Hypoxic microsphere with ultraviolet shielding shell structure and preparation method of hypoxic microsphere
A technology of shell structure and external shielding is applied in the field of hypoxic microspheres with ultraviolet shielding shell structure and its preparation, which can solve the problems of not reaching photo-oxidation reaction, unsolving dissolved oxygen, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
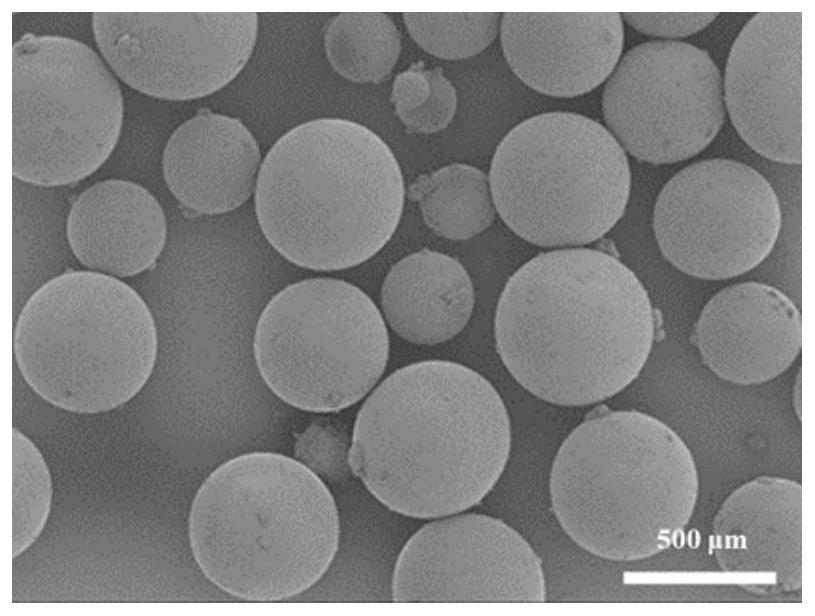
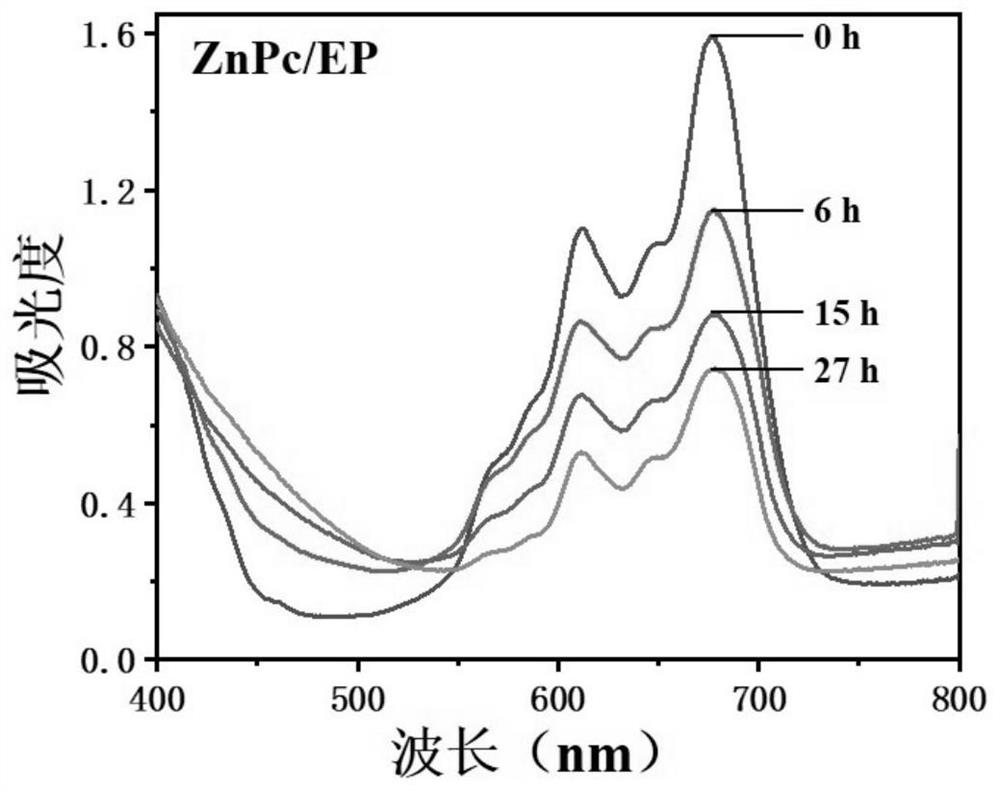
[0028]1. The organic dye selected is commercially available ZnPc, accurately weigh 0.15g ZnPc and dissolve it in 10g MXDA, then add 0.15g hydrotalcite, 0.15g nano-magnesium silicide with a size distribution of 20-50nm and 0.15g TEMP, and ultrasonically disperse evenly for backup. use. Add 5g of emulsifier OP-10 to 100ml of deionized water, stir evenly at 80°C, add 5g of epoxy resin monomer DGEBA, emulsify in a homogenizer for 10min to form an oil-in-water emulsion, and keep stirring in a water bath at 80°C. 1.0 g of the ZnPc-containing curing agent MXDA prepared above was added to the emulsification system, and cured at 80°C for 3 hours to obtain epoxy resin microspheres ZnPc / EP containing ZnPc dyes. The prepared ZnPc / Ep microspheres had an average particle size of 350 μm.
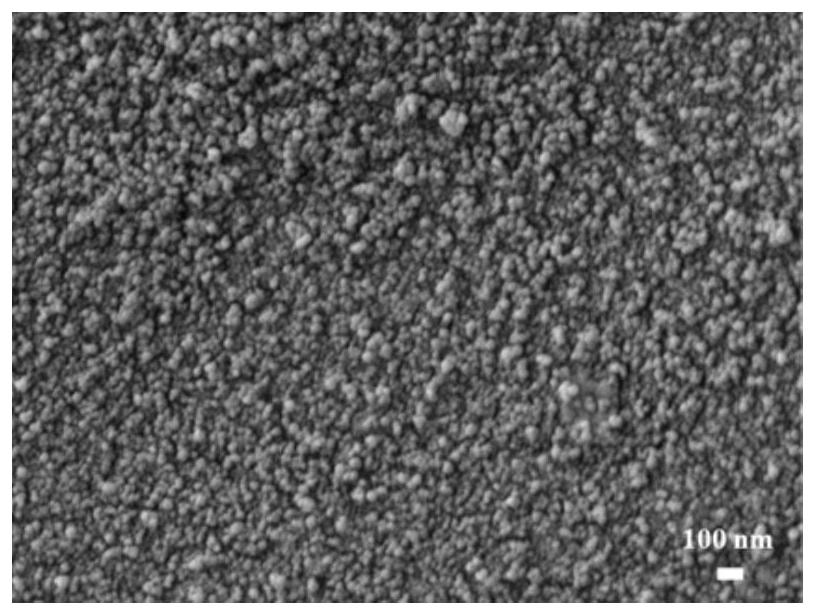
[0029] 2. Add the prepared ZnPc / EP microspheres into the round-bottomed flask, then add 3 ml of deionized water, 3.6 ml of ammonia water, and 60 ml of ethanol, and keep the water bath at 60°C. Dissolve 1...
Embodiment 2
[0031] 1. The organic dye selected is commercially available ZnPc, accurately weigh 0.05g ZnPc and dissolve it in 10g MXDA, then add 0.15g montmorillonite, 0.15g nano-magnesium silicide with a size of 20-50nm and 0.15g DPBF, and ultrasonically disperse evenly for backup. use. Add 4g of emulsifier OP-10 to 100ml of deionized water, stir evenly at 85°C, add 3g of epoxy resin monomer DGEBA, emulsify in a homogenizer for 10min to form an oil-in-water emulsion, and keep stirring in a water bath at 85°C. 0.6 g of the ZnPc-containing curing agent MXDA prepared above was added to the emulsification system, and cured at 85 °C for 2 h to obtain epoxy resin microspheres ZnPc / EP containing ZnPc dye.
[0032] 2. Add the prepared ZnPc / EP microspheres into the round-bottomed flask, then add 3 ml of deionized water, 3.6 ml of ammonia water, and 60 ml of ethanol, and keep the water bath at 60°C. Dissolve 0.5g TEOS in 20ml absolute ethanol, then add 45mg TiO 2 , ultrasonically dispersed unifo...
Embodiment 3
[0036] 1. The organic dye selected is commercially available ZnPc. Accurately weigh 0.24g of ZnPc and dissolve it in 10g of DETA, then add 0.2g of hydrotalcite and 0.2g of nano-magnesium silicide with a size of 20-50nm, and ultrasonically disperse it uniformly for later use. Add 7g of emulsifier OP-10 to 100ml of deionized water, stir evenly at 70°C, add 8g of epoxy resin monomer DGEBA, emulsify in a homogenizer for 10min to form an oil-in-water emulsion, and keep stirring in a water bath at 70°C. 1.6 g of the ZnPc-containing curing agent DETA prepared above was added to the emulsification system, and cured at 70°C for 5 hours to obtain epoxy resin microspheres ZnPc / EP containing ZnPc dyes. The prepared ZnPc / Ep microspheres had an average particle size of 415 μm.
[0037] 2. Add the prepared ZnPc / EP microspheres into the round-bottomed flask, then add 3 ml of deionized water, 3.6 ml of ammonia water, and 60 ml of ethanol, and keep the water bath at 60°C. 2g of TEOS was dissol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com