Internal memory type anti-falsification processor and security method
A technology of internal memory and memory, which is applied in the direction of memory system, architecture with a single central processing unit, electrical digital data processing, etc. It can solve problems that have not been proposed, single program, and no proposal.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
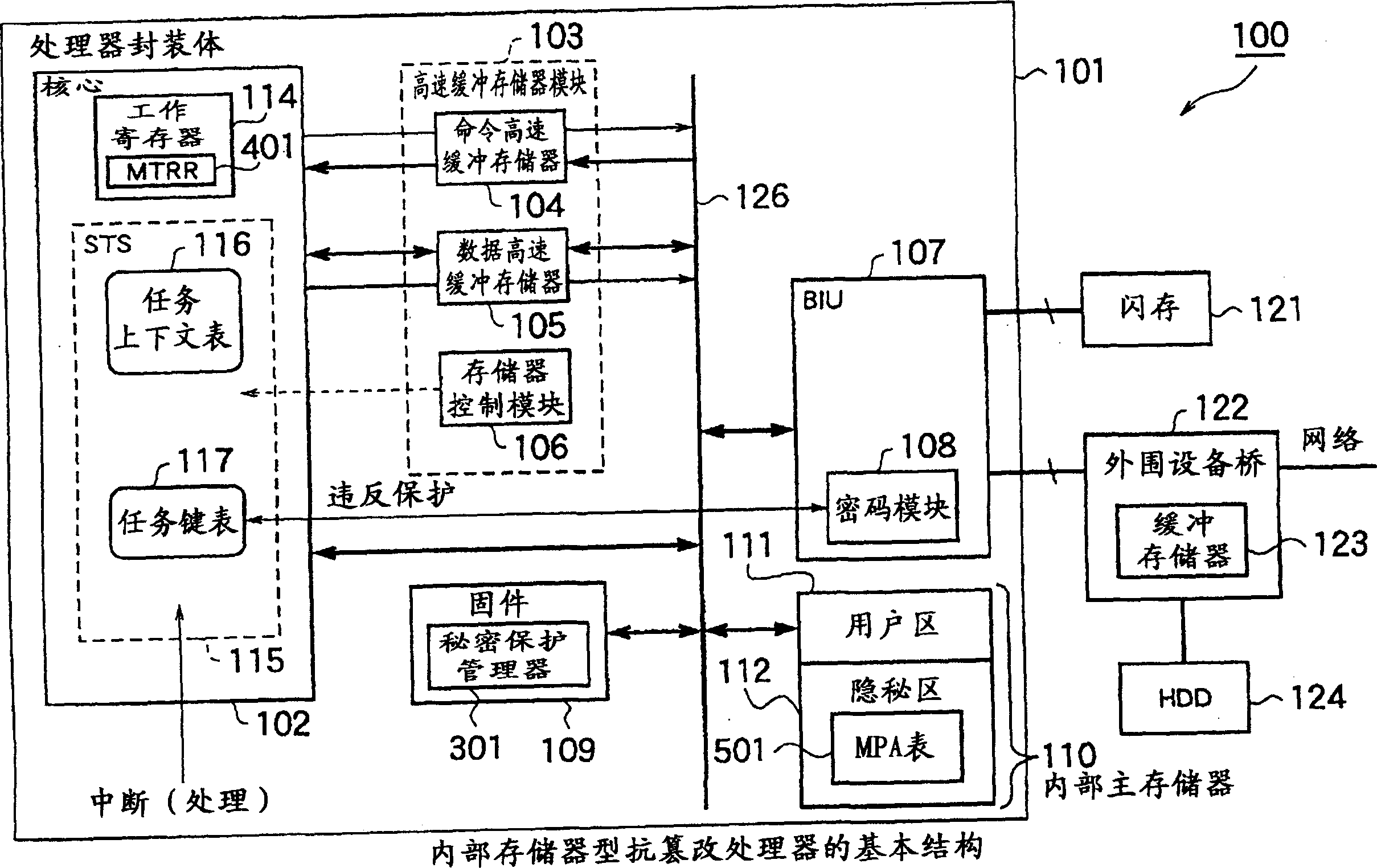
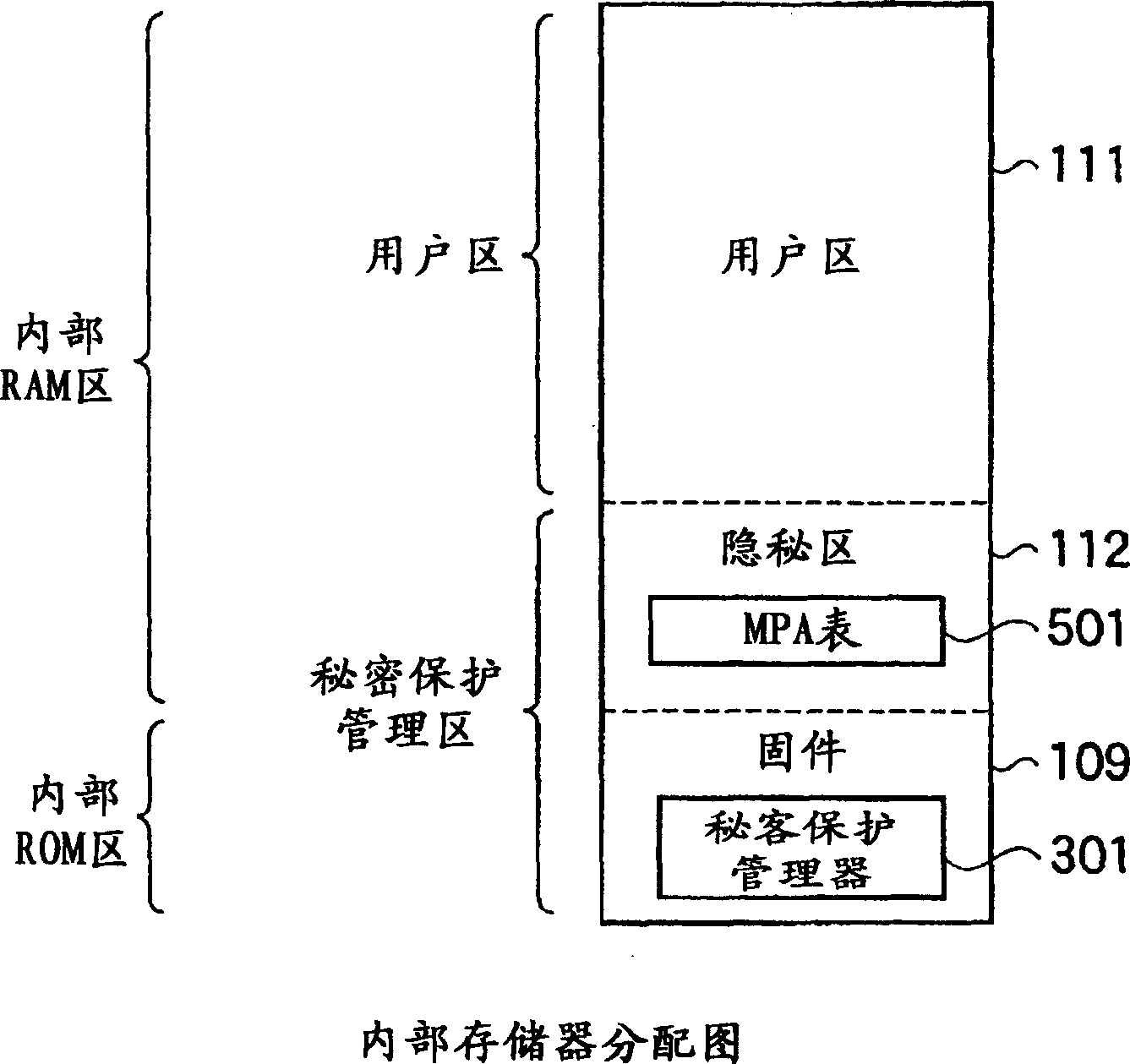
[0056] figure 1 It is a schematic configuration diagram of an internal memory type tamper-resistant processor according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The processor 100 has a processor core 102, a cache memory module 103, a bus interface unit (BIU) 107, a firmware (ROM) 109 including a secret protection manager (secrecy management unit) 301, and an internal memory in a processor package 101. 110, which are connected to each other through an internal bus 126.
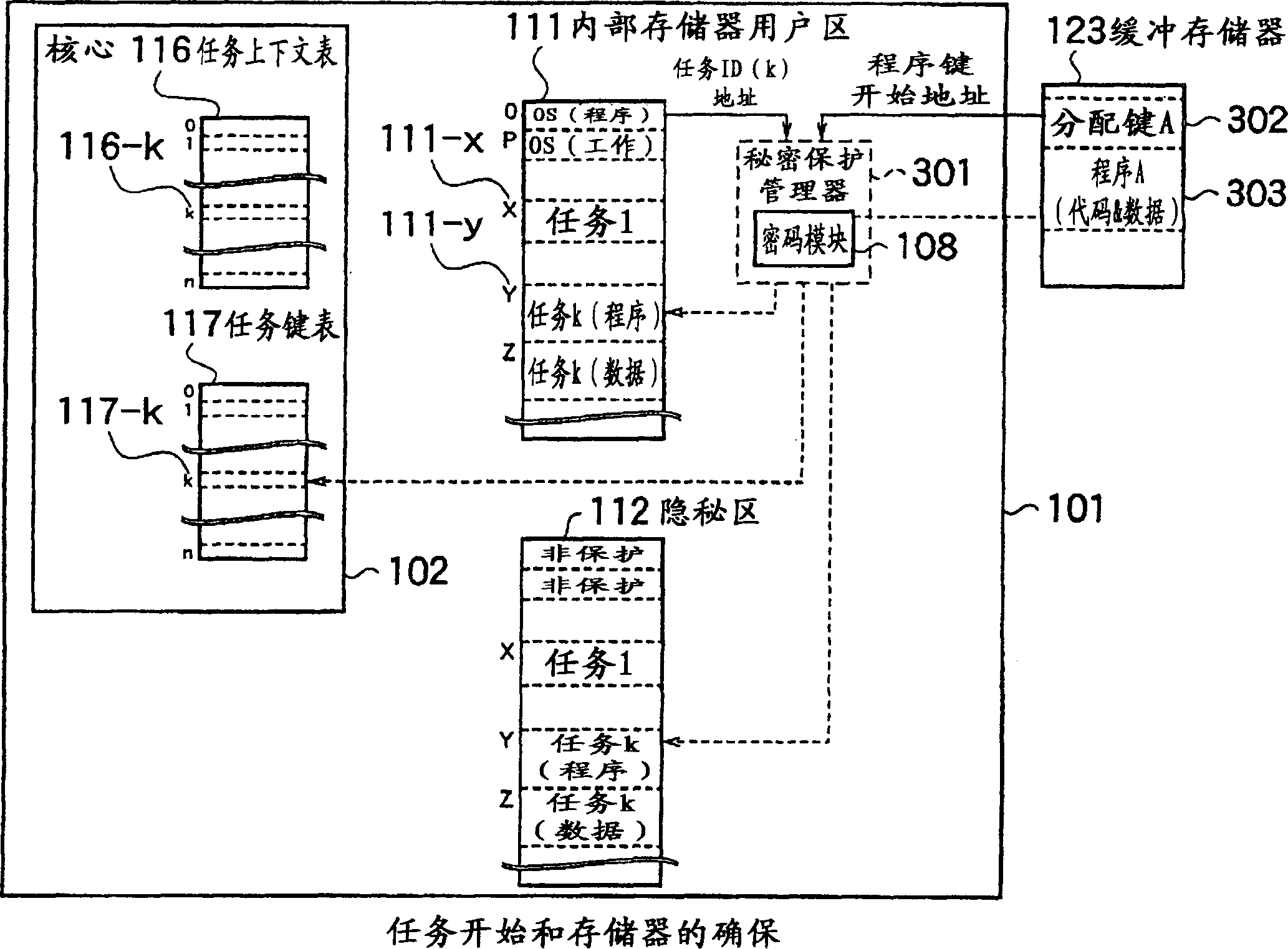
[0057] The processor core 102 has a work register 114 used by a program being executed and a task switching unit (STS: secure task switcher) 115 . The working register 114 includes an MTR (memory type range) register 401 . The MTR register 401 stores a requested protection attribute (RPA: requested protection attribute) for specifying whether a task requires privacy for an access target, that is, an internal memory area (ie, a memory page). The task switching unit 115 has a task context table 116 correspon...
Embodiment 2
[0110] In Embodiment 1, the setting of the confidentiality attribute of the internal memory is performed according to an explicit command issued by the task. In Embodiment 2, the setting of the memory security attribute is performed automatically when the memory is accessed. That is, in the state that the memory page is not kept secret (that is, the memory protection attribute MPA is 0), if the task accesses the memory in the state that requires secrecy (that is, the value of the protection attribute RPQ is 1), it will automatically be in the corresponding MPA entry Set the memory protection bit to 1 in the field. At the same time, the memory contents are initialized with random numbers. With this structure, the content security of the memory is further improved.
[0111] When accessing the memory, it is the same as the first embodiment except that the security attribute is automatically set for the target memory area. The following describes in detail the setting of the au...
Embodiment 3
[0126] In Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, it is explained that the microprocessor with the real address mode is used as the object, so that the security of the secret of the task and the memory management based on the OS coexist, and at the same time, the communication between the task and the OS is ensured, and the A consistent, secure approach to memory operations.
[0127] Embodiment 3 relates to an internal memory type processor having a virtual storage mechanism. In particular, prevention of memory page swapping attacks, which is a problem in processors having virtual memory structures, is described.
[0128] In a system with a virtual storage mechanism, the OS can assign an arbitrary page of physical memory to an arbitrary virtual address. In addition, this assignment can be assigned differently depending on the task. For the description of the allocation, a table on the internal main memory called a page table is used. The page table will be described later.
[0129]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com