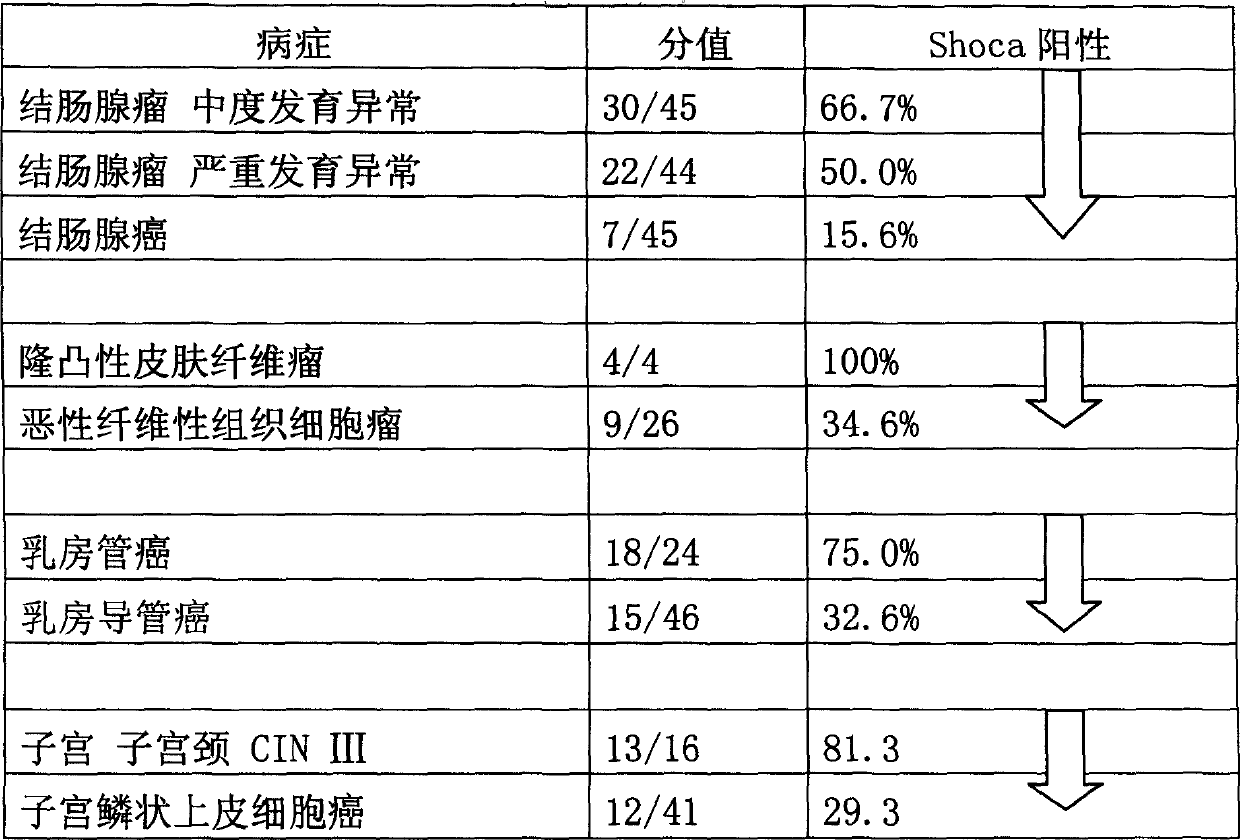
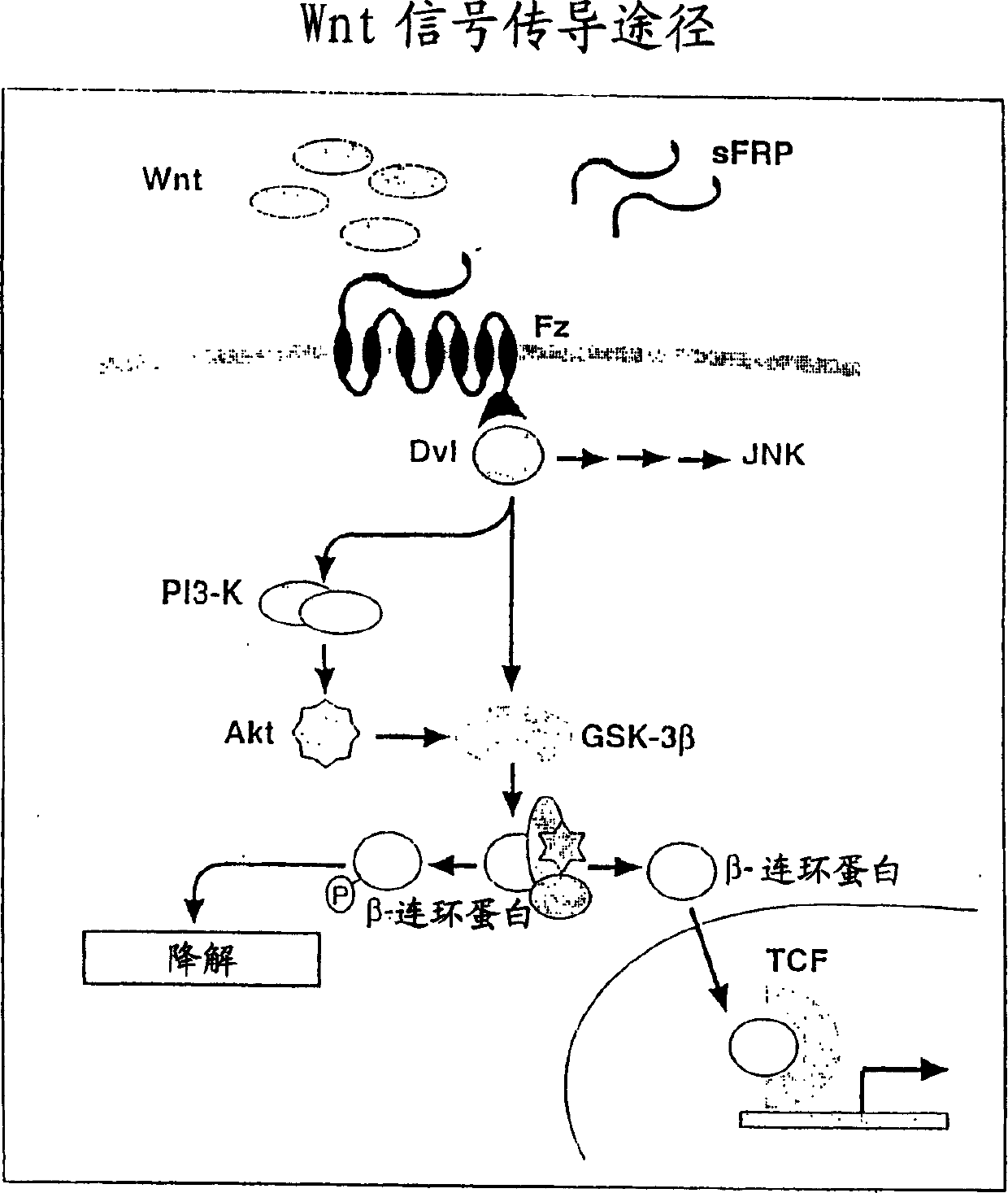
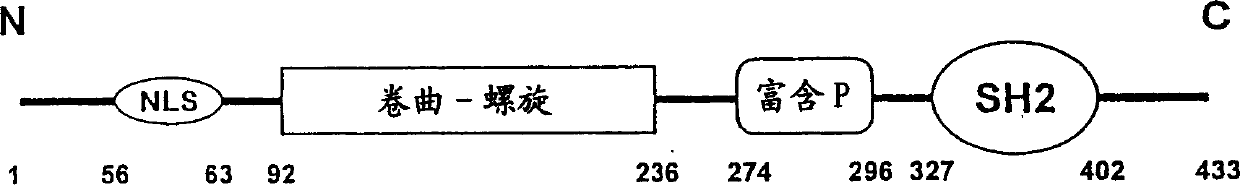
Nucleic protein 'Shoca'-a component of wnt signal transmission channel
A technology of signal transduction and pathway, applied in the field of signal protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0181] Example 1. Shoca-1, a novel gene involved in wnt-mediated signaling.
[0182] The present inventors have recently identified a novel gene in mouse and human tissues, the product of which is directly involved in wnt-mediated signaling. The gene (SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 3) encodes the SH2 domain of the adapter protein containing 52kDa (proved by Western blot hybridization experiment), thus the gene is named Shoca (SH2-domain containing adapter protein)- 1. Subsequently, another gene similar to Shoca (SEQ ID NO: 5) was identified by using EST analysis in the common domain. The presence or function of these genes in any species has not been reported so far.
[0183] Mouse Shoca-2 was discovered by a blast search in the EST database using the cDNA sequence of mouse Shoca-1. To obtain the full-length coding sequence, 5' and 3' RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) was performed using partial EST sequences. Afterwards, the full-length cDNA having the same sequence as...
Embodiment 2
[0187] Example 2. Production of Shoca-specific antibodies
[0188] Antibody preparation A
[0189] The anti-Shoca-1 antibody (rabbit polyclonal serum) used to determine the subcellular localization was produced in the inventor's institute. Different batches were used whereby animals were bled at different times after repeated booster immunizations. The immunogen is a mouse Shoca-1 derived peptide coupled to the carrier protein KLH:
[0190] Peptide Shoca #0: NH 2 -CLPDTSPPSPLTGPDRTWERPLRC-CONH 2
[0191] This peptide represents a stretch of 22 amino acids corresponding to residues 272 to 293 of mouse Shoca-1. For booster immunization, N-terminal and C-terminal cysteine residues were introduced to form loops on the protein carrier.
[0192] Antibody preparation B
[0193] The anti-Shoca-1 antibody used in the staining experiment of Example 5 was raised in two rabbits by Eurogentec and is also representative of a polyclonal preparation. All preparations used for staini...
Embodiment 3
[0217] Example 3. Shoca-1 and Shoca-2 expression profiles
[0218] Shoca-1 is expressed in mouse thymocytes as early as when thymic primordia are first detected, and it is also present in the thymus of nude mice. Thus, Shoca-1 expression is independent of thymic lymphopoiesis, and specifically the structural cross-talk between thymocytes and thymic epithelial cells. Shoca-1 expression was also detected in the bone marrow, particularly in mesenchymal cells known to support blood cell production. Although Northern blot analysis (Northern blot analysis) was not sensitive enough to detect specific transcripts, PCR analysis revealed that brain, kidney and lung were other sites where Shoca-1 was expressed in low abundance (Fig. 6). In contrast, Shoca-2 expression was more common in different tissues (Fig. 6).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com