Motor driving device and method thereof
A motor-driven, motor technology, applied in the direction of the stopped device, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate stop position of the motor, difficult reversal detection, long time required, etc., to achieve the effect of noise, smooth switching, and noise reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
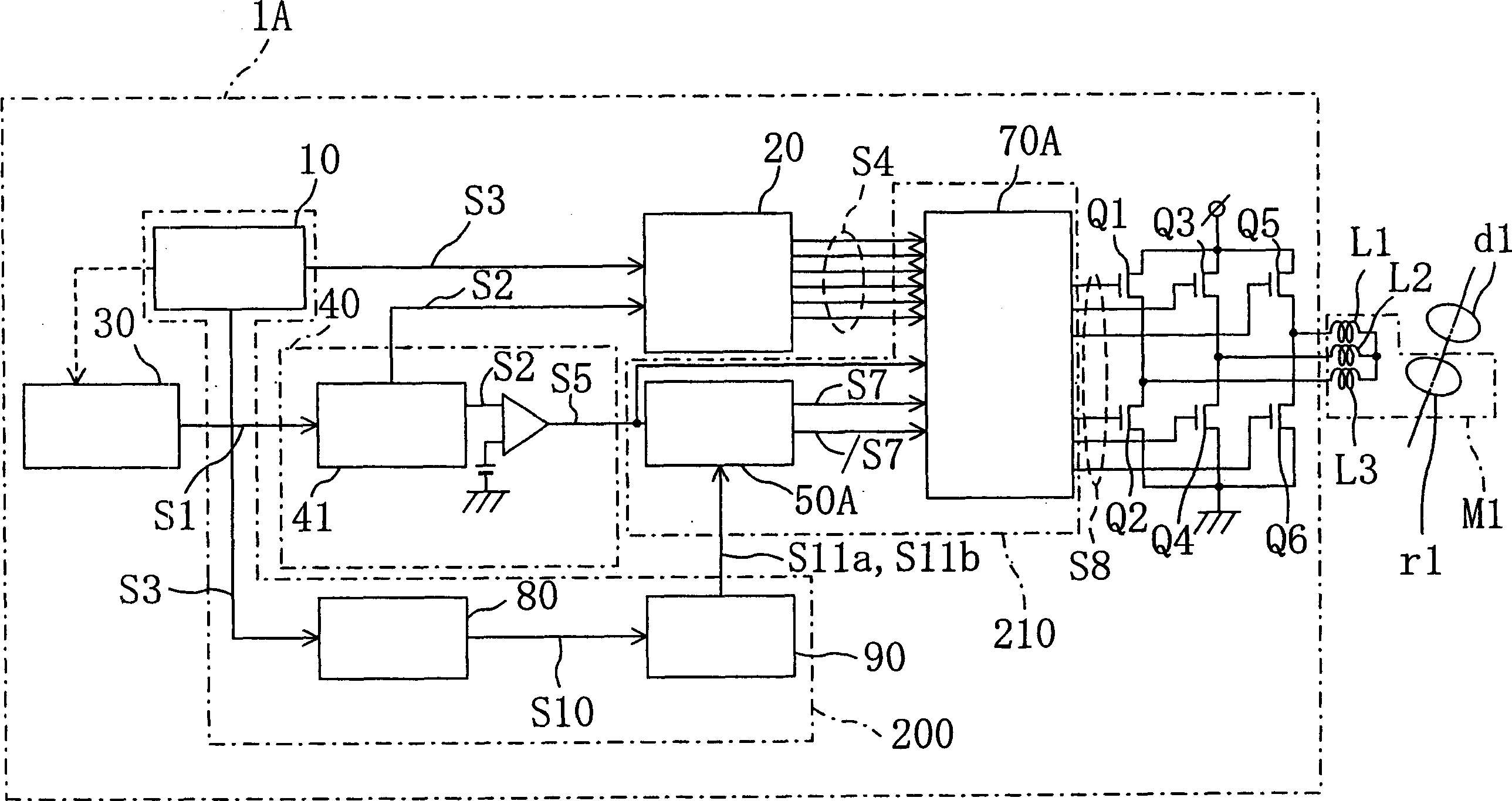
[0048] figure 1 It is a figure showing the structure of the motor drive apparatus 1A of Example 1 of this invention.
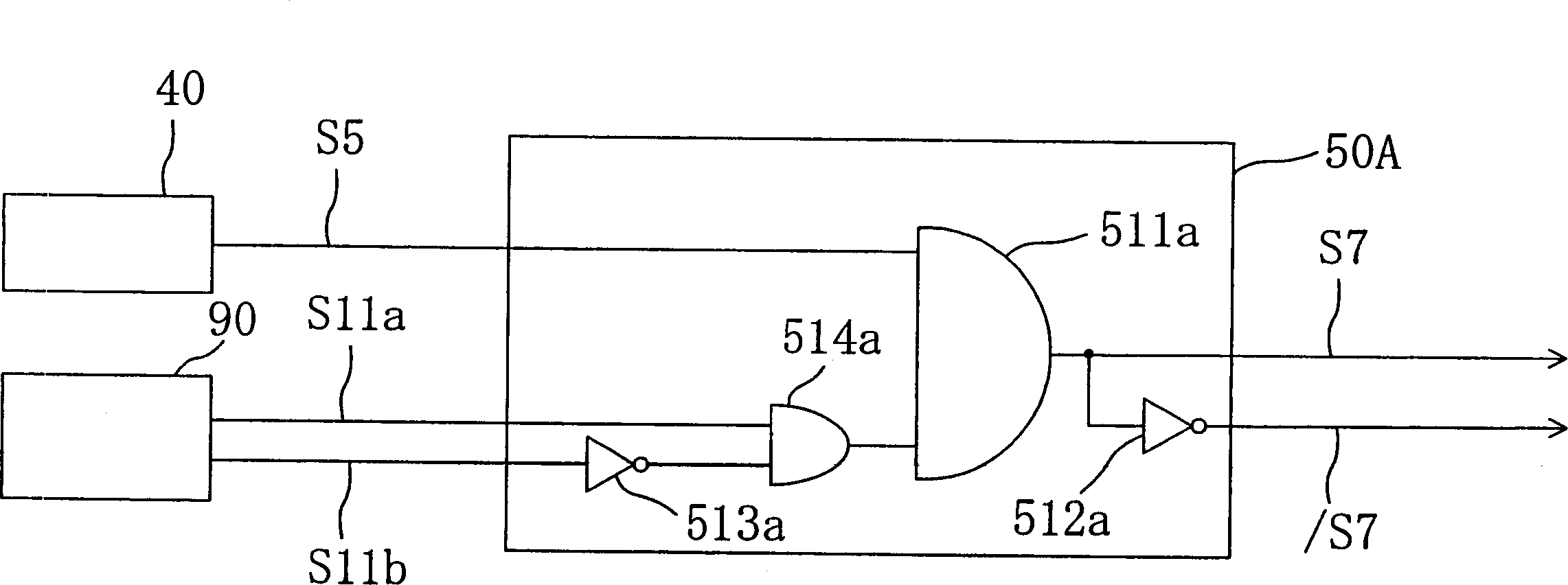
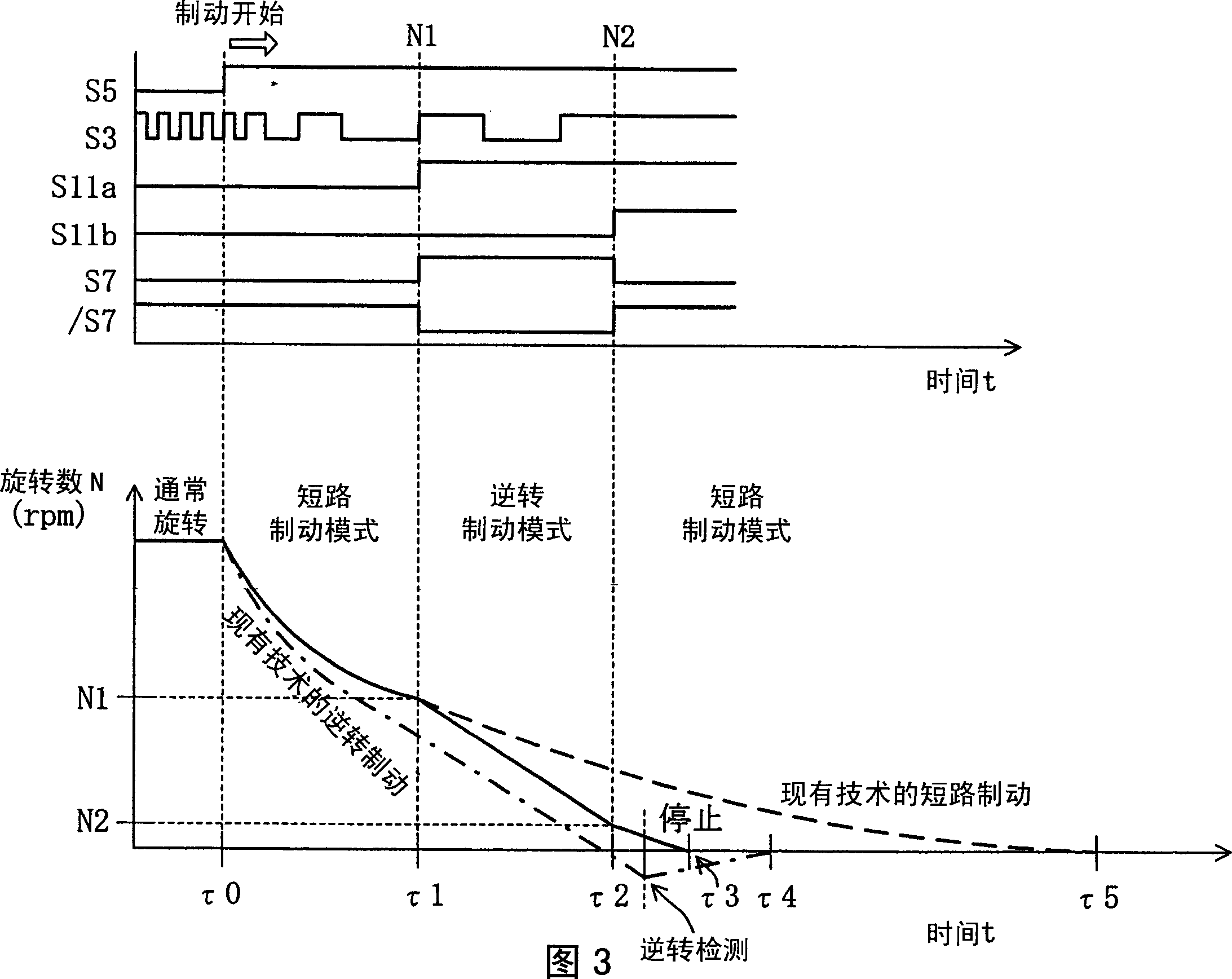
[0049] figure 1 The shown motor drive device 1A, like the conventional example, includes: a position detection device 10, an energization switching signal generating device 20, a rotation control device 30, a braking command generating device 40, a braking mode switching device 50A, an energizing Control signal generator 70A, and power transistors Q1 to Q6. It also includes: a rotation detection device 80 that detects the number of rotations per unit time of the rotor r1 based on the position signal S3 output by the position detection device 10 and outputs a signal S10 corresponding to the number of rotations; The number of rotations and the equivalent rotation identification device 90 whether the output signal S10 of the rotation detection device 80 reaches the preset reference value corresponding to the predetermined number of rotations. Further, outsid...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Figure 4 It is a figure which shows the structure of the motor drive apparatus 1B which concerns on Example 2 of this invention.
[0063] Figure 4 The motor drive unit 1B shown is in the figure 1 In addition to the components of the motor drive device 1A shown, a clock signal generating device 100 for supplying a clock signal S12 for switching the braking mode to the braking mode switching device 50B is provided.
[0064] Next, the operation of the motor drive device 1B configured as described above will be described.
[0065] The rotation detection device 80 detects the number of rotations of the rotor r1 per unit time according to the position signal S3 output by the position detection device 10 , and outputs a signal S10 corresponding to the number of rotations to the rotation identification device 90 . And, when the rotation identification device 90, when the signal S10 from the rotation detection device 80 is less than the reference value corresponding to the...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Figure 7 It is a diagram showing an example of a circuit configuration of a motor drive device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0077] Figure 7 The motor drive device 1C shown is in the figure 1In addition to the constituent parts of the motor driving device 1A shown, a detection device 110 for detecting the current value after receiving the current value signal S13 indicating the current value of the current flowing through the motor windings L1 to L3, and The current value of the current value detection signal S14 from the current value detection device 110 is compared with a predetermined current value (reference value) set in advance and the current value identification signal S15 is output to the current value identification device 120 of the braking mode switching device 50C. .
[0078] Next, the operation of the motor drive device 1C configured as described above will be described.
[0079] The current value detection device 110, for e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com