Freeze-thaw meat identification model and identification method based on low-field nuclear magnetic resonance data
A low-field nuclear magnetic resonance and identification model technology, which is applied to the identification model and identification field of frozen-thawed meat, can solve the problems of long identification time, high identification cost, cumbersome identification process, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the quality control of raw meat
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
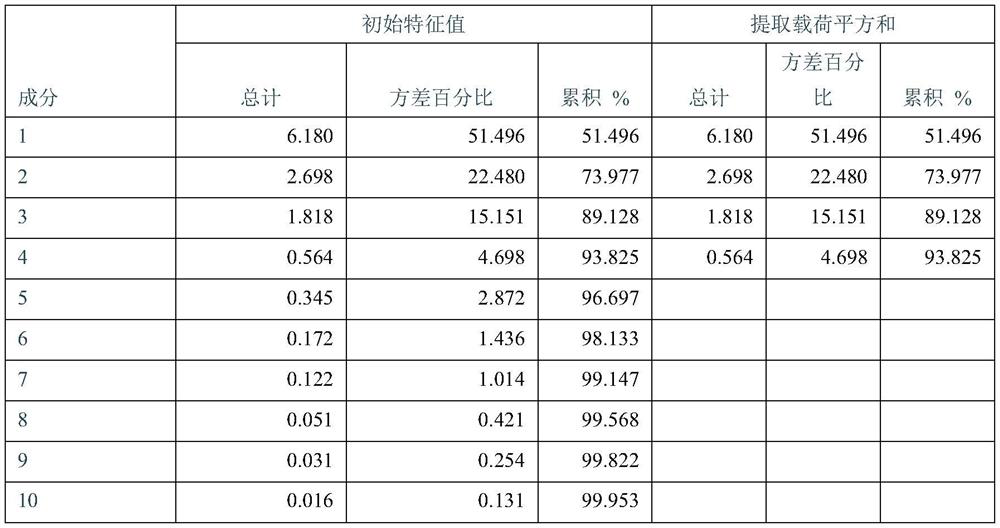
[0038] The establishment of embodiment 1 model
[0039] Tenderloins from 9 different Landrace pigs were purchased from farmers’ markets, and 2 pieces were purchased from each pig, totaling 18 pieces. Then after removing the fat and connective tissue on the surface, keep about 500g long strips for later use.
[0040] After removing the front 1cm of meat from each piece of fresh pork tenderloin, cut a 1cm thick piece of meat, take about 4g of meat from the center, and put it in a sample bottle as a control sample. Two samples of No. 1 tenderloin were taken as parallel samples for investigation. Take 1 sample for the rest.
[0041] The remaining samples were frozen in a freezer at -18°C, taken out after three days, thawed in a freezer at 4°C for one night (12 hours) and then taken out. After removing the front 1cm meat of each tenderloin, cut a piece of 1cm thick meat Take about 4 g of meat from the center, put it in a sample bottle, and repeat the above steps for a total of 6 ...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The inspection of embodiment 2 model
[0081] Two methods of back-substitution validation and cross-validation were used to test the model, and the results are shown in Table 6.
[0082] Table 6 Classification results of discriminant studies
[0083]
[0084] It can be seen from Table 6 that the above discriminant model has a correct rate of 95.5% for the original cases, especially for the control group, there is no wrong case. At the same time, the correct rate of the case-control group is still 100% in the cross-validation, and the total correct discrimination rate in the cross-validation can reach 94.6%. The data of the two verification methods are close, which also shows that the model is stable. It can be seen that the frozen-thawed meat discrimination model constructed on the basis of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance detection data disclosed by the present invention is feasible to distinguish frozen-thawed meat, and can meet the requirements of actual dete...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Embodiment 3 detection example explanation
[0086] After removing the fat and connective tissue on the surface of the sample, cut off 1cm of meat at the front, then cut a 1cm thick piece of meat, take about 4g of meat from the center, and put it in a sample bottle for testing;
[0087] First, put the samples to be tested in a water bath at 32°C (the working temperature of the instrument) for 15 minutes before putting them into the sample tube of the instrument.
[0088] Then, put the sample to be detected into a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance instrument, and adopt the CPMG sequence detection method. Instrument parameters: radio frequency delay (RFD) = 0.08ms, pre-amp position (PRG) = 1, analog gain (RG) = 20.0db, digital gain (DRG) = 3, main frequency (SF) = 21MHz, sampling frequency (SW) = 100kHz, sampling points (TD) = 1000062, waiting time (TW) = 20000ms, echo time (TE) = 0.5ms, echo number (NECH) = 10000, accumulation times (NS) = 4.
[0089] The data proce...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap