Methods of forming non-volatile resistance variable devices and methods of forming silver selenide comprising structures
A resistance device, silver selenide technology, applied in the direction of electric solid devices, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in forming silver selenide
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] Detailed description of the preferred embodiment
[0026] The present disclosure is filed to further the fundamental purpose of the United States patent law, which is "to further the advancement of science and art" (Title 1, paragraph 8).
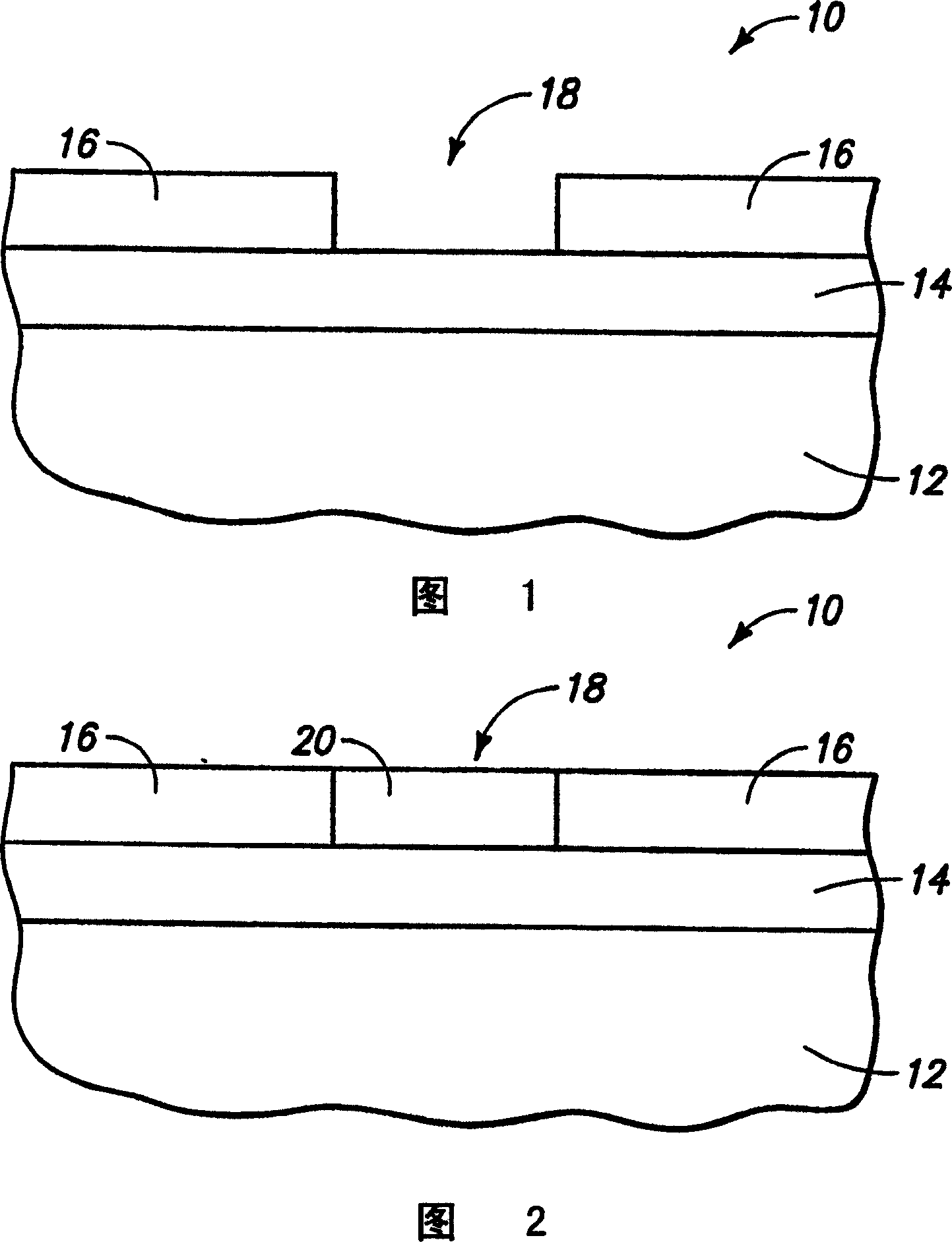
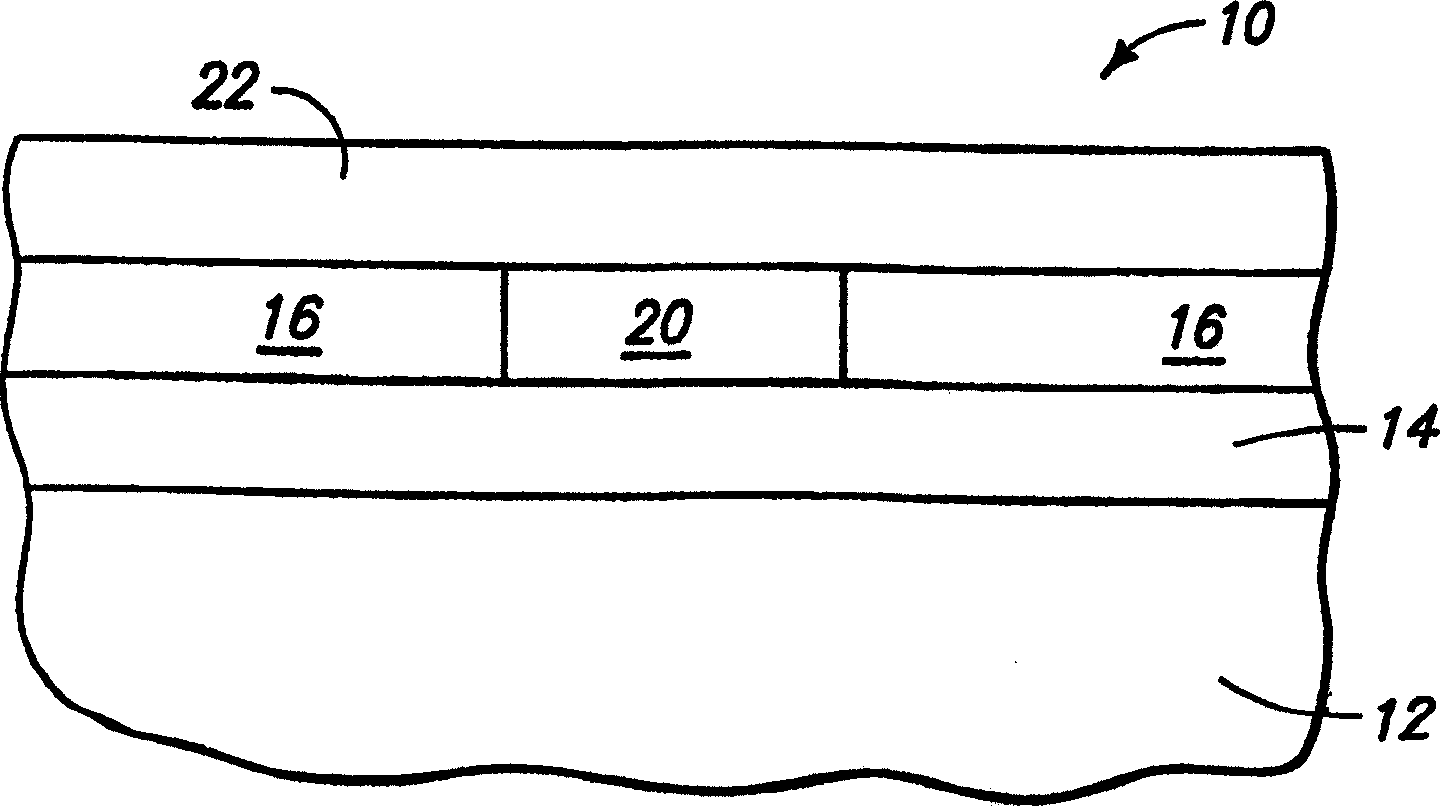
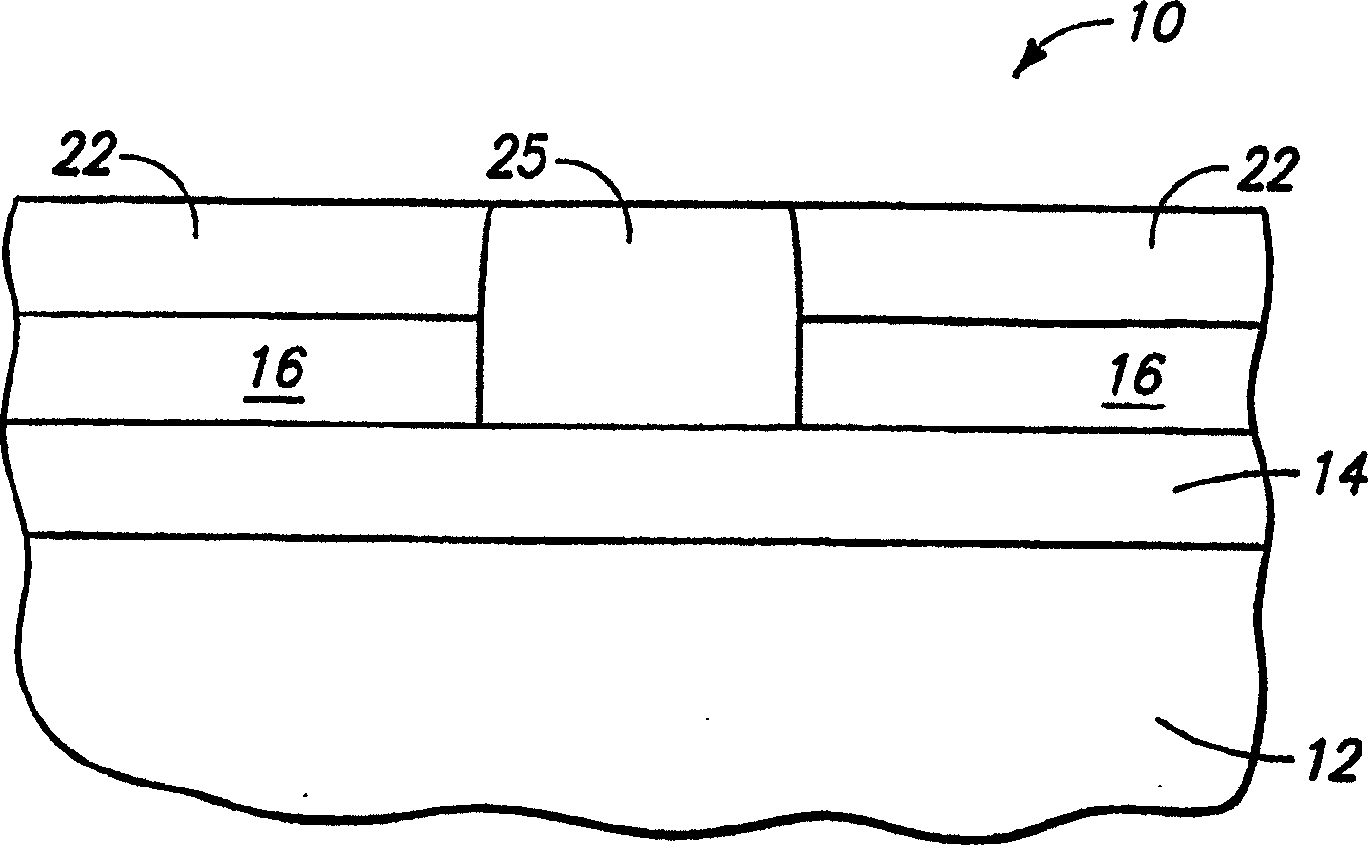
[0027] First refer to Figure 1 to Figure 8 Exemplary embodiments for forming non-volatile variable resistance devices are described. FIG. 1 depicts a substrate fragment 10 comprising a base substrate 12 and a first conductive electrode material 14 formed thereon. Base substrate 12 may include any suitable support substrate, for example, a semiconductor substrate including bulk monocrystalline Silicon. In the context of this document, the terms "semiconductor substrate" or "semiconducting substrate" are defined to mean any construction comprising semiconducting material, including but not limited to bulk semiconducting material such as a semiconducting wafer (either independently or in In a component on which other materials are c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com