Semiconductor momory
A storage device and semiconductor technology, applied in the fields of semiconductor devices, information storage, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of not finding a solution to shorten the length of the bit line wiring, shrinking the 2-port SRAM cell, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
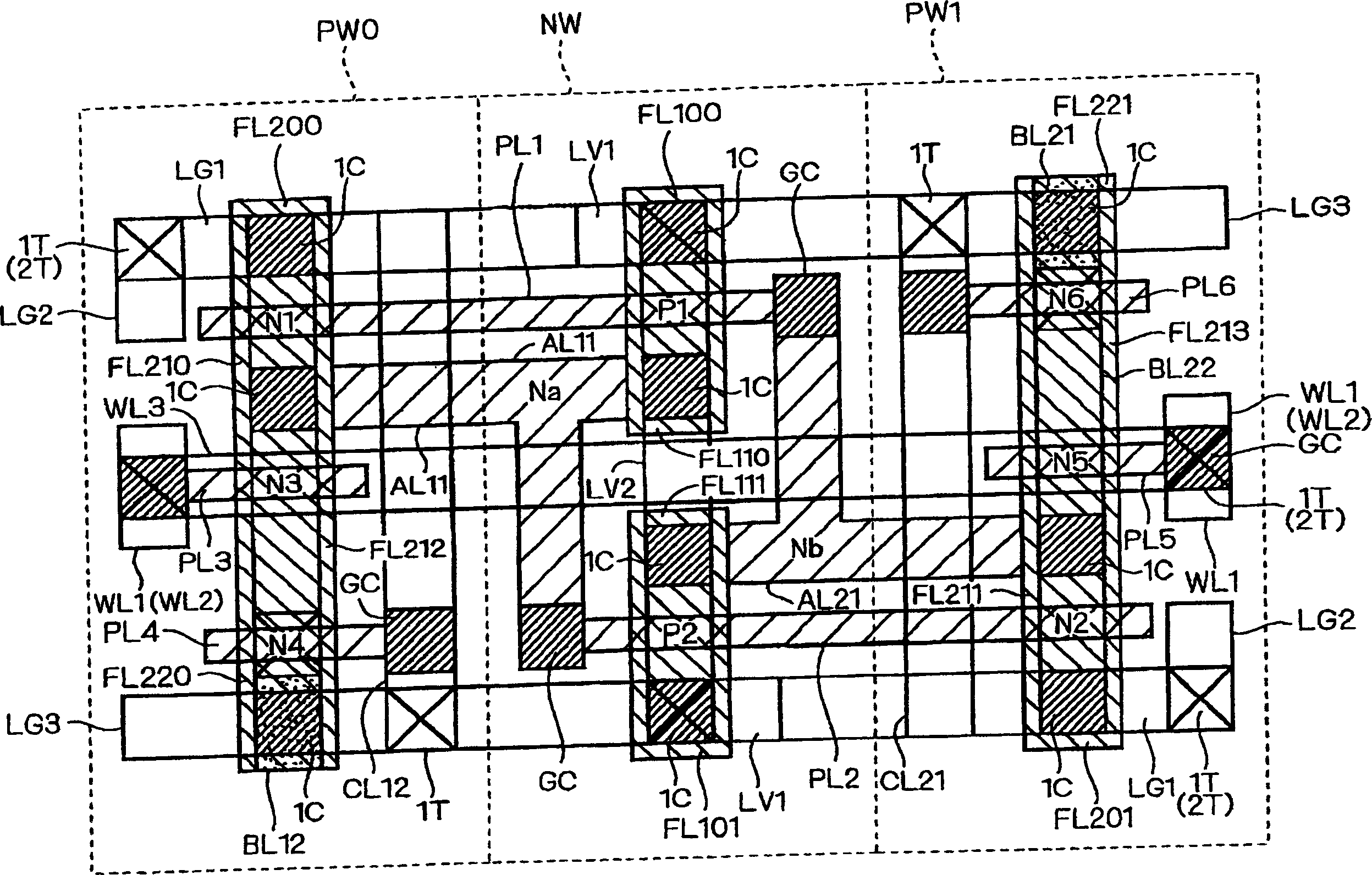
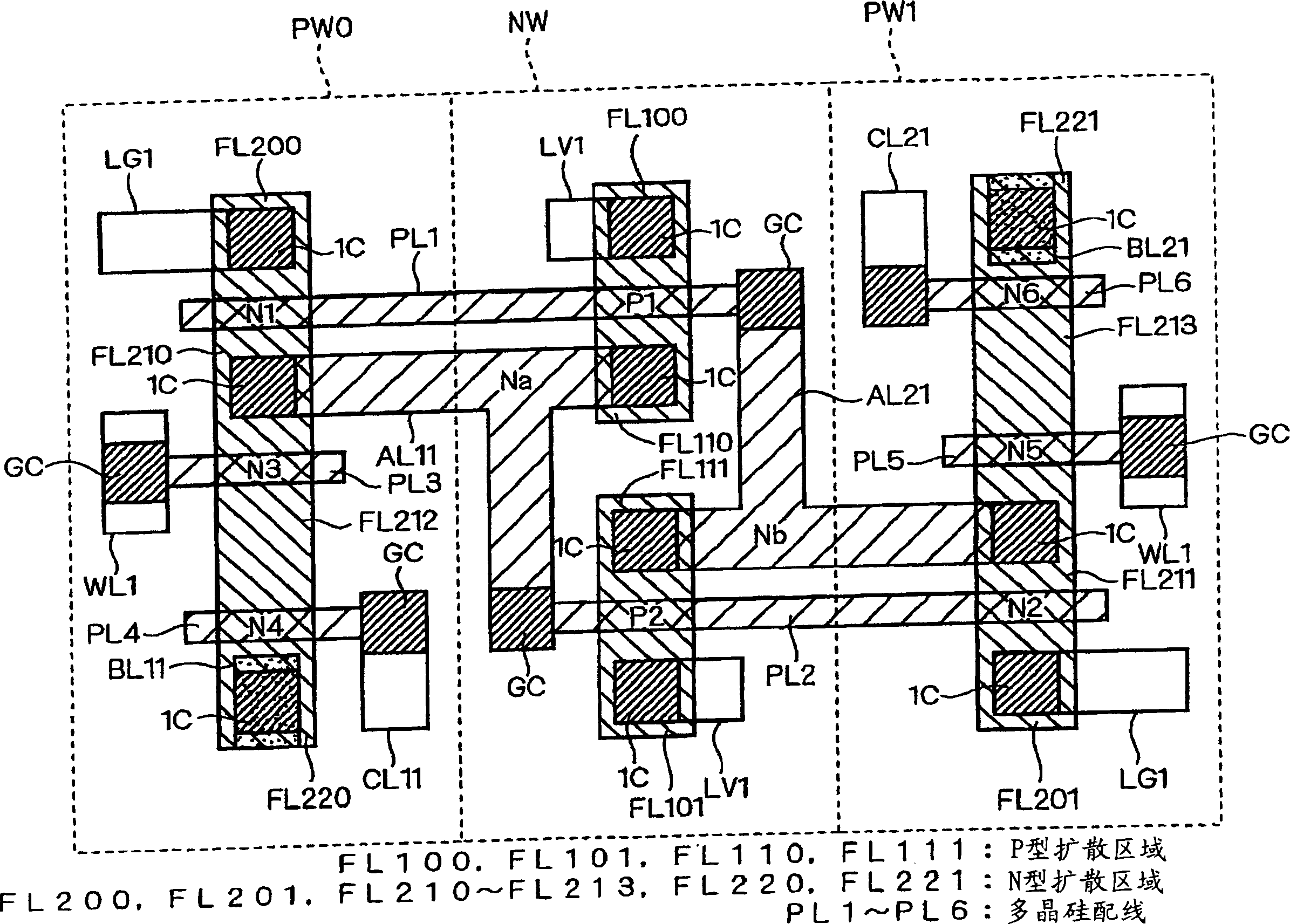
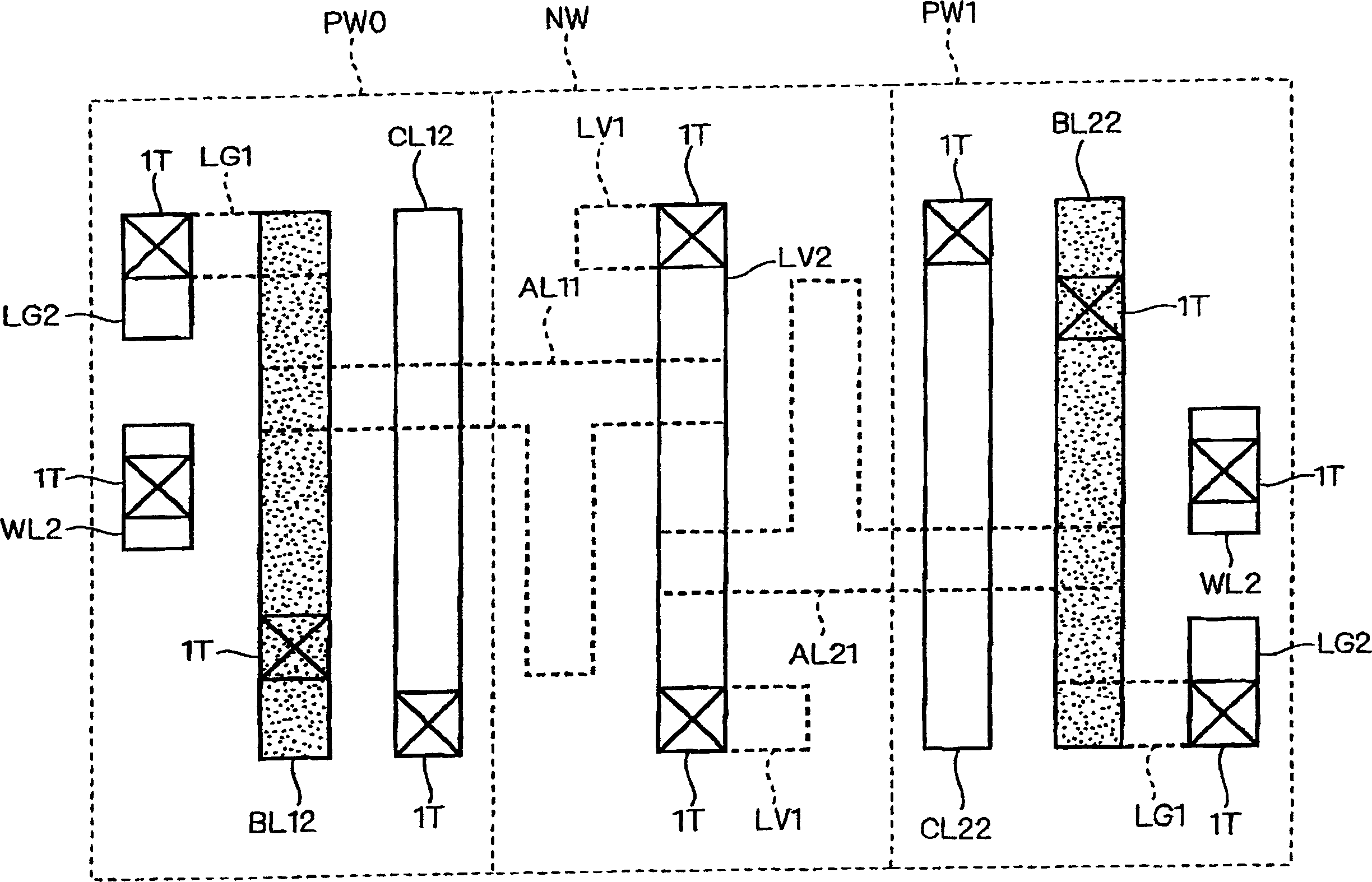
[0060] figure 1 It is an explanatory diagram showing the design structure on the entire layer of the memory cell of the SRAM according to the first embodiment of the present invention. figure 2 is the main expression figure 1 An explanatory diagram of the design structure under the 1st aluminum wiring layer. image 3 is the main expression figure 1 An explanatory diagram of the design structure of the second aluminum wiring layer. Figure 4 is the main expression figure 1 An explanatory diagram of the design structure of the third aluminum wiring layer. which is, Figure 2 ~ Figure 4 is for easy understanding figure 1 The design scheme structure shown is divided into each wiring layer shown in the figure 1 Supplementary Fig. Figure 5 yes means Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 A circuit diagram of an equivalent circuit of the memory cell of Embodiment 1 shown. exist figure 1 in, sometimes omitted Figure 2 ~ Figure 4 Part of the symbol shown.
[0061] Such as Figure...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Figure 6 It is an explanatory diagram showing the design structure on the entire layer of the memory cell of the SRAM according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Figure 7 is the main expression Figure 6 An explanatory diagram of the design structure under the 1st aluminum wiring layer. Figure 8 is the main expression Figure 6 An explanatory diagram of the design structure of the second aluminum wiring layer. which is, Figure 7 and Figure 8 for easy understanding Figure 6 The design scheme structure shown is divided into each wiring layer shown in the Figure 6 Supplementary Fig. exist Figure 6 in, sometimes omitted Figure 7 and Figure 8 Part of the symbol shown. in addition, Figure 6 ~ Figure 8 The equivalent circuit diagram of the memory cell shown in Embodiment 2 and Figure 5 Example 1 shown is the same.
[0100] Next, differences from Embodiment 1 will be described. Such as Figure 6 ~ Figure 8 As shown, the NMOS transist...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Figure 9 It is an explanatory diagram showing the design structure on the entire layer of the memory cell of the SRAM according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Figure 10 is the main expression Figure 9 An explanatory diagram of the design structure under the 1st aluminum wiring layer. Figure 11 is the main expression Figure 9 An explanatory diagram of the design structure of the second aluminum wiring layer. which is, Figure 10 return Figure 11 is for easy understanding Figure 9 The design scheme structure shown is divided into each wiring layer shown in the Figure 9 Supplementary Fig. exist Figure 9 in, sometimes omitted Figure 10 and Figure 11 Part of the symbol shown. in addition, Figure 9 ~ Figure 11 The equivalent circuit diagram of the memory cell shown in Embodiment 3 and Figure 5 Example 1 shown is the same.
[0106] Next, differences from Embodiment 2 will be described. N-type diffusion region FL210 is electrically...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com