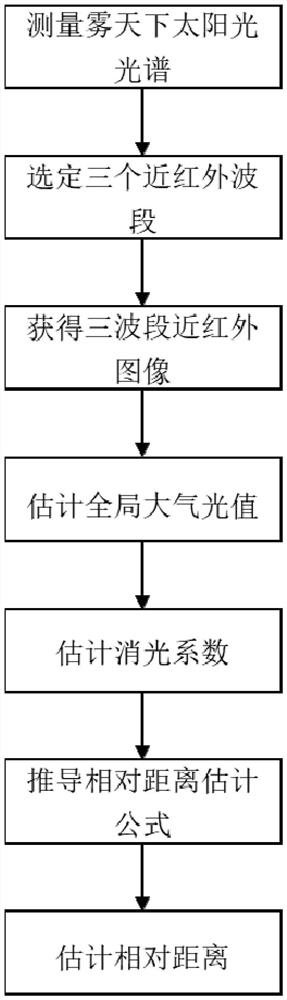
Building relative distance estimation method based on near-infrared tri-spectral imaging
A near-infrared imaging and relative distance technology, which is applied in the field of image visual distance estimation, can solve the problems of unstable sensor signals, inability to image and estimate distance, and error in estimation results, so as to broaden the band range, improve accuracy, and overcome large errors Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0069] The present invention is described in further detail now in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
[0070] It should be noted that terms such as "upper", "lower", "left", "right", "front", and "rear" quoted in the invention are only for clarity of description, not for Limiting the practicable scope of the present invention, and the change or adjustment of the relative relationship shall also be regarded as the practicable scope of the present invention without substantive changes in the technical content.
[0071] As shown in the accompanying drawings, an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for estimating the relative distance of buildings based on near-infrared three-spectrum imaging;
[0072] Specifically, it is realized through the following steps:
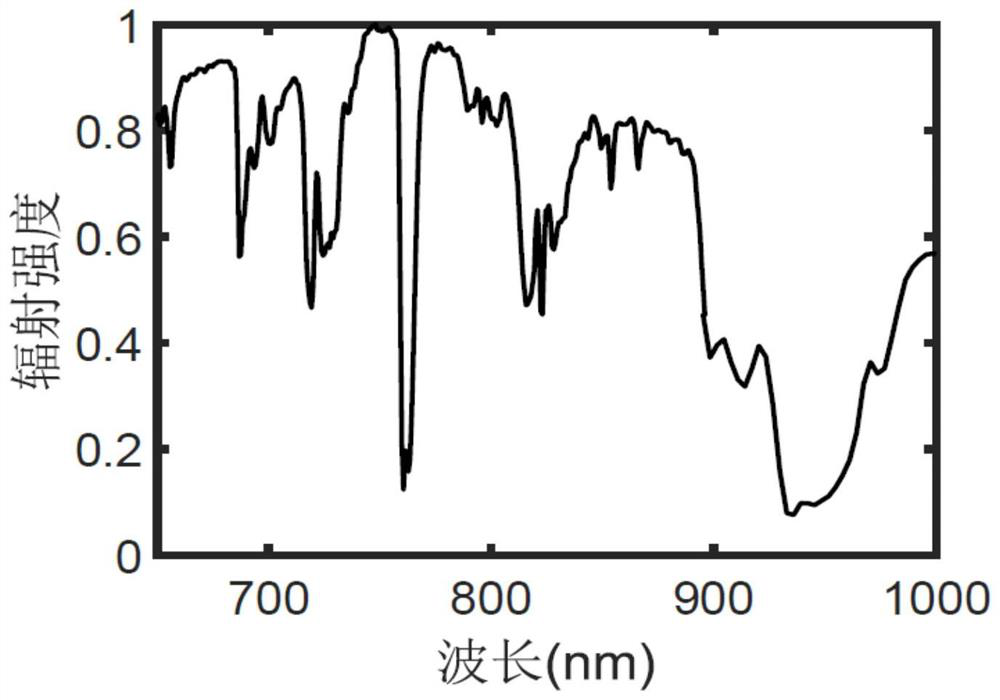
[0073] Step 1: Measure the spectrum of sunlight under fog using a standard white target and a spectrometer.
[0074] Specifically, it is realized through the following steps:
[0075] Step 101, sele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com