Cross-ice medium acoustic communication waveform design method
A waveform design and acoustic communication technology, applied in electromagnetic wave transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems affecting communication effects, communication efficiency degradation, and increasing the difficulty of detection at the receiving end, so as to increase communication concealment and improve communication Effects of distance and communication reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
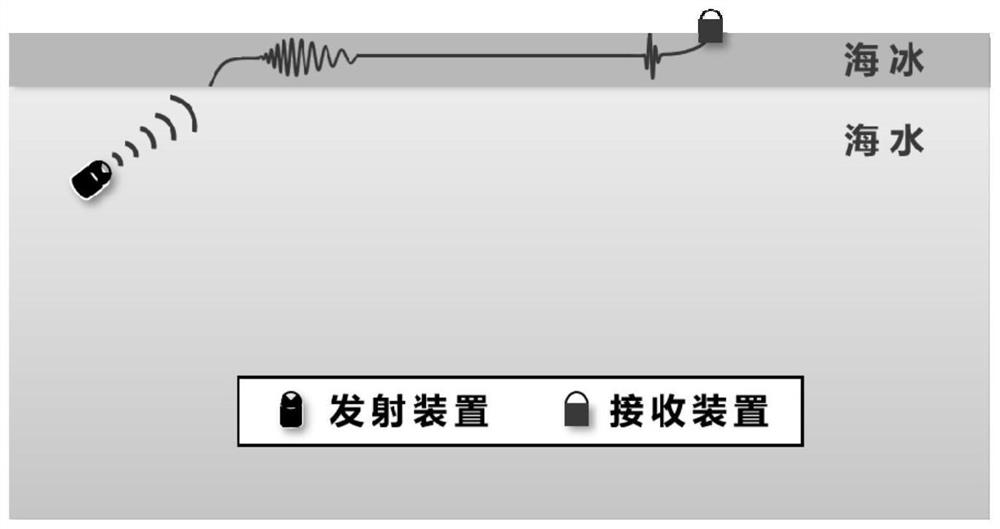
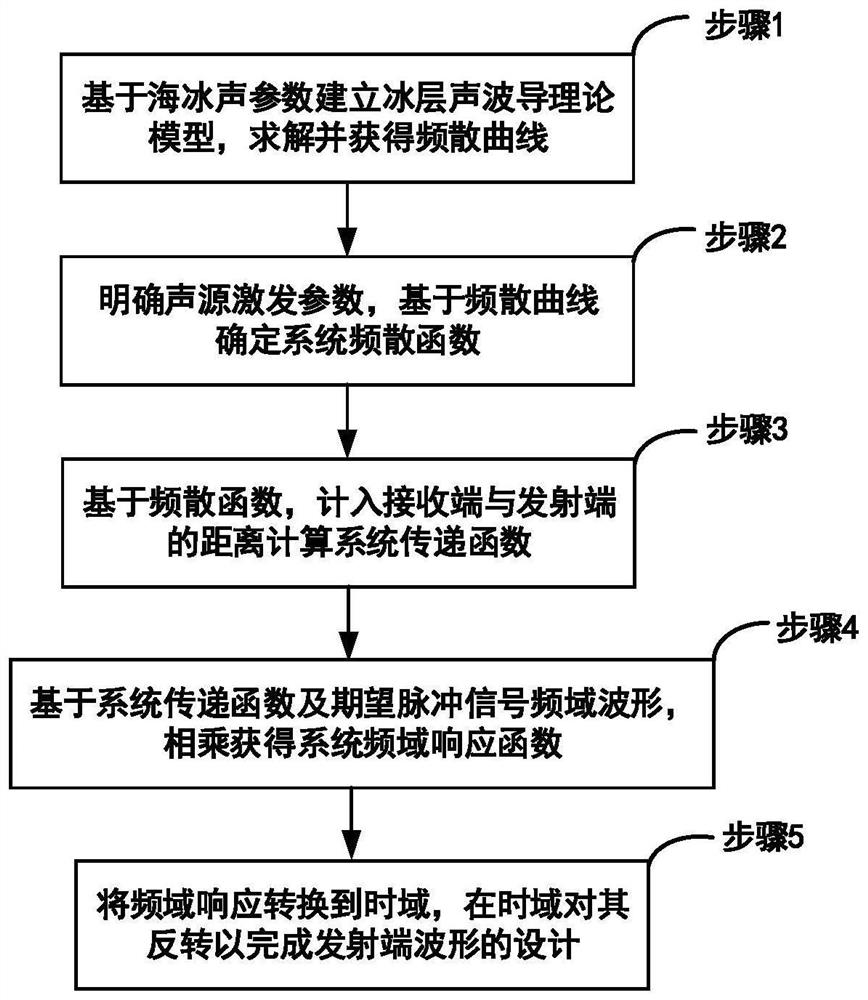
[0057] Step 1: Based on the acoustic parameters of sea ice (thickness, density, and sound velocity), the corresponding theoretical model of the ice layer acoustic waveguide is established in combination with the elastic wave theory, and the dispersion equation is solved to obtain the group velocity dispersion curve.
[0058] The waveguide dispersion curve of the ice layer is obtained by solving the dispersion equation describing the wave characteristics of the elastic guided wave of the ice layer. The dispersion equation of the ice waveguide is as follows, which is related to the sea ice acoustic parameters (thickness, density, sound velocity):
[0059]
[0060] in,
[0061]
[0062]
[0063] In the formula, ρ 1 、c l 、c t are the density of sea ice, the velocity of longitudinal wave, and the velocity of shear wave, h is the thickness of sea ice, ρ 2 , c are the density of seawater and the velocity of longitudinal waves, k is the number of traveling waves, and c p ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com