Washing machine, conductivity sensor in washing machine, and controlling method of the same
A conductivity sensor, washing machine technology, applied in the control device of washing machine, other washing machines, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of reducing washing efficiency, adjusting washing machine, not raising, etc., to improve washing efficiency, prevent misoperation, and improve reliability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0049] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 The first embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail.
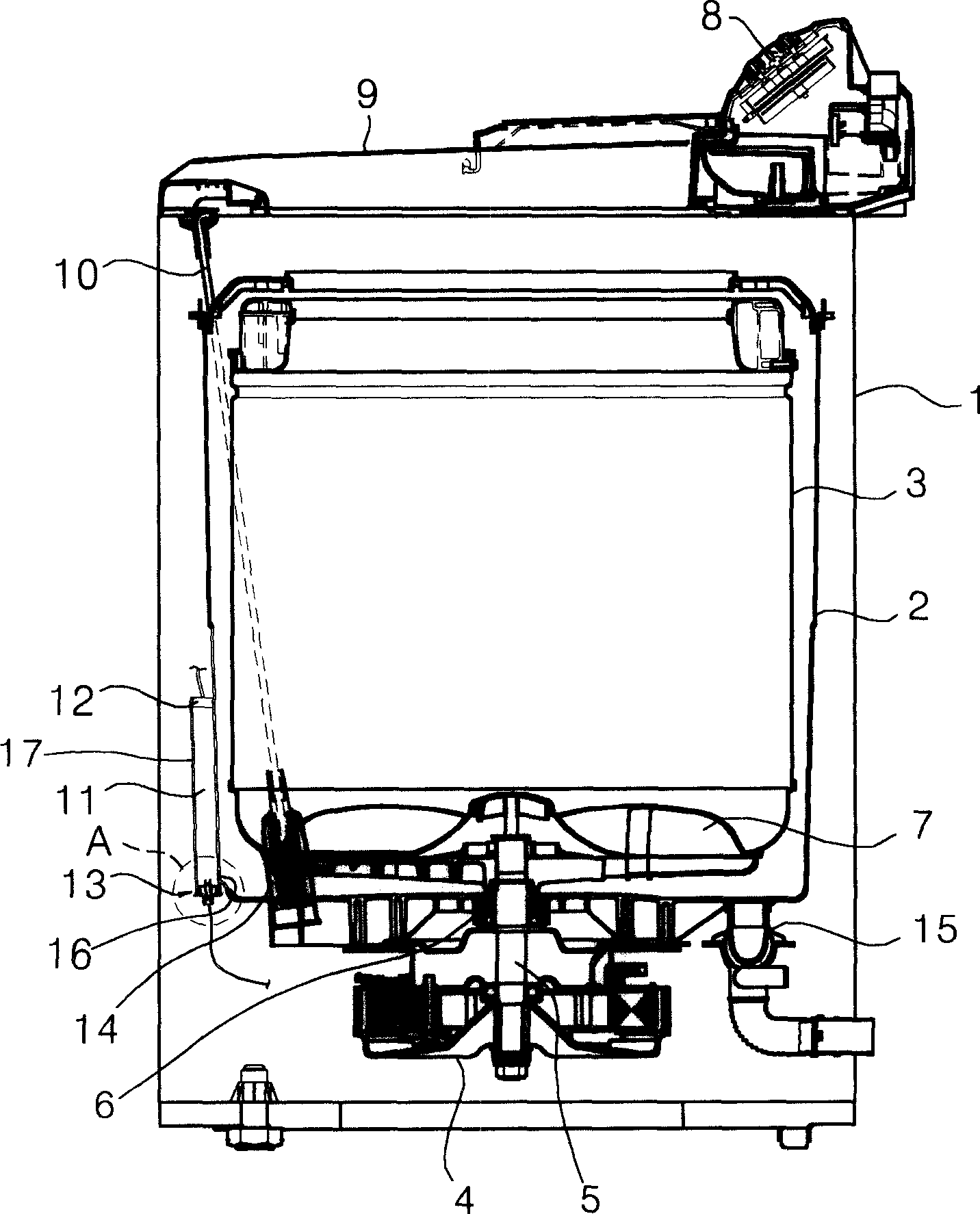
[0050] figure 1 is a sectional view of the washing machine according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0051] refer to figure 1, the washing machine according to the present invention comprises: a casing 1 forming an outer shell; an outer tub 2 firmly suspended in the casing 1 by a plurality of suspending members 10 for containing washing water; The lower part of 10 is a shock absorber 14 to reduce the vibration of the outer cylinder 2; one is rotatably installed inside the outer cylinder 2 for receiving the laundry to be washed and the inner cylinder 3 provided by the water supply valve for washing water; one is rotatably installed The lower part of the inner cylinder 3 is an agitator 7 for agitating the flow of washing water; a drive motor 4 driven by an external power supply; a drive shaft 5 arranged in the middle of the drive motor 4; a dr...
no. 2 example
[0069] Refer below Figure 4 to Figure 6 The second embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail.
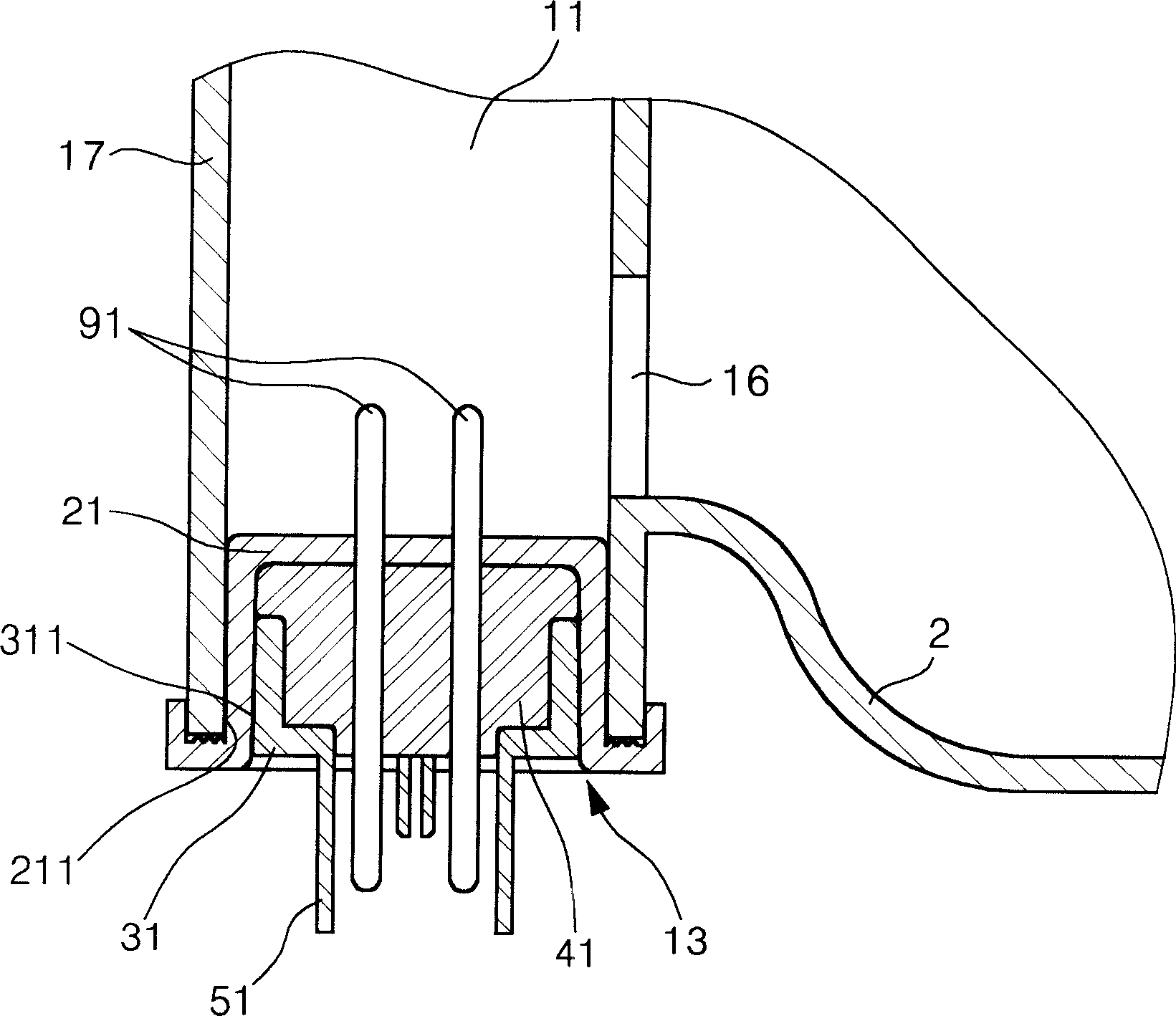
[0070] Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view of a conductivity sensor and its mounting structure according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0071] refer to Figure 4 , the conductivity sensor according to the second embodiment of the present invention includes a pair of electrodes 91, an upper protection member 21, a lower protection member 31, a sealing member 41, an upper fixing portion 211 and a lower fixing portion 311, these members The same as in the first embodiment described above. The difference is that the conductivity sensor further includes a connector 52 protruding downward from the lower protective member 31, and a receiver 62 formed in the connector 52 and fixed to the lower portion of each electrode to apply current, wherein each electrode The lower part forms a round rod shape.
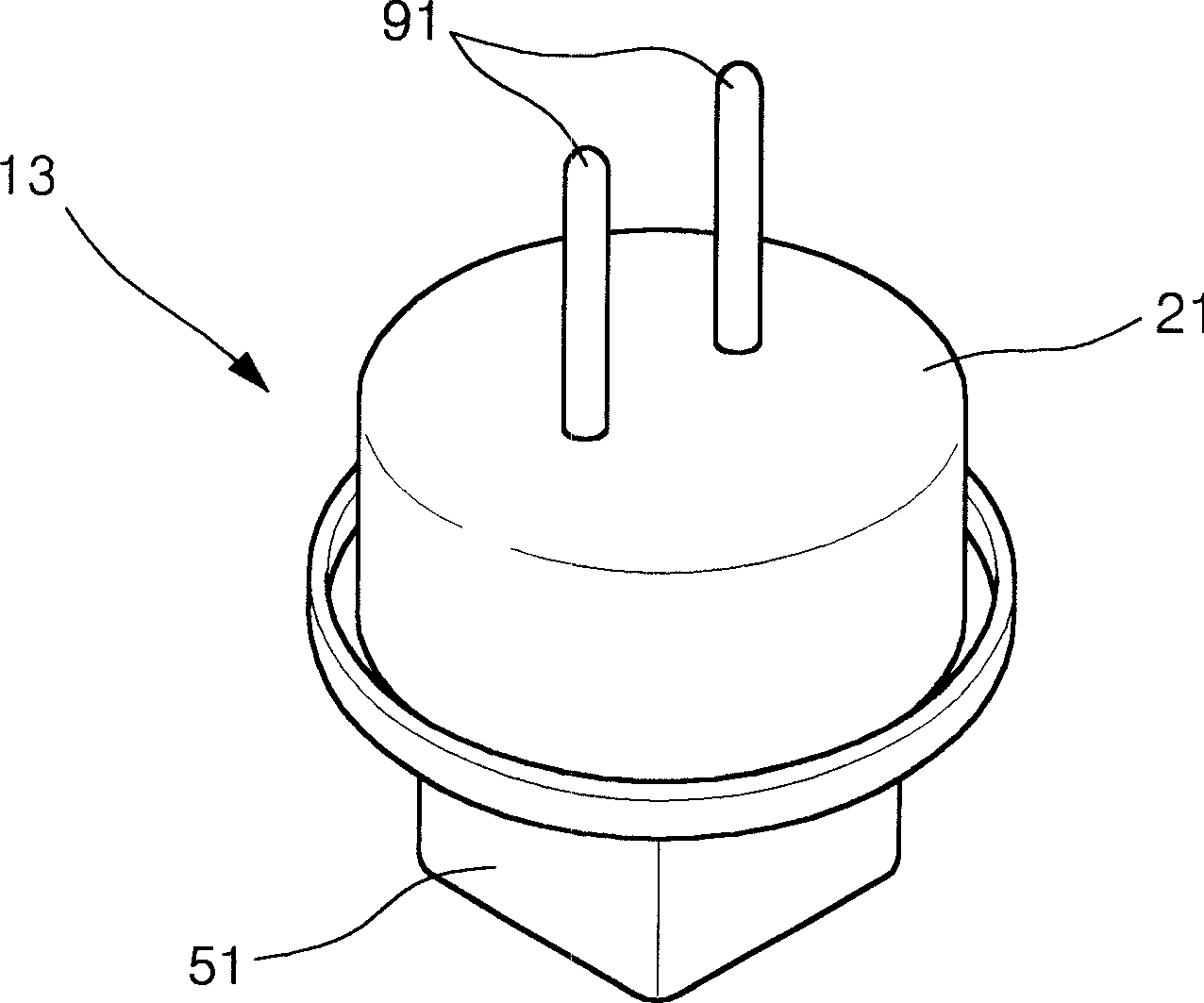
[0072] Figure 5 is a perspective view of ...
no. 3 example
[0076] Refer below Figure 7 and Figure 8 A third embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail. The third embodiment provides a structure that can prevent the misoperation of the electrode 91, which may be caused by foreign substances entering the gas chamber. The air chamber is in the shape of a hollow rod extending up and down. Foreign matter, such as lint or dirt contained in the wash water, may additionally be introduced and accumulate in the interior of the air chamber. If a foreign substance intervenes between the electrodes, the conductivity is irregularly changed, so that the amount of current cannot be accurately detected. For example, if foreign substances get between the electrodes, they act as a conductor or insulator, making it impossible to accurately measure conductivity. Therefore, in this embodiment, means for preventing the introduction of foreign substances is further provided between the electrodes.
[0077] Figure 7 is a cross-se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com