Methods of treating cancer
A technology for cancer and cancer cells, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, antineoplastic drugs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
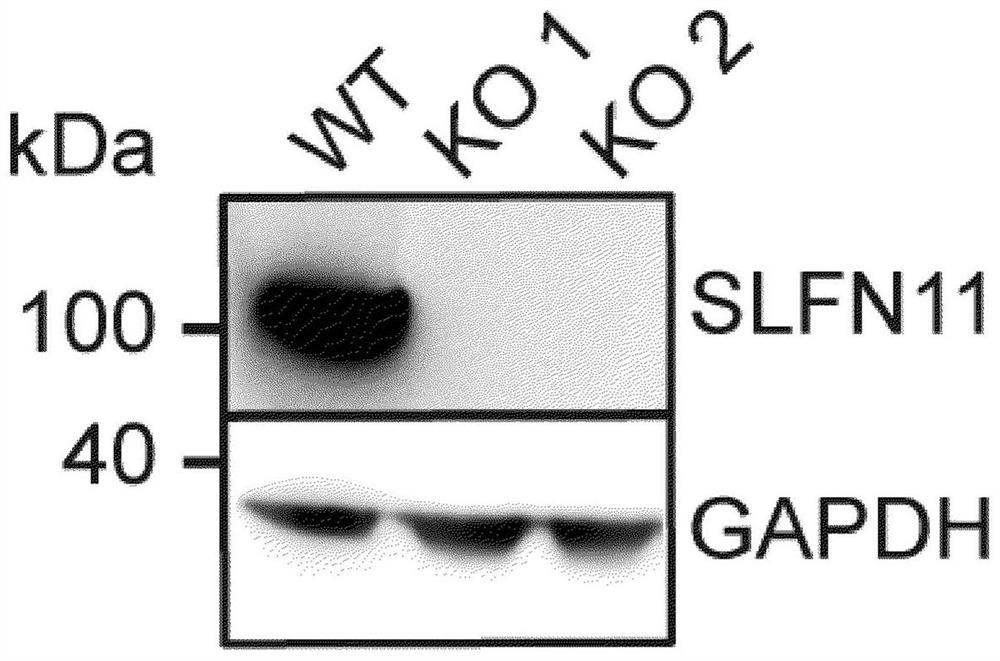
[0057] Example 1: Development of an FFPE IHC assay specific for SLFN11 and characterization of the DU145SLFN11 KO cell line.
[0058] method
[0059] Knockdown of SLFN11 in DU145 prostate cancer cells by CRISPR / Cas9. Using in-house CRISPR3 software designed to target exon 4 ( The sgRNAS of SLFN11 in the prospacer sequence adjacent motif is bold), synthesized by Integrated DNA Technology (IDT), and cloned into a vector (azPGE02-Cas9-T2A-GFP) containing Cas9 and GFP cassettes . The vector was then transfected into DU145 prostate cancer cells using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermofisher Scientific). After 48 hours, the pooled single cells with the highest green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression were sorted into 96-well plates. Clones that have lost the wild-type allele are expanded to obtain cell lines from single clones. Two SLFN11-deficient clones were delineated and selected for pharmacological studies (clone KO1 and clone KO2). Cell lysates from SLFN11-perfect (wt) and ...
example 2
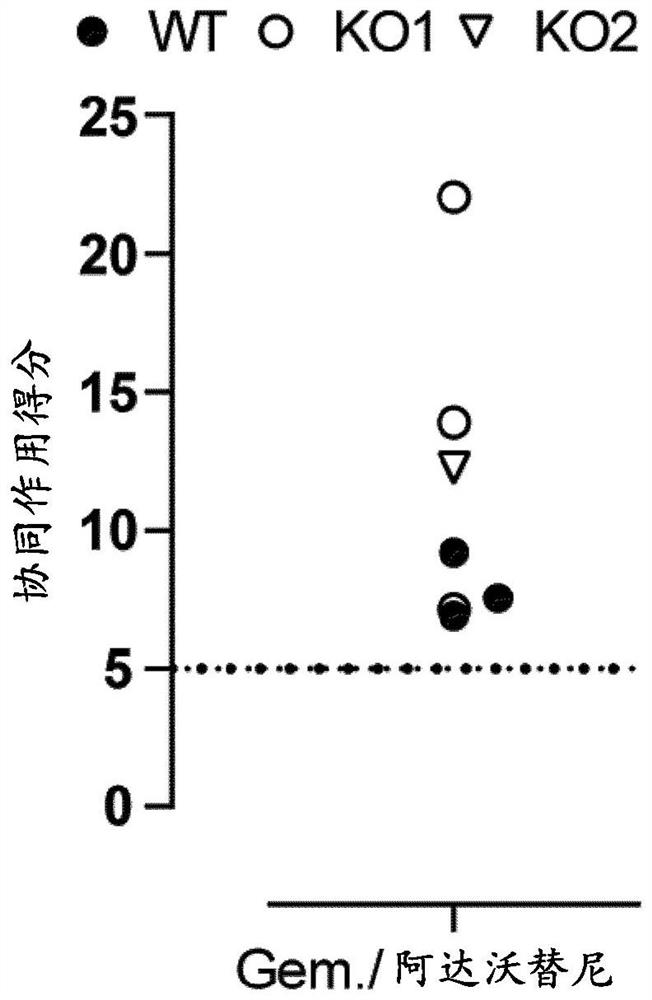
[0063] Example 2: Resistance to DDA in DU145 SLFN11 KO cells can be reversed by combination treatment with WEE1 inhibitors.
[0064] method
[0065] Adavotinib was synthesized at AstraZeneca. Gemcitabine, cisplatin, hydroxyurea (HU) and etoposide were obtained from Tocris and camptothecin from Sigma. Stock solutions of gemcitabine (50 mM), cisplatin (1.67 mM) and HU (1 M) were prepared in aqueous solution; all other drugs were dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) (10 mM) at a concentration of 10 mM.
[0066] DU145 isogenic cells (WT and SLFN11 KO) were seeded in 384-well plates and allowed to settle overnight. Figure 2A Immunoblots of SLFN11 WT and KO DU145 isogenic cells used in the experiments are shown. KO 1 and KO 2 are two different CRISPR-KO clones. Cells were dosed with compound solutions (containing the highest doses of 3 μM adavotinib, 0.1 μM gemcitabine and 1 μM etoposide) in a 6x6 concentration matrix using an Echo 555 (LabCyte Corporation). After five cons...
example 3
[0071] Example 3: Resistance to gemcitabine in SLFN11 deficient cell lines can be reversed by combination treatment with WEE1 inhibitors.
[0072] method
[0073] SLFN11 RNA-seq data (log2 RPKM values) were downloaded from Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) (Barretina J. et al., Nature, 2012;483:603-607), and drug response data (log(IC 50) and the area under the dose-response curve (AUC)) were downloaded from the cancer database drug sensitivity (Yang W et al., Nucleic Acids Res [nucleic acid research], 2013; 41: D955-61). Cell lines with CCLE RNA seq log2 RPKM values below 1 were defined as SLFN11-deficient, and cell lines with log2 RPKM values greater than 1 were defined as SLFN11-perfect. Nineteen pancreatic cell lines in 384-well plates were dosed with increasing concentrations of adavotinib and gemcitabine in a 6x6 concentration matrix using Echo 555 (LabCyte, Inc.). Doses ranged from 0-3 μM for adavotinib and 0-0.3 μM for gemcitabine; in both cases a 1 :3 dilut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com