Lung disease lesion unsupervised segmentation method based on knowledge distillation
A lung disease, unsupervised technology, applied in the fields of medical image processing and computer vision, can solve problems such as insufficient performance and insufficient knowledge distillation, and achieve the effects of easy collection, easy construction, and insufficient labeled data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
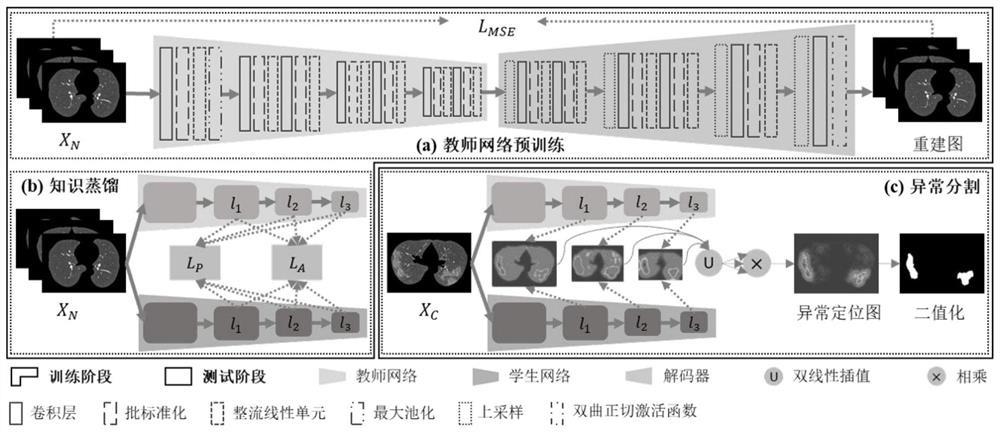
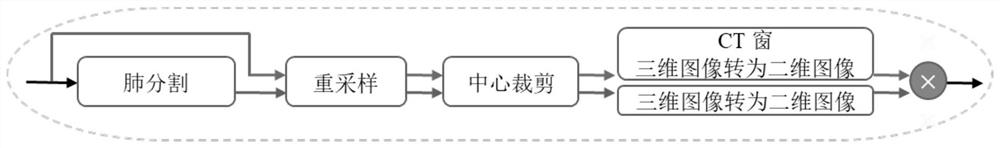
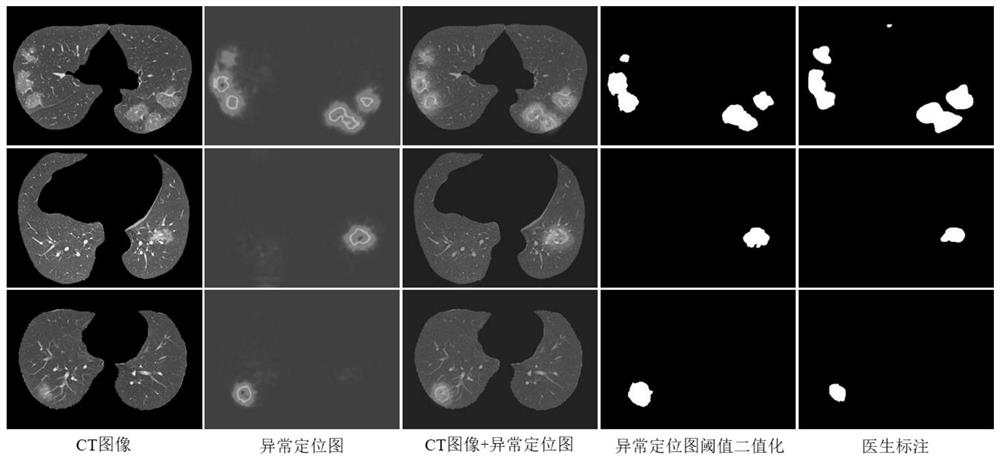
[0052] The unsupervised segmentation method of lung disease lesions based on knowledge distillation proposed by the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with examples and accompanying drawings:
[0053] The present invention designs pixel-level and affinity-level knowledge distillation to realize unsupervised segmentation of lung disease lesions, and only uses normal CT images for training to achieve more accurate lesion segmentation. The specific implementation process is as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0054] 1) Collect initial data:
[0055] 1-1) Collect the training data set. The experiment uses a private normal data set. A total of 69 normal lung CT images are collected for training, and the axial image resolution is 512×512.
[0056] 1-2) Collect test data sets. The experiment uses three new coronary pneumonia data sets for testing, all of which are lung CT images diagnosed with new coronary pneumonia. Dat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com