Anti-reflection coatings and coated articles
An anti-reflection and product technology, which is applied in the direction of coating, layered products, metal material coating technology, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the amount of reflected light
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0052] According to the invention, the perceived reflectance F is found from all combinations of coating thicknesses, and the set of thicknesses that minimizes F is chosen. Starting with the glass:PrO:TiO:MgF system described above, this calculation was done and calculated a minimum perceived reflectance of 104 which is 18% of the uncoated product and a drop of 35% from the textbook coating. %. The absolute minima of perceived reflectance for these materials (shown in Figure 6) correspond to the following physical thicknesses: 100 nm of PrO, 25 nm of TiO and 87 nm of MgF.
example 2-19
[0055] The thickness combinations listed in Table I do not exclude other combinations with F-values within 25% (or other desired lower percentage) of the minimum value of 104. However, after examining the 16000+ permutations, it is found that only examples 1-13 meet this judgment condition.
[0056] Those of ordinary skill in the art know that using linear algebra and calculus can solve Equation 7 (F, F min , 1.25F min , or any other desired value and range of F). For an alternative to performing manual calculations, linear algebra software can be used. Non-limiting examples of such software include Mathematic (Wolfram Research, Champaign-Urbana, IL), Matlab (TheMathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA), Macsyma (Macsyma Inc., Arlington, MA), and MaPle (Waterloo MaPle, Inc. ., Waterloo, Ontario, Canada). Calculation and analysis of F can also be performed using electronic data software such as Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA) and Lotus 1-2-3 (Lotus Development Corp., Cambridge MA)...
example 20-30
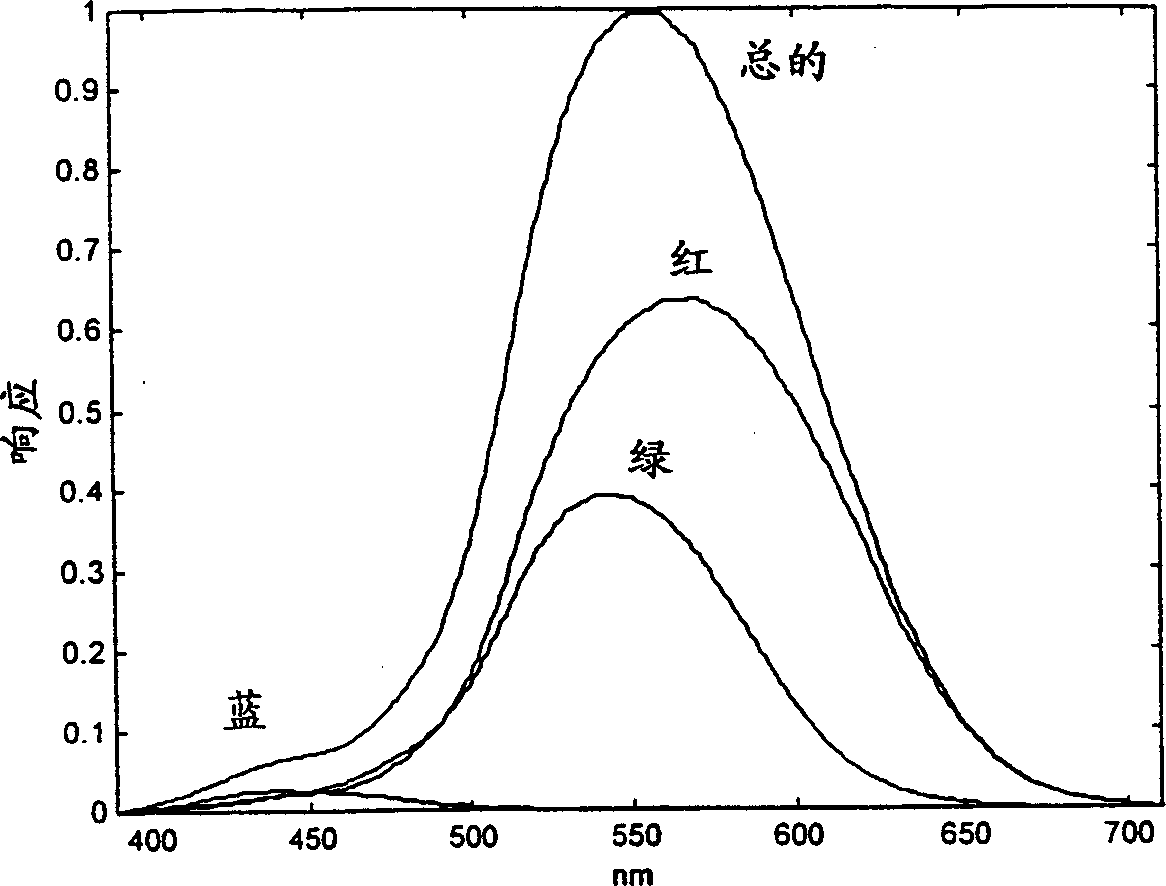
[0067] A second embodiment of the AR coated article of the present invention is a computer monitor or video screen having a glass surface. Anti-reflection coatings are required for these articles because overhead or window illumination produces reflected images that impair the visibility of the image projected onto the display screen. The photopic response S(λ) of the observer is as follows figure 1 shown. However, the angular components of S(λ, θ) are substantially different from those of glasses. Assuming top lighting in a specific working environment and using a simple geometry, the sample S(λ, θ) is as Figure 12 shown. The perceived reflectance of the uncoated screen was 717, while noting that the textbook PrO:TiO:MgF coating was 258, or 36% of the uncoated display. Using the method described above, it was found that F was reduced to 191 with minimum values (26.6% of the uncoated display) at layer thicknesses of 60 nm of PrO, 80 nm of TiO and 120 nm of MgF. Indicat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com