Low power apparatus and method to multiply frequency of a clock
A clock frequency multiplication and frequency technology, applied in the direction of automatic power control, pulse technology, pulse processing, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the quantization noise of the PLL frequency divider, increasing the PLL noise, and high loop filter capacitor layout area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
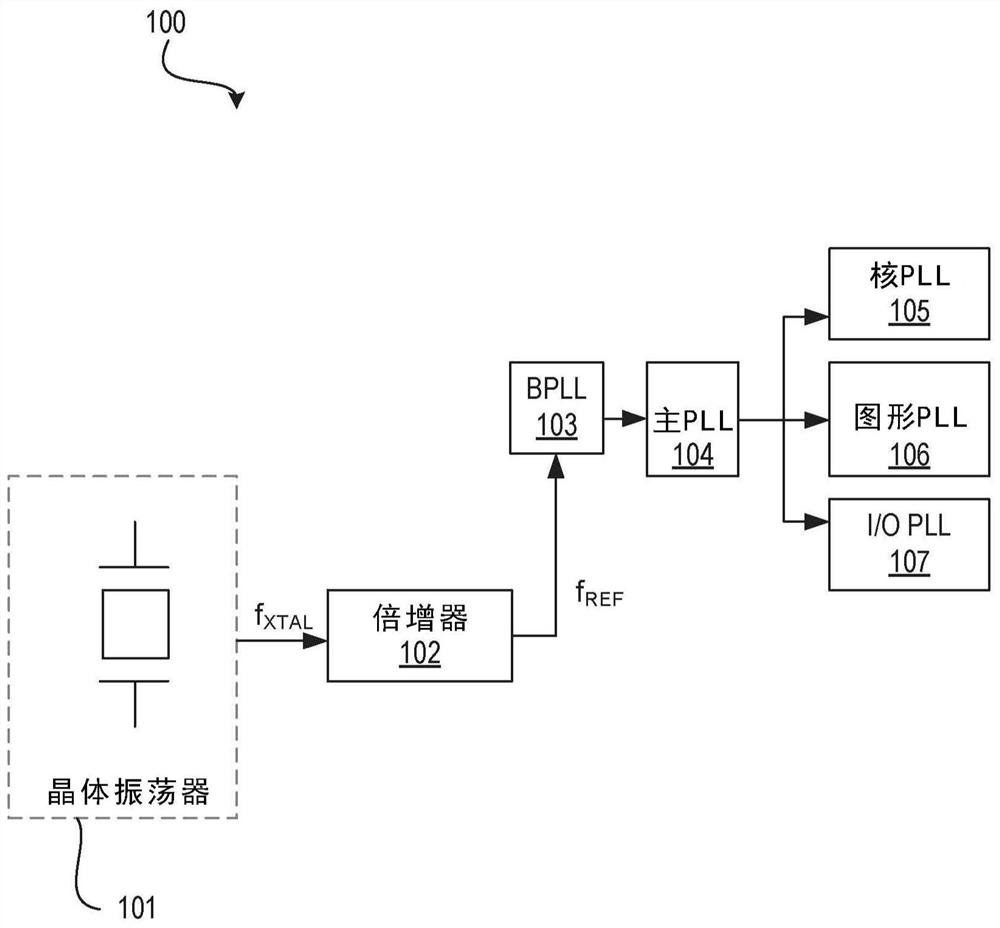
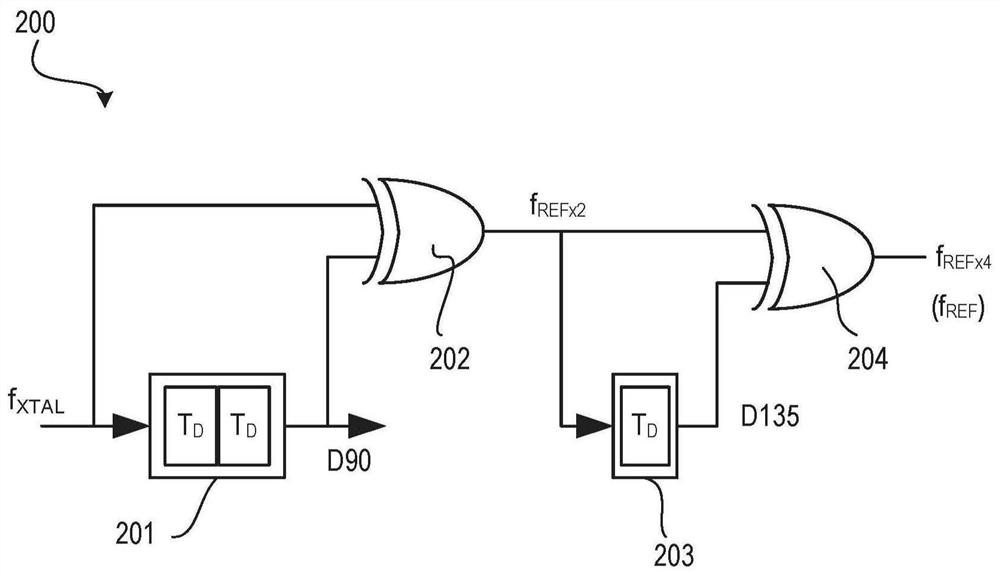
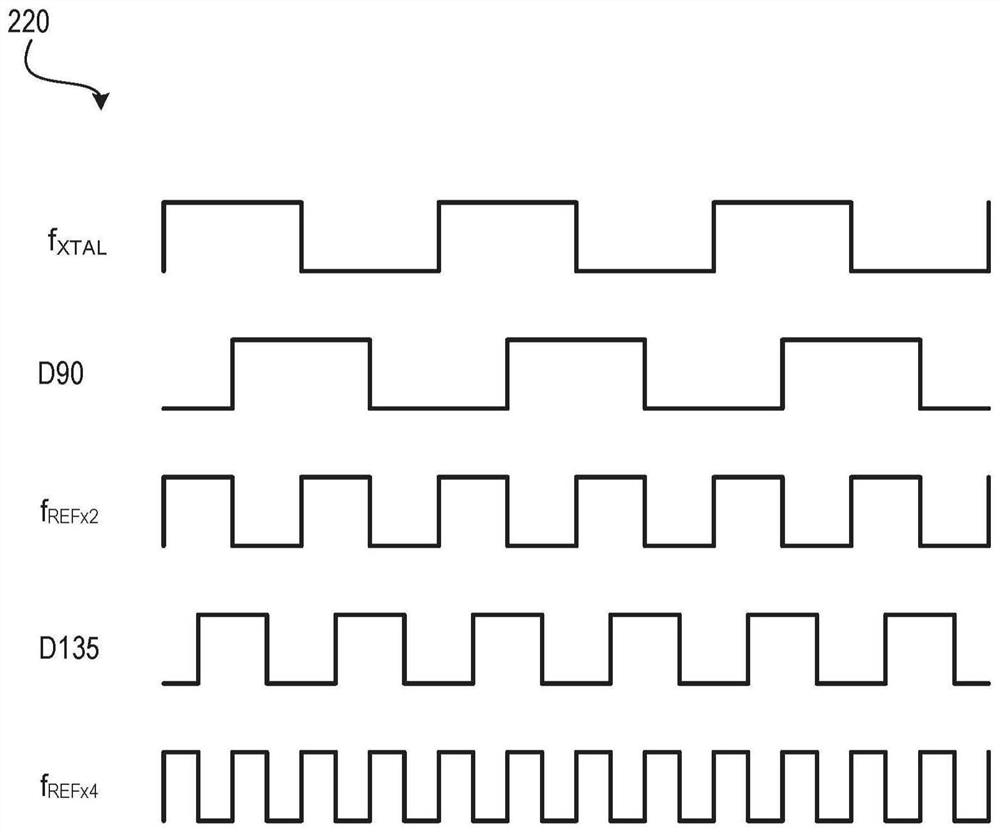
[0103] Example 1: An apparatus comprising: a duty cycle correction (DCC) circuit for receiving a first clock having a first frequency to generate an output substantially corrected for a duty cycle error; and a multiplier circuit coupled to an output of a DCC circuit, wherein the multiplier circuit is used to generate a second clock having a second frequency higher than the first frequency, wherein the multiplier circuit includes a delay line for delaying the output of the DCC circuit and generating a phase shifted signal ; and a comparator for comparing the output of the DCC circuit with the phase-shifted signal.
example 2
[0104] Example 2: The apparatus of Example 1, wherein the delay line is a first delay line, wherein the phase shifted signal is a first phase shifted signal, and wherein the multiplier circuit comprises a second delay line for delaying the first phase shifted signal and generate a second phase-shifted signal.
example 3
[0105] Example 3: The apparatus of Example 2, wherein the multiplier circuit comprises: an inverter to invert the second phase-shifted signal; and a phase detector to receive the output of the inverter and the output of the DCC circuit.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com