Functional fragments for reprogramming, combinations and uses thereof
A functional and functional protein technology, applied in the field of biotechnology and gene therapy, can solve the problems of low transformation efficiency, difficult clinical application, and limit the proliferation ability of glioma cells, so as to achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] Example 1 Functional fragments of single transcription factors promote the transdifferentiation of glial cells into neurons
[0164] First, we used the in vitro model of glial cell transdifferentiation to conduct preliminary screening and obtained a batch of transcription factors that can induce glial cell transdifferentiation into neurons. The coding sequences of the transcription factors used and the transformation efficiency are shown in Table 1. Show. The transformation efficiency in Table 1 is the number of positive cells with both co-localization of neuronal positive markers and detection of spontaneous postsynaptic currents. In the study, at least 20 NeuN were tested per transcription factor on average. positive transdifferentiated cells.
[0165] Table 1 In vitro glial cell transdifferentiation efficiency of single transcription factors
[0166] transcription factor Human (wild type) Transdifferentiation efficiency mouse (wild type) Transdiff...
Embodiment 2
[0169] Example 2 Functional fragments of single transcription factors promote transdifferentiation of glial cells in the dorsal midbrain
[0170] According to the in vivo model of glial cell transdifferentiation, we tried to use the transcription factors screened in Example 1 to induce glial cells in the dorsal midbrain, as shown in the following table (Table 2). Different transcription factors showed significantly different transformation efficiencies. .
[0171] Table 2. In vivo glial cell transdifferentiation efficiency of single transcription factor (sequence shown in Example 1)
[0172]
[0173]
[0174] On the basis of the in vivo model, we further conducted a detailed study on the expression elements of the AAV expression vector, and found at least three technical improvements that can significantly increase the transformation efficiency of glial cells.
[0175] (1) Insertion of VP16 fusion protein
[0176] VP16 is the activation domain (SEQ ID NO: 45) of the VP...
Embodiment 3
[0187] Example 3 The combination of functional fragments of transcription factors further increases the efficiency of glial cell transdifferentiation
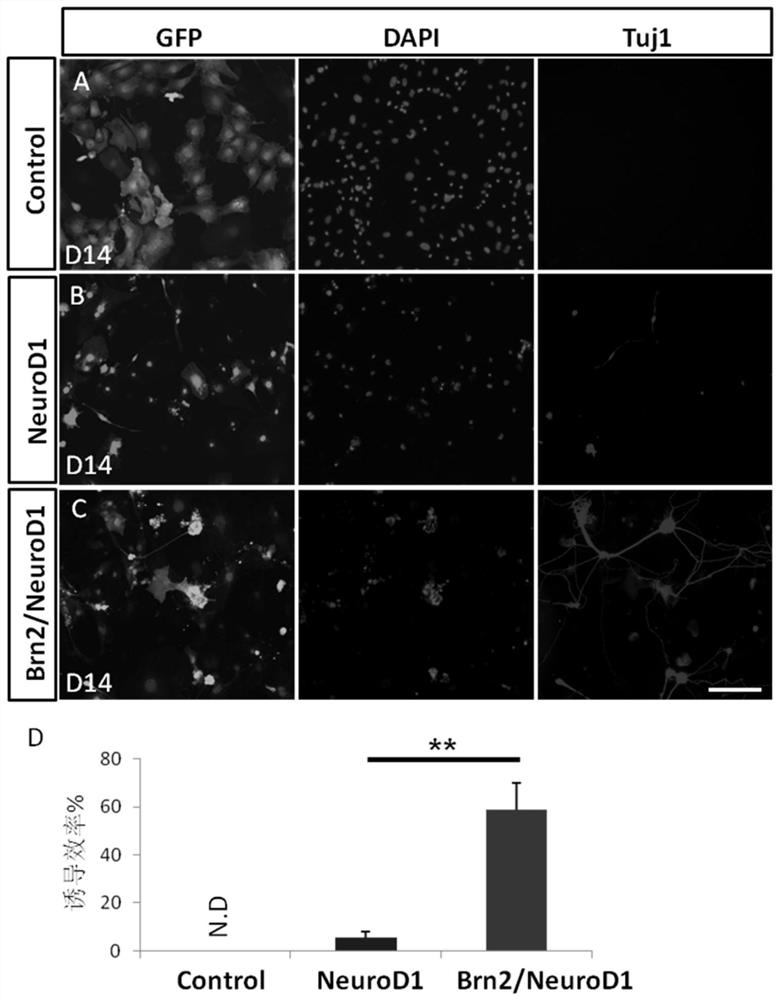
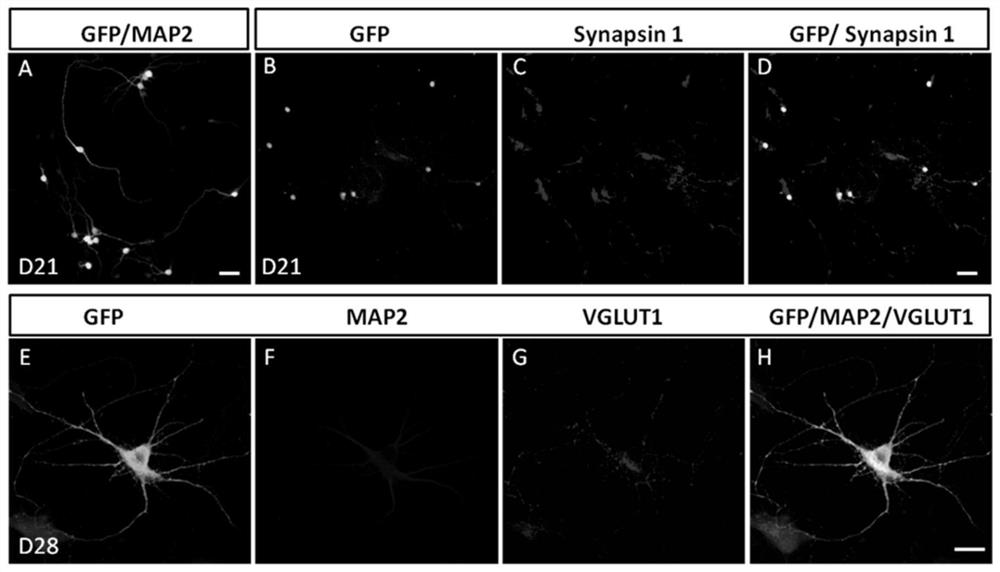
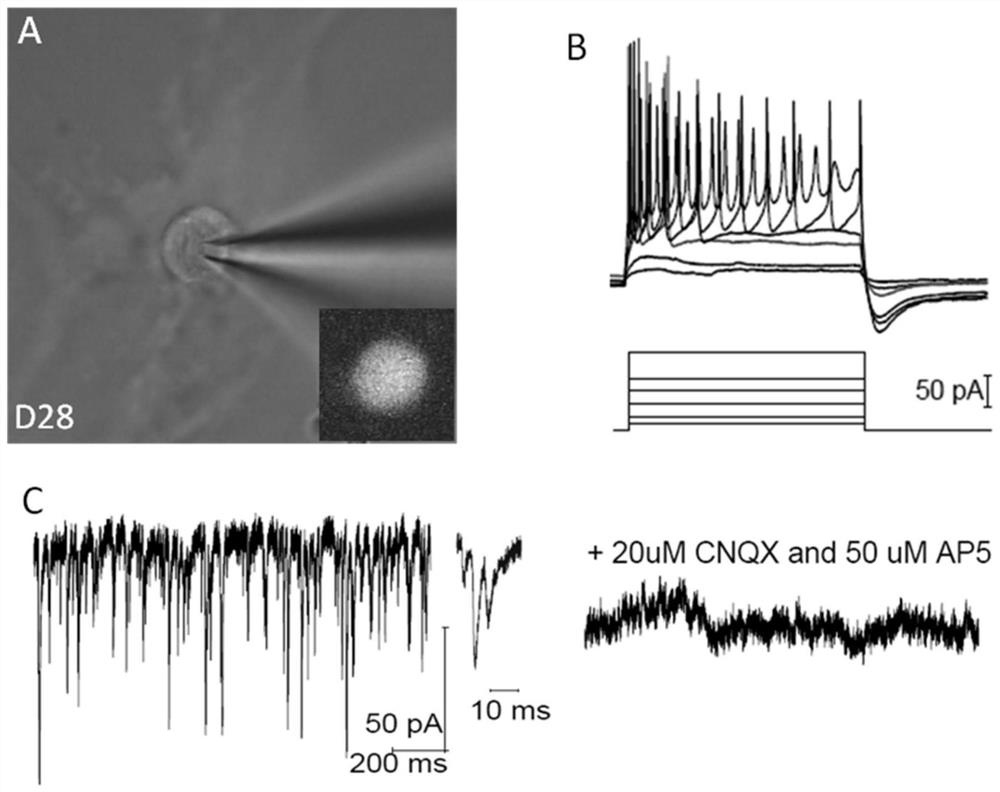
[0188] According to the transdifferentiation model of glial cells in vitro and in vivo, combined with the vector transformation strategy described in Example 2, we firstly expanded the selected transcription factors into random combinations. Wherein, different transcription factors can be expressed in the same vector at the same time, or expressed in different expression vectors respectively, and the expression ratios described in the following table are the molar concentration ratios of the functional proteins expressed in the actual study. In NeuroD1, Brn2, Gsx1, Tbr1, Dlx2, Ptf1a, Pax6, Otx2 transcription factors, we unexpectedly obtained several groups of single transcription factors with low efficiency, but the combination can significantly improve the efficiency of transcription factors, and the expression of functional pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com