Plasticized specimen for displaying anatomical characteristics of fascia fiber construction and anatomy method
A technology of anatomy and fascia, applied in teaching models, preservation of human or animal bodies, instruments, etc., to achieve high social and economic benefits and wide application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
An anatomical method for displaying the anatomical features of fascial fibers in this embodiment includes the following steps:
1. Anatomy
After the iliotibial band around the knee joint that has been separated from the human body is fixed with formalin solution, the fascia and its related structures in the target area are dissected to obtain fascia specimens.
[0022] bleach
The fascia specimens were bleached with 5% hydrogen peroxide and observed once an hour to prevent over-bleaching. After about 24 hours, they were soaked and rinsed with small running water for 1 day.
[0023] dehydration
Expand the specimen and cut through the non-primary observation area to flatten the fascia specimen. Specimens were fixed using splint grids and dehydrated by immersion in acetone liquid at -25°C and -15°C, respectively. First dehydration, 90% acetone at -25°C, 3 days. Second dehydration, 95% acetone at -15°C, 4 days.
[0024] degreased
3 times degreasing in acetone liquid at ro...
Embodiment 2
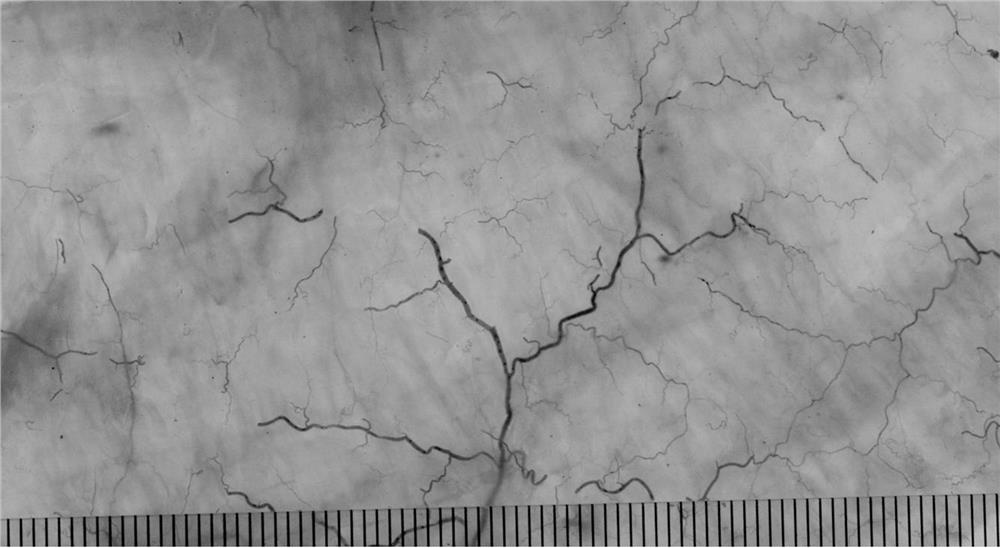
Referring to Embodiment 1, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the parts that have been separated from the human body or large animals in this embodiment are the ligaments and fascia around the knee joint.
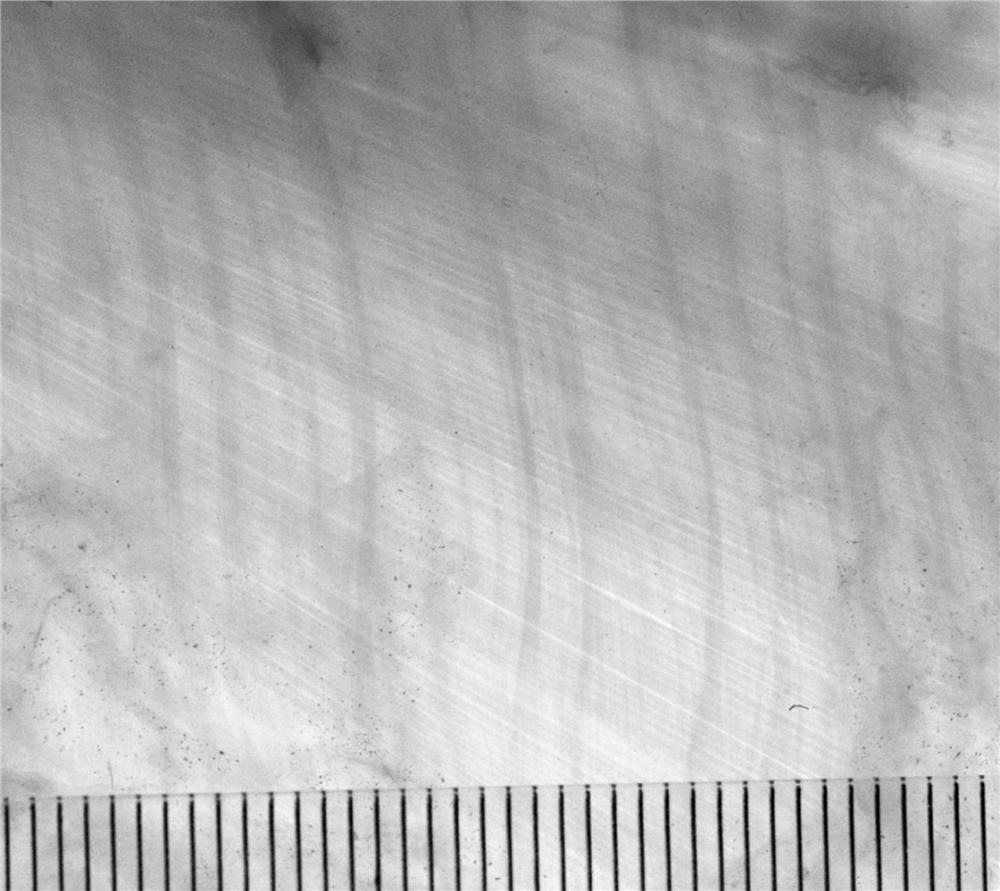
[0029] The produced plastinated specimens are shown in figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
Referring to Embodiment 1, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the part that has been separated from the human body or large animal in this embodiment is the middle layer of the thoracolumbar fascia.
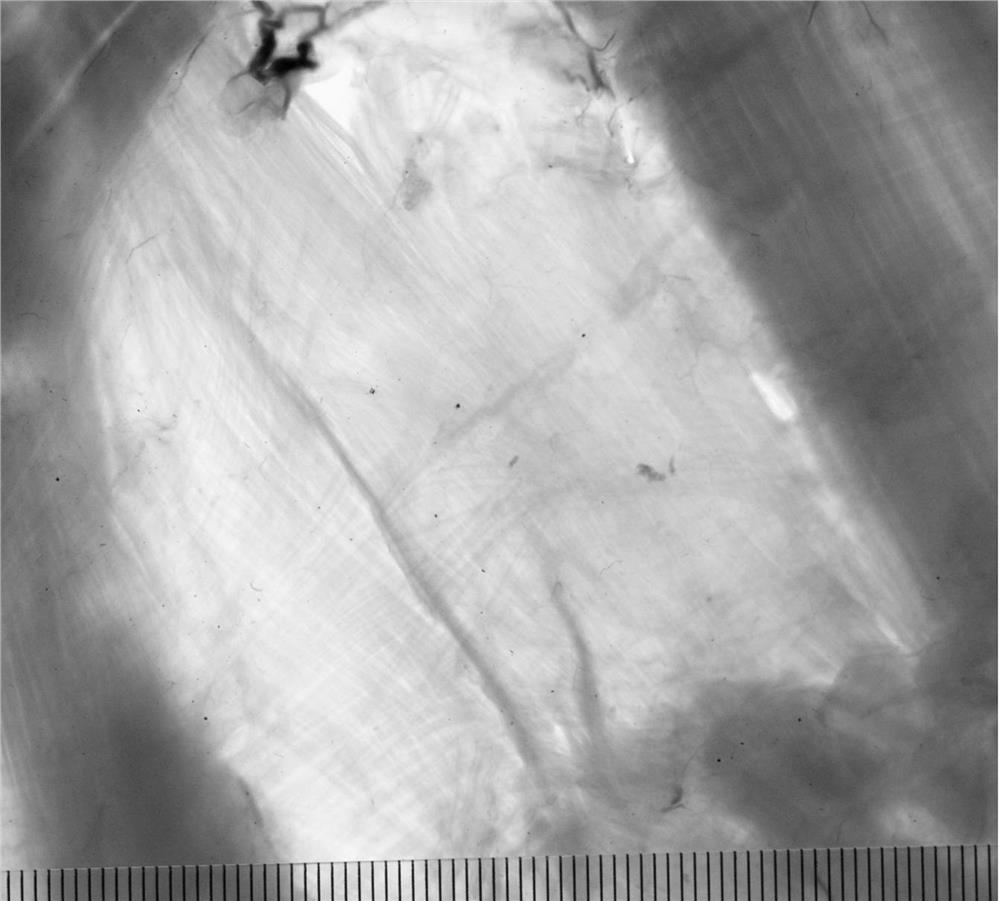
[0031] The produced plastinated specimens are shown in image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com