in step S8. The rule is:
[0075] a: The pixel point at the lower right corner of the λ×λ pixel in the center of the sliding window is used as the pixel point at the initial position of the image. After the depth value estimation of the window is completed, the sliding window slides along the negative direction of the x-axis with the step size λ to continue the depth estimation until it reaches the leftmost border of the image;
[0076] b: The sliding window returns to the rightmost boundary of the pixel at the initial position of the image, slides once along the negative direction of the y-axis with a step size λ, and then continues to slide according to the above rule a; repeat a and b until all pixels of the image are completed depth estimation.
Embodiment 3
[0078] A camera includes an electro-hydraulic adjustable focus lens, the electro-hydraulic adjustable focus lens is connected with a control module, the control module is connected with a processor module and a storage module; one or more programs are stored on the storage module, when one or more The program is executed by the processor module, so that one or more processors implement any step in the monocular depth estimation method based on the electro-hydraulic adjustable focus lens described in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com