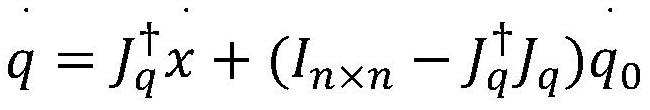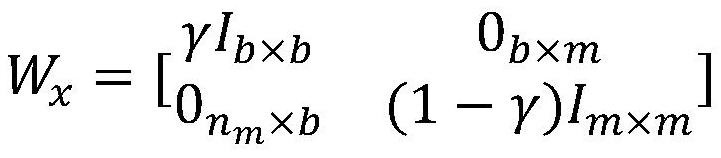Mobile operation mechanical arm tail end force application control method and system
A mobile operation and control method technology, applied in the direction of manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of no consideration of force application capacity/operability, no consideration of inherent differences, and many degrees of freedom, so as to achieve improvement. Operability, avoiding instability, and improving the effect of exerting force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
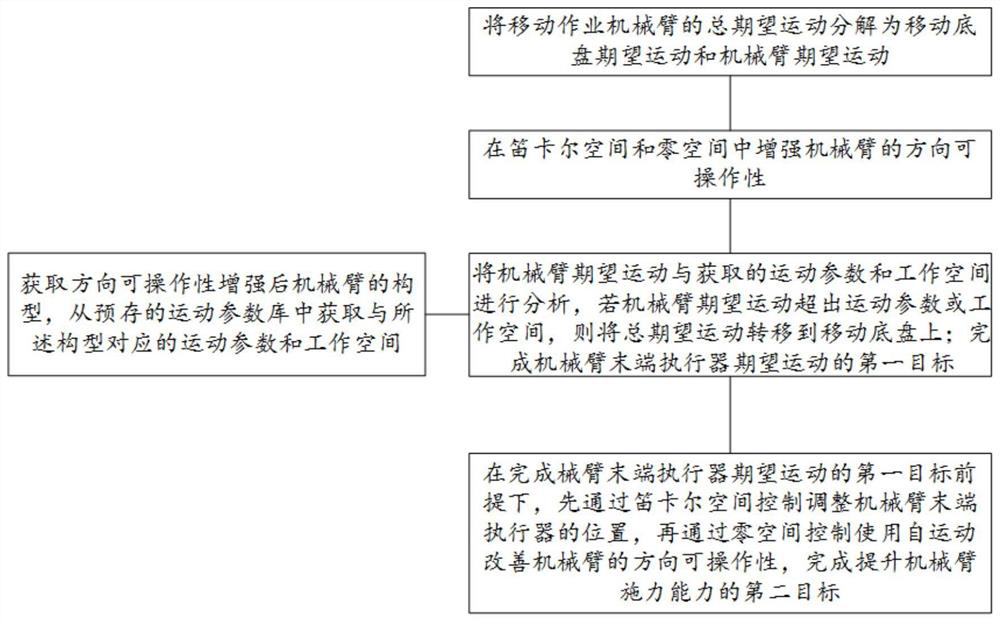
[0043] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for controlling the end force application of a mobile working manipulator, including:
[0044] S1. Decompose the total desired motion of the mobile working manipulator into the desired motion of the mobile chassis and the desired motion of the manipulator through a weighted matrix;
[0045]The total desired motion of the mobile working manipulator can be understood as the desired motion of the mobile manipulator system during the moving work, which may include desired speed and desired trajectory, etc. The mobile manipulator system may include a mobile chassis and a manipulator; this implementation For example, the total desired motion of the mobile working manipulator can be set as the desired mobile manipulator system speed, including the manipulator joint speed and the Cartesian speed of the mobile chassis.
[0046] S2. Enhance the directional maneuverability of the robotic arm in Cartesian space and nu...
Embodiment 2
[0084] This embodiment provides a force application control system for the end of a mobile working manipulator, including:
[0085] A desired decomposition module, configured to: decompose the total desired motion of the mobile working manipulator into the desired motion of the moving chassis and the desired motion of the manipulator;
[0086] The workspace determination module is configured to: obtain the configuration of the manipulator, and obtain the motion parameters and workspace corresponding to the configuration from the pre-stored motion parameter library;
[0087] The first control target control module is configured to: if the desired motion of the manipulator exceeds the motion parameters or the working space, transfer the total desired motion to the mobile chassis to complete the first control goal of controlling the desired motion of the end effector of the manipulator;
[0088]The second control target control module is configured to: under the premise of comple...
Embodiment 3
[0091] This embodiment provides an electronic device, including a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and running on the processor, the processor implements the mobile operation described in Embodiment 1 when the processor executes the program The steps in the method of controlling the force applied at the end of the manipulator.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com