Accessing legacy applications from internet
A technology of application program and service program, applied in the direction of inter-program communication, multi-program device, program control design, etc., can solve the problems of not providing user interface effectiveness, slow display data flow, sacrificing application program performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
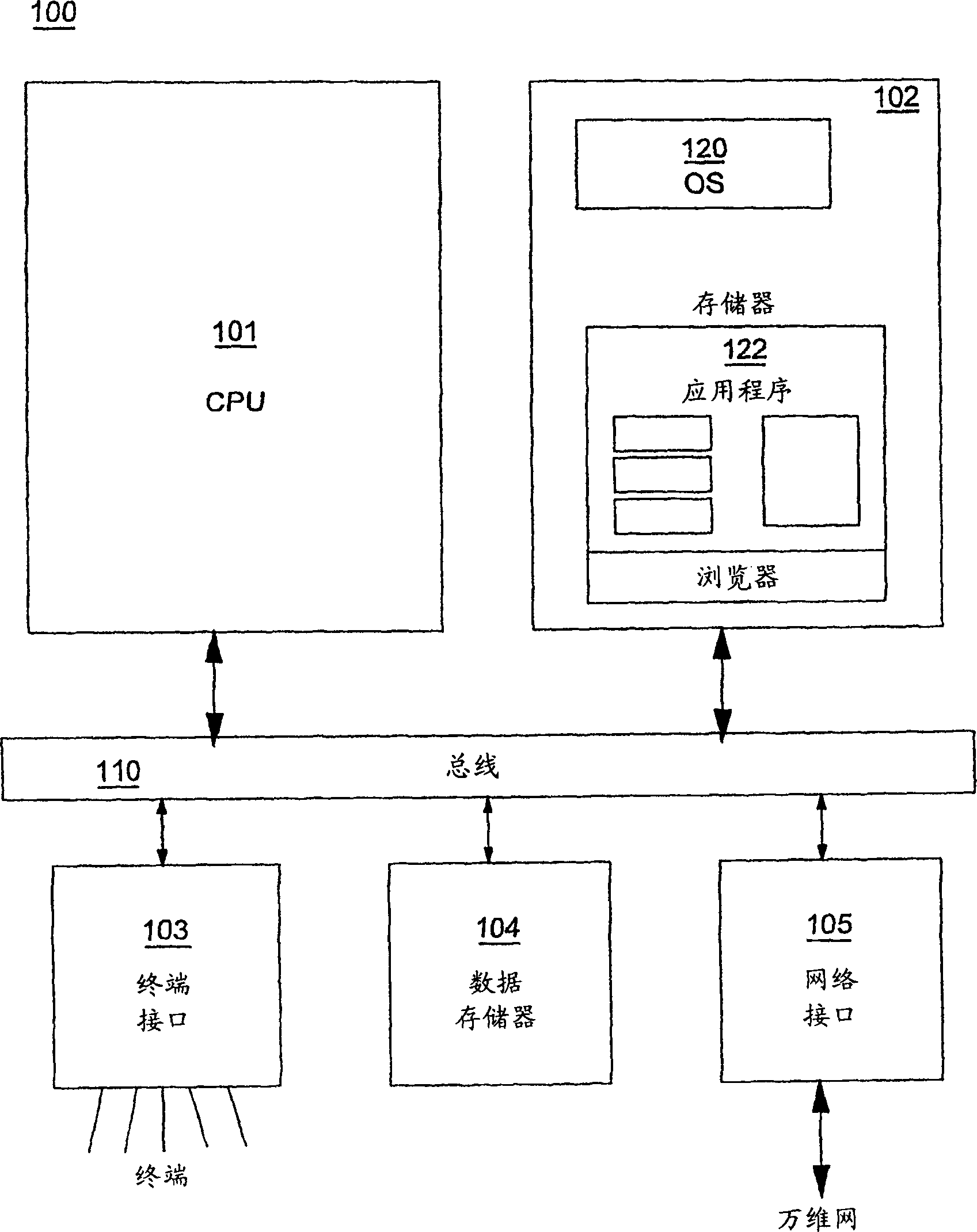
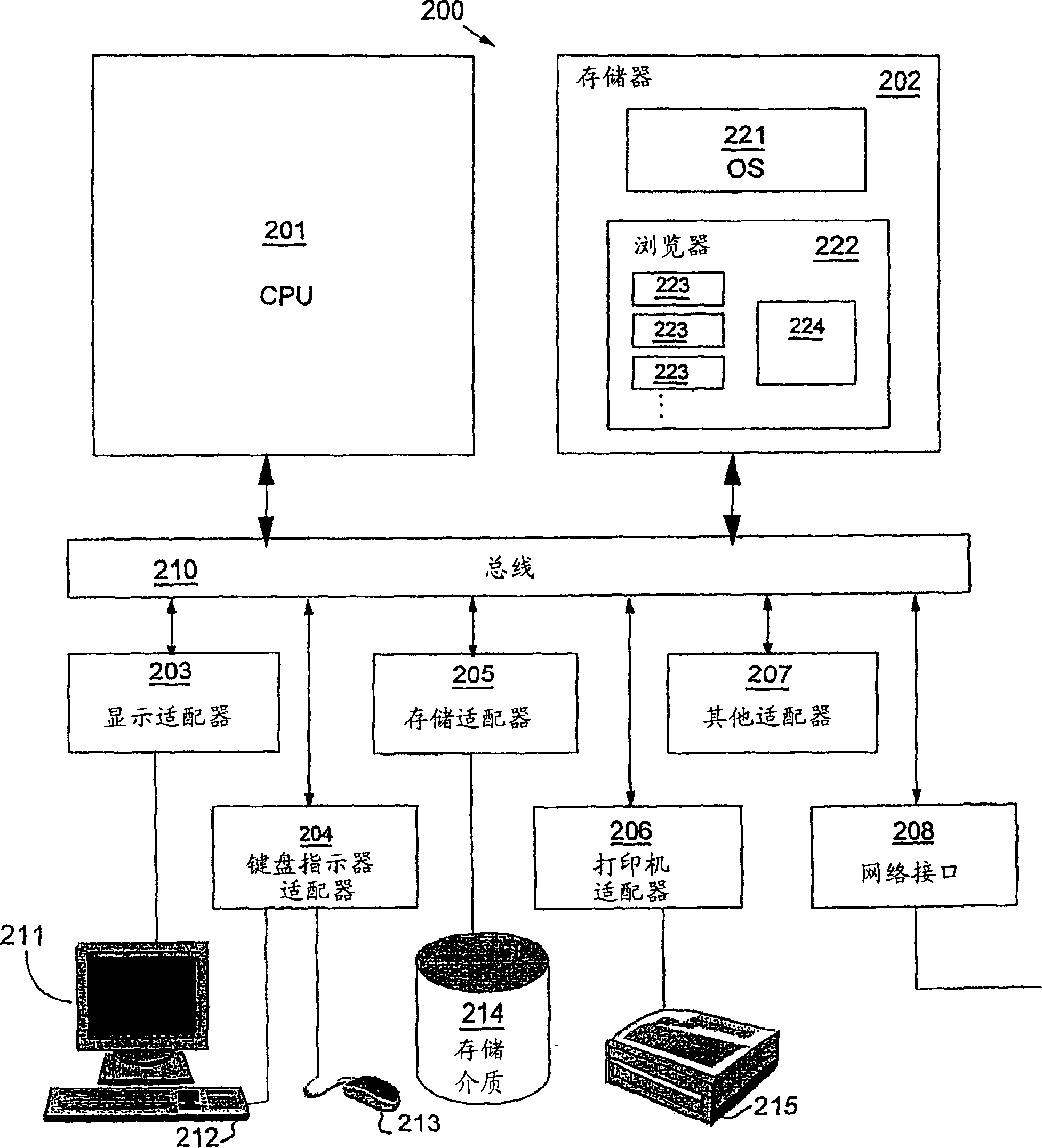
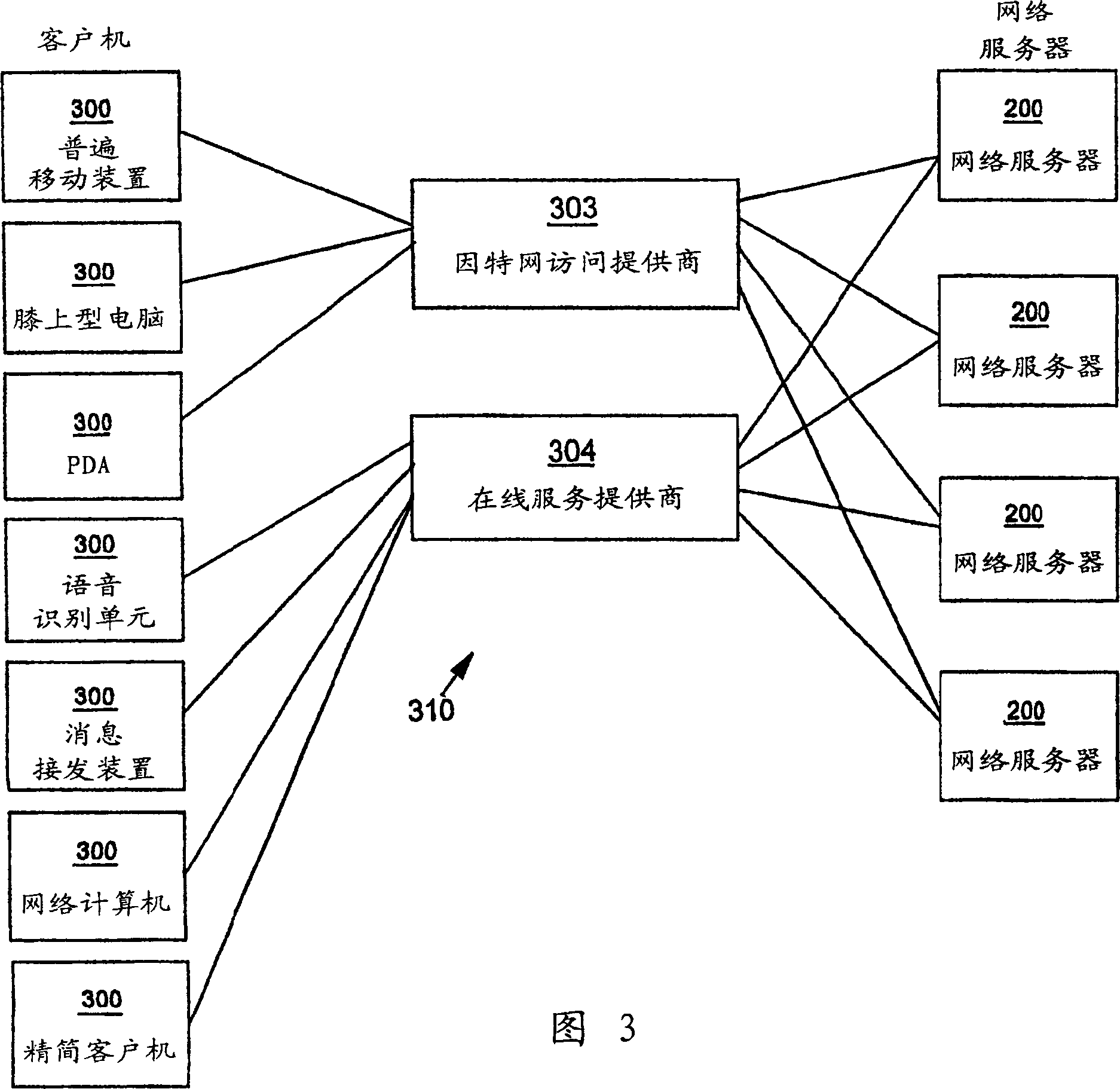
[0024] Referring to the drawings, wherein like numerals denote like parts throughout the several views, figure 1 A high level block diagram of a computer system 100 according to one embodiment of the present invention is shown. The computer system 100 may include a central processing unit (CPU) 101, a main memory 102, a terminal interface 103, a data storage 104, and an interface 105 to a network such as the Internet. Various devices communicate with each other via the internal communication bus 110 . CPU 101 is a general-purpose programmable processor that executes instructions stored in memory 102; although figure 1 A single CPU is shown, it being understood that computer systems having multiple CPUs may be used. The memory 102 is a random access semiconductor memory for storing data and programs; the memory is shown conceptually as a single monolithic entity, but it is known that memory is often configured as a combination of multiple cache memories and other storage devi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com