Analog based speaker thermal protection in class-d amplifiers
An amplifier circuit and resistor technology, applied in the layout of amplifier protection circuit, amplifier, low frequency amplifier, etc., can solve the problem of not sensing speaker temperature, audio amplifier system relying on speaker feedforward protection, audio amplifier system low maximum allowable power, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
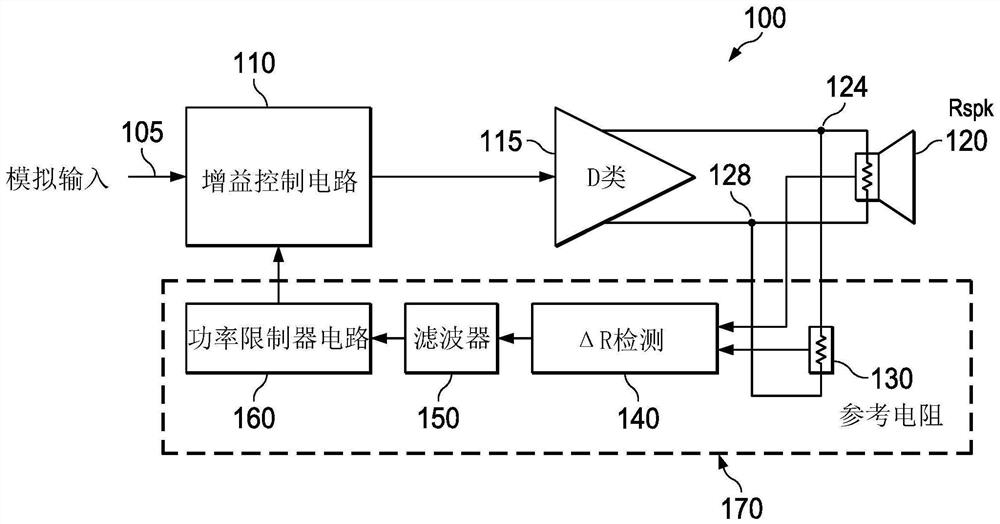
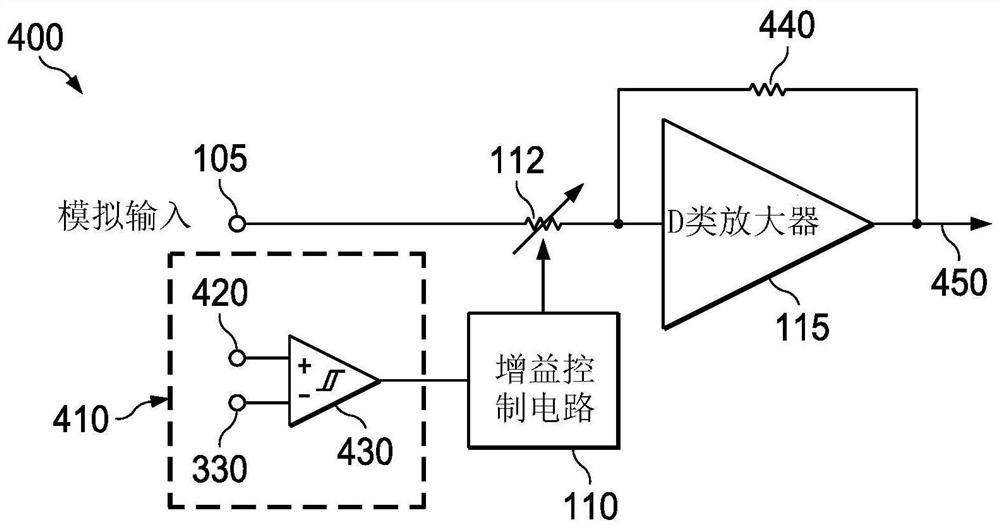
[0014] The disclosed thermal protection circuits for audio amplifier systems are analog circuits and occupy less area on a semiconductor die than thermal protection circuits that rely on digital signal processing and associated ADCs. The example thermal protection circuit also determines the temperature of the connected speakers and allows the audio amplifier system to achieve less conservative audio output signal thresholds and increased maximum allowable power compared to audio amplifier systems that rely on feed-forward thermal protection.
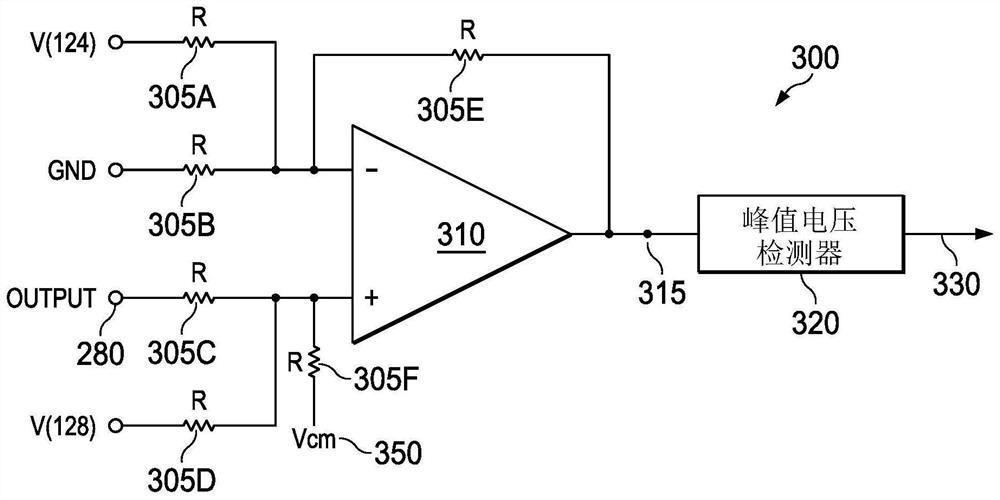
[0015] An example thermal protection circuit compares the output load current to a known reference current. The reference current is calibrated to match the resistance of the loudspeaker at a known temperature, which is referred to herein as the resistance of the loudspeaker at time t0 under resting conditions, and can be determined at the time of manufacture. The difference between the two currents is caused by an increase in the tempe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com