Electrode applied to solid-state battery and solid-state battery
A technology of solid batteries and solid electrolytes, applied in battery electrodes, solid electrolytes, positive electrodes, etc., can solve problems such as hindering ion conduction, and achieve high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
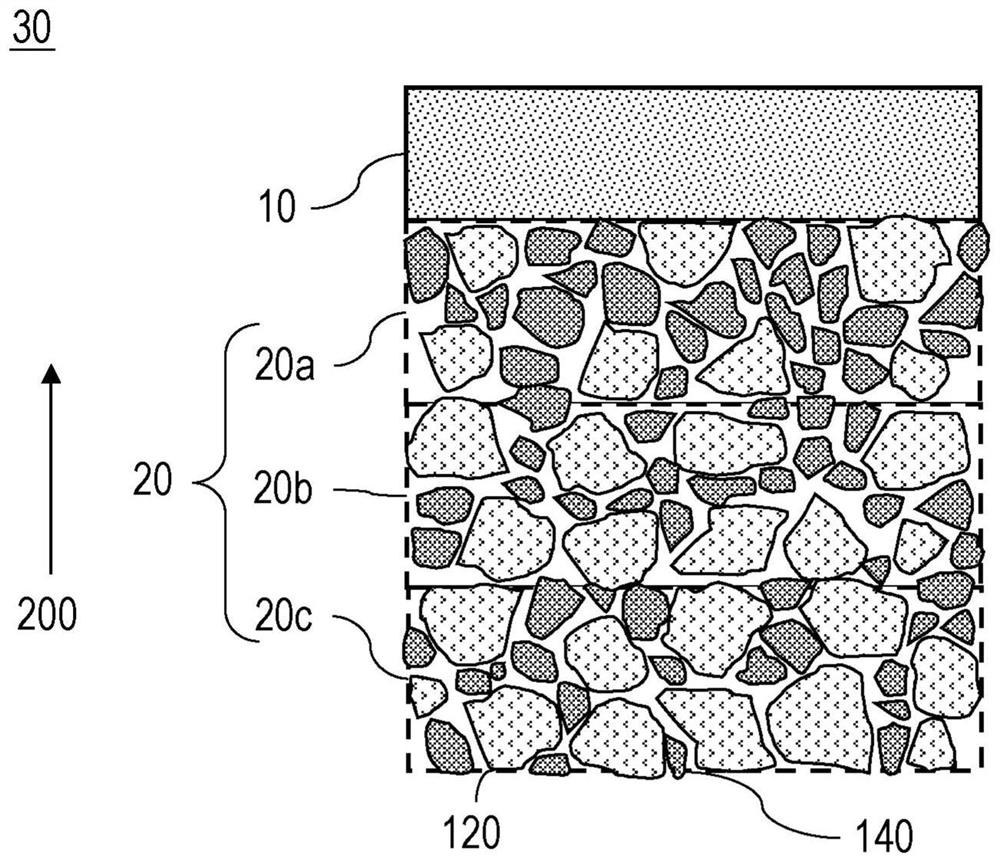
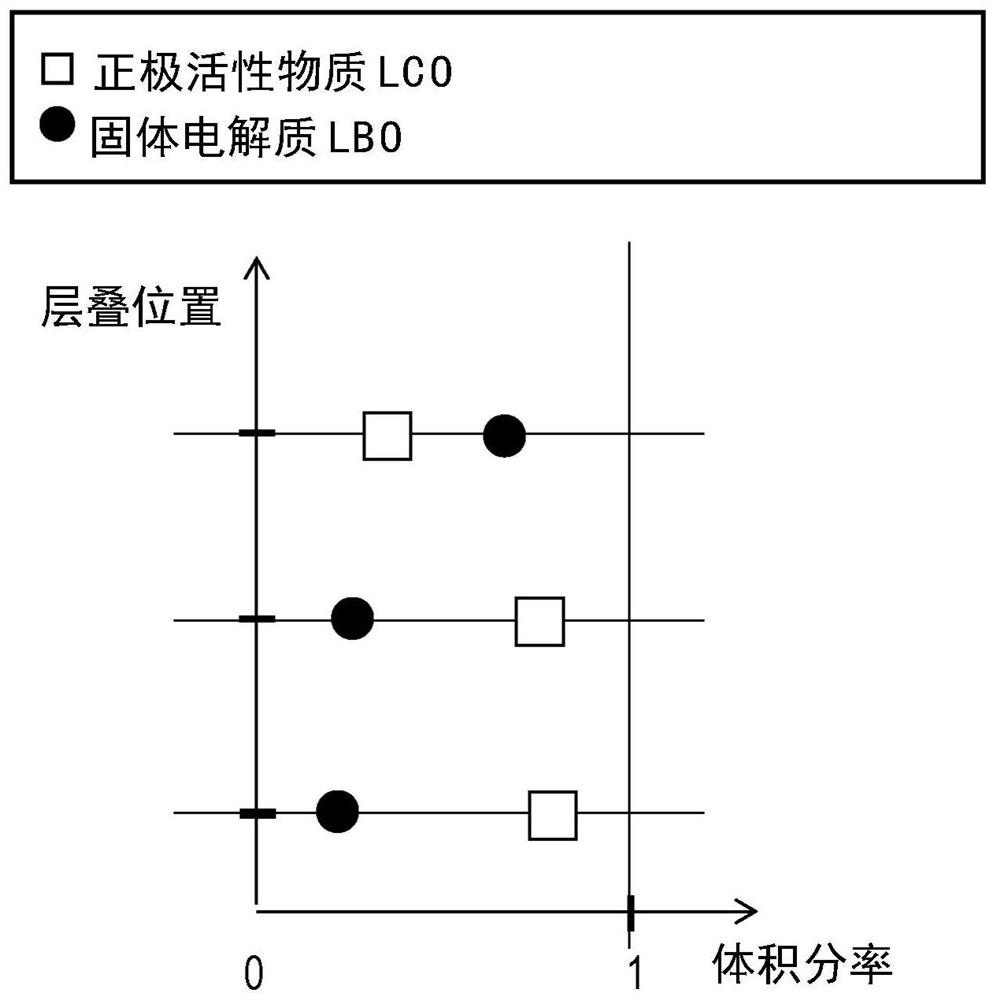
[0036] The positive electrode including the positive electrode active material layer 20 will be described as an electrode according to the first embodiment. Figure 1A is a cross-sectional structural view illustrating the positive electrode 30 according to the first embodiment of the present implementation, Figure 1B It is a graph illustrating the volume fraction distribution of components contained in the positive electrode active material layer 20 in the layer thickness direction 220 .
[0037] Such as Figure 1A As shown, the positive electrode 30 includes a current collector layer 10 and an active material layer 20 including a positive electrode active material 120 and a solid electrolyte 140 . The active material layer 20 may also be called a composite active material layer.
[0038] The current collector layer 10 is a conductor that conducts electron conduction between an unillustrated external circuit and the active material layer. For the collector layer 10 , a self-...
no. 2 example
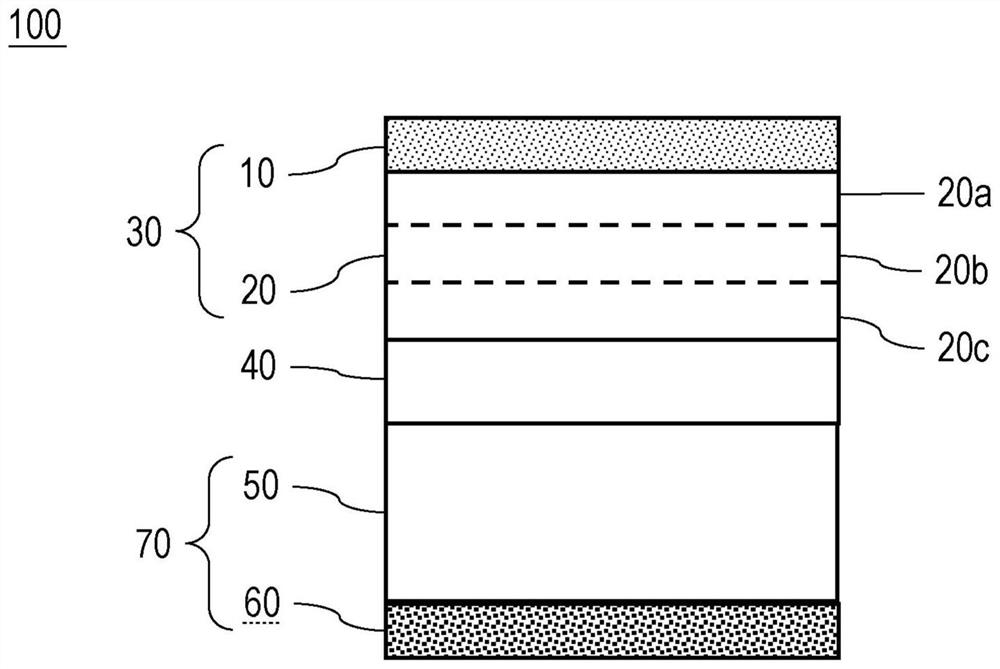
[0048] This embodiment is an embodiment in which the positive electrode 30 of the first embodiment is used to form the solid battery 100 . In other words, the positive electrode 30 according to the first embodiment is applied to the positive electrode of the solid battery 100 . The solid battery 100 includes the solid electrolyte layer 40 on the surface opposite to the collector layer 10 side of the cathode active material layer 20 . The solid battery 100 includes the negative electrode 70 on the side opposite to the side in contact with the positive electrode active material layer 20 of the solid electrolyte layer 40 . The negative electrode 70 includes the negative electrode active material layer 50 on the side opposite to the side in contact with the positive electrode active material layer 20 of the solid electrolyte layer 40 . The negative electrode 70 includes the negative electrode collector layer 60 on the side opposite to the side in contact with the solid electrolyt...
no. 3 example
[0054] The positive electrode 30 according to this embodiment is different from the positive electrode 30 according to the first embodiment. The volume fraction distribution of the positive electrode active material 120 and the solid electrolyte 140 contained in the positive electrode active material layer 20 in the stacking direction 200 is as follows: Figure 3Ashown. Except that even in the positive electrode active material layer 20a closest to the current collector layer 10, the volume fraction of the positive electrode active material 120 (LCO) is lower than that of the solid electrolyte 140 (LBO), the positive electrode according to this embodiment Active material layer 20 is the same as in positive electrode 30 according to the first embodiment. Regarding the solid battery using the positive electrode 30 according to the present embodiment, as in the first embodiment, the influence of cracks or the like due to the volume change of the positive electrode active material...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com