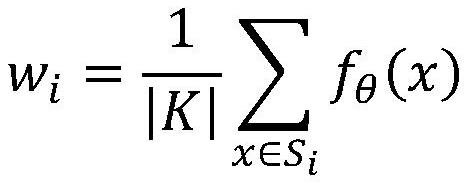Method for identifying few samples based on brain-computer interface
A brain-computer interface and recognition method technology, applied in medical science, diagnosis, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve problems such as less exploration, and achieve the effect of improving performance and generalization performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
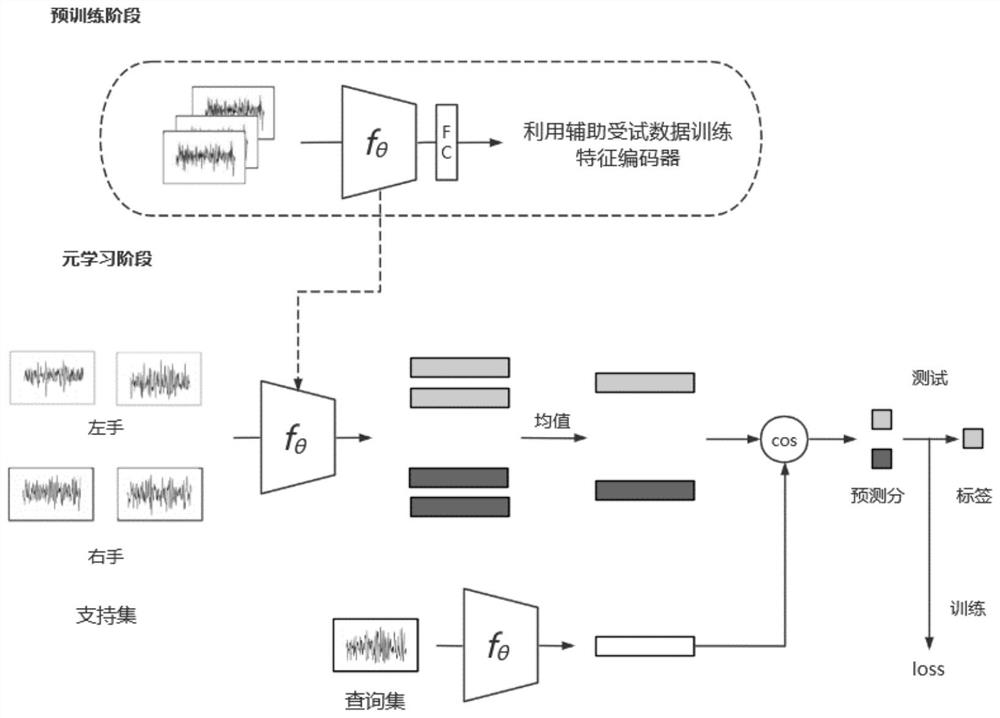
[0033] refer to figure 1 , which is an embodiment of the present invention, provides a few-sample identification method based on a brain-computer interface, including:
[0034] S1: Obtain the EEG data of 1 target subject and m auxiliary subjects performing N-type motor imagery tasks.
[0035] It should be noted that each class of target subjects only has K labeled samples, where, usually K≤5, the auxiliary subjects have a relatively large amount of labeled data under each type of task;
[0036] The objective of the present invention is to use the data from the auxiliary subjects to build a model with better performance for the target subjects, and the overall process includes two stages of pre-training and meta-learning.
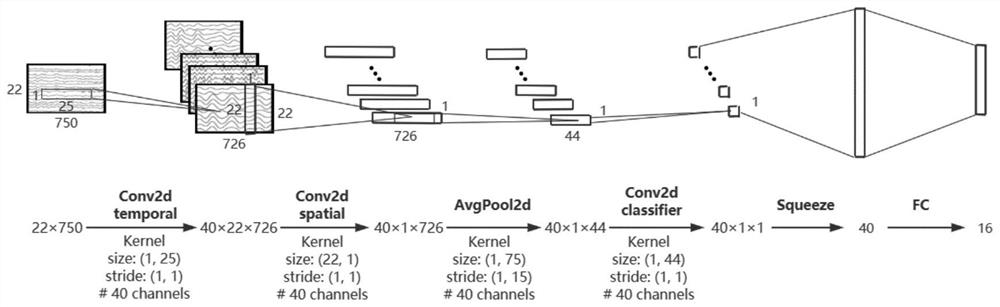
[0037] S2: In the pre-training stage, the auxiliary subject data is used to learn the feature encoder fθ of EEG, and it is used as the initial model parameter in the subsequent meta-learning stage.
[0038] It should be noted that this step specifically incl...
Embodiment 2
[0056] like figure 1 ~ is another embodiment of the present invention, which is different from the first embodiment in that it provides a verification test based on a few-sample identification method in a brain-computer interface, which is a test of the technology used in this method. The effect is verified and explained, the present embodiment adopts the traditional technical scheme and the method of the present invention to carry out a comparative test, and compares the test results by means of scientific demonstration to verify the real effect of the method, specifically:
[0057] (1) Obtain the EEG data of 1 target subject and 8 auxiliary subjects performing two types of motor imagery tasks (left-hand motor imagery and right-hand motor imagery, respectively), where each type of target subject has K (K is 1 or 5) Annotated samples, auxiliary subjects have a relatively large amount of labeled data under each type of task. This embodiment is described in detail with an EEG d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com