Information-epidemic disease co-evolution analysis method under action of dynamic multi-source information and behavior response
A multi-source information and collaborative evolution technology, applied in the field of information-epidemic collaborative evolution analysis, can solve the problem of ignoring the temporal characteristics of individuals in a layer, not considering the partial mapping relationship of corresponding nodes between layers, and being unable to accurately describe information-epidemic collaboration evolutionary process etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
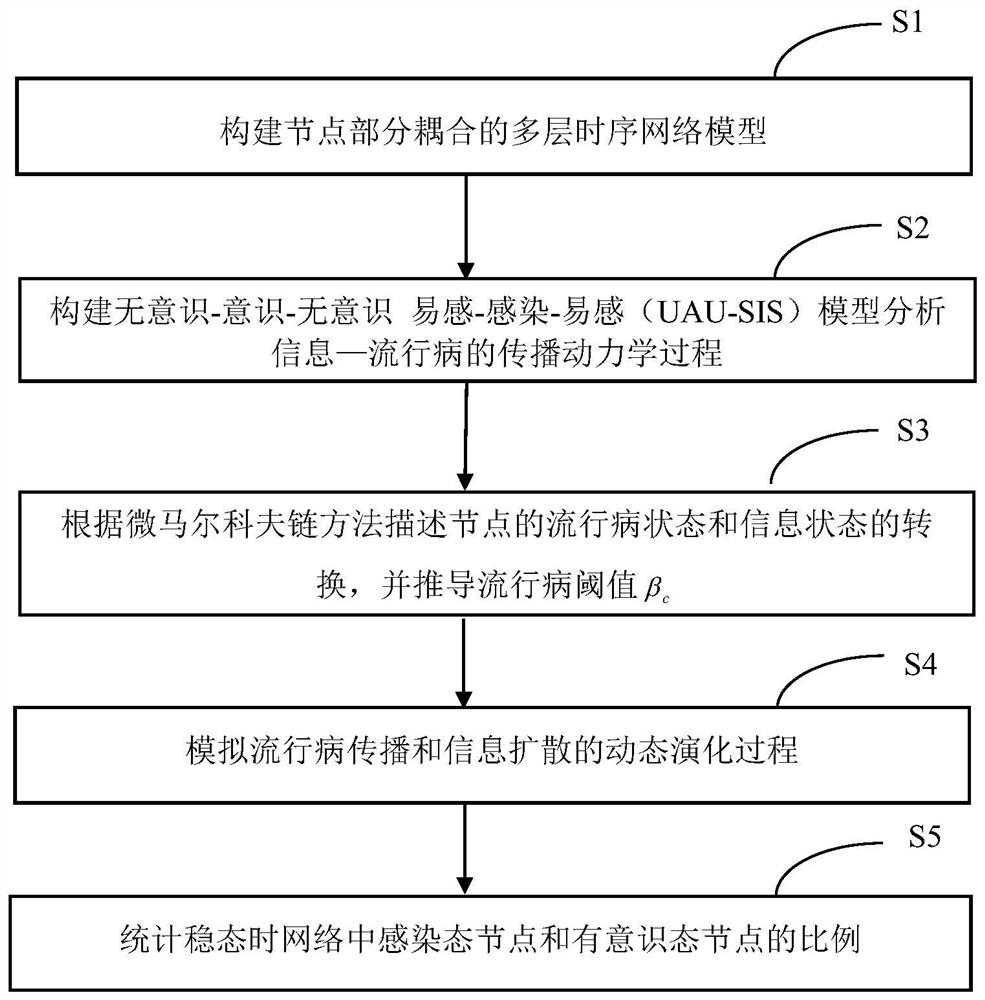
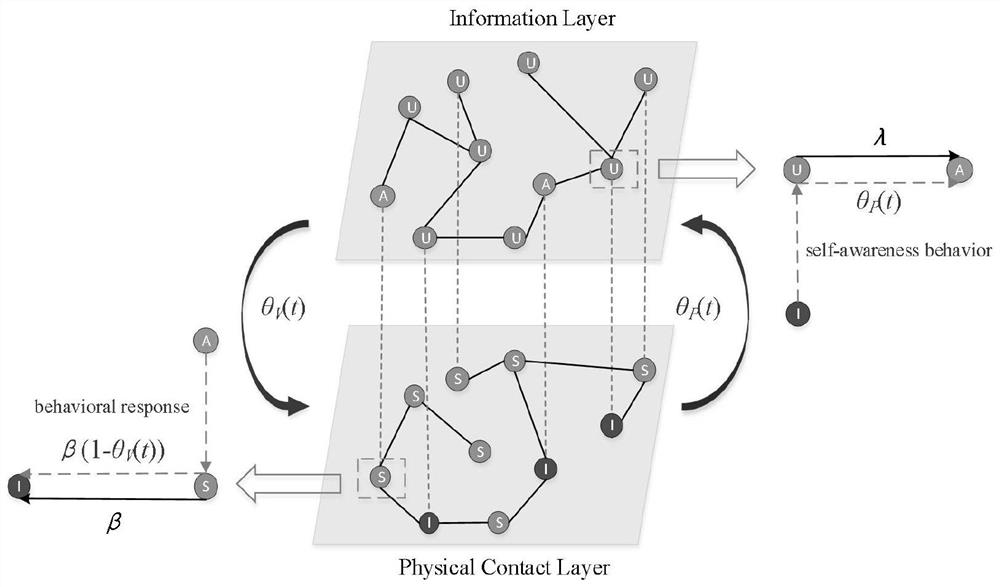
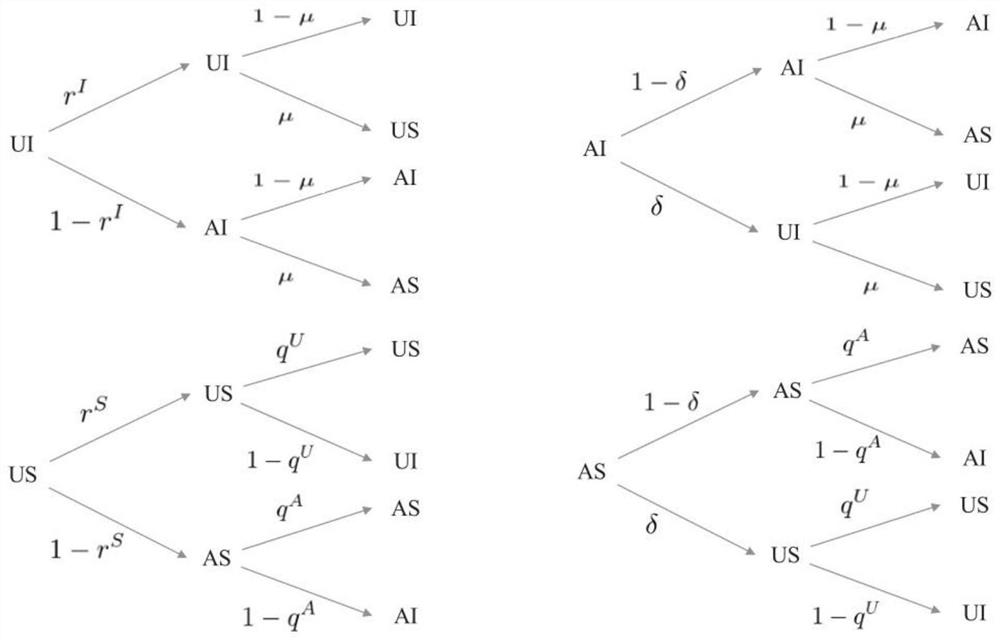
[0067] see figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 , an information-epidemic co-evolution analysis method under the action of dynamic multi-source information and behavioral response, applied to the multi-layer time series network with partial node coupling, information-epidemic co-evolution technology under the action of dynamic multi-source information and behavioral response In the field, the operation steps are as follows:
[0068] Step S1.1: Using the vector (a i ,b i ) to represent the activity of node i in the physical contact layer and the information layer, respectively obeying the exponent γ a and gamma b A power-law distribution for :
[0069] Step S1.2: Use the vector C=[c 1 ,c 2 ,...,c N ] to represent the mapping relationship between network layers, and the interlayer coupling coefficient φ( N represents the total number of nodes). For node i, if there is an inter-layer mapping relationship (c i = 1), then node i can receive multi-source information or...
Embodiment 2
[0112] This embodiment is basically the same as the above-mentioned embodiment, and the special features are as follows:
[0113] Step S1: This step is the same as the first embodiment;
[0114] Step S2: This step is the same as the first embodiment;
[0115] Step S3: This step is the same as the first embodiment;
[0116] Step S4: Simulate the dynamic evolution process of epidemic spread and information diffusion, including:
[0117] Step S4.1: Given individual self-awareness and response strengths P and V of behavioral responses;
[0118] Step S4.2: Randomly initialize a certain proportion of nodes as I-state nodes and A-state nodes;
[0119] Step S4.3: Every time Δt, the nodes in the information layer and physical layer evolve according to the rules of steps S1.3-S1.5;
[0120] Step S4.4: Carry out numerical simulation according to formula (7) to determine the average self-awareness and behavioral response of the individual as and where β max i...
Embodiment 3
[0133] This embodiment is basically the same as the above-mentioned embodiment, and the special features are as follows:
[0134] Step S1: This step is the same as the first embodiment;
[0135] Step S2: This step is the same as the first embodiment;
[0136] Step S3: This step is the same as the first embodiment;
[0137] Step S4: Simulate the dynamic evolution process of epidemic spread and information diffusion, including:
[0138] Step S4.1: Given the information dissemination rate λ and the epidemic infection rate β, set the response strength P and V of individual self-awareness and behavioral response to vary from 0 to 1;
[0139] Step S4.2: Randomly initialize a certain proportion of nodes in the physical contact layer as I-state nodes and A-state nodes;
[0140] Step S4.3: Every time Δt, the nodes in the information layer and physical layer evolve according to the rules of steps S1.3-S1.5;
[0141] Step S4.4: Calculate the ratio of I-state nodes a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com